Indian people facts for kids

|
|
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 1.4 billion | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Indian diaspora: c. 17.9 million |
|
| 4,946,306 | |
| 3,255,864 | |
| 2,975,000 | |
| 2,803,751 | |
| 1,858,755 | |
| 1,825,000 | |
| 1,614,000 | |
| 1,560,000 | |
| 1,000,000 | |
| 894,500 | |
| 796,001 | |
| 700,000 | |
| 700,000 | |
| 650,000 | |
| 600,000 | |
| 500,000-1,000,000 | |
| 161,000-1,000,000+ | |
| 468,524 | |
| 465,000 | |
| 400,000 | |
| 327,000 | |
| 315,000 | |
| 297,300 | |
| 250,300 | |
| 240,000 | |
| 197,301 | |
| 155,178 | |
| 148,000 | |
| 120,000 | |
| 85,000 | |
| 58,983 | |
| 46,000 | |
| 24,550+ | |
| 23,254 | |
| 21,584 | |
| 20,000+ | |
| 9,900 | |
| 1,218 | |
| Languages | |
Languages of India, including:
|
|
| Religion | |
| Majority: Minorities: | |
Indian people or Indians are the citizens of the Republic of India. In 2022, India's population was about 1.4 billion people. They belong to many different ethnic groups. The UN predicted that India would become the world's most populated country by April 2023. It would then hold about 17.50% of the global population.
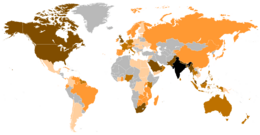
Many Indians also live outside India. This group is called the Indian overseas diaspora. They live in places like the Arab states of the Persian Gulf and the Western world.
The word "Indian" usually means people from today's Republic of India. Before 1947, it also included people from what are now Pakistan and Bangladesh. This was before the Partition of India.
Sometimes, in North America, people use "Asian Indian" or "East Indian". This helps tell them apart from the indigenous peoples of the Americas. These terms are used because of a historical mistake. Early European explorers wrongly thought they had reached India. Today, terms like "Indigenous," "Amerindian," or "Native American" are more commonly used for native populations.
Understanding the Name "Indian"
The name Bhārata has been used by people in the Indian subcontinent since 1949. This name comes from ancient texts called the Vedas and Puranas. These texts refer to the land of India as Bhārata varṣam.
The word "Indian" comes from the Greek word Indía. This word meant the area beyond the Indus river. The name ultimately comes from Sindhu, which is the Sanskrit name for the Indus river. It also means "river" in general.
A Brief History of India
India has a very long and rich history. It includes ancient settlements and societies. The Indus Valley civilization mixed with Indo-Aryan culture to form the Vedic Civilization. This led to the growth of Hinduism.
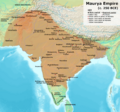
Many powerful empires and dynasties ruled India for over two thousand years. These included the Maurya Empire, Gupta Empire, and Mughal Empire. The Maurya Empire was one of the first great empires. It ruled much of South Asia around 300 BC.
The Gupta Empire period is known as the "Golden Age of India". During this time, Indian culture, ideas, and religions like Hinduism and Buddhism spread across Asia. Indian mathematicians like Aryabhata invented the concept of zero. They also developed the decimal system.
Later, the Chola Empire in the south had strong trade links with the Roman Empire. The Rashtrakuta dynasty was also very powerful. The Chola dynasty became a major power in South Asia and South-East Asia.
The Mughal Empire brought much of India under one rule. India's economy grew strong, and culture flourished. New groups like the Marathas and Sikhs gained power during this time.
In the 18th century, the British East India Company began to take control. This led to British India. In the 20th century, a movement for independence began. India gained freedom from the United Kingdom in 1947. The country was then divided into India and Pakistan.
Indian Culture and Traditions
India is one of the world's oldest civilizations. Indian culture is a mix of many different cultures. It has been shaped by thousands of years of history. Dharmic religions have greatly influenced Indian philosophy, literature, architecture, art, and music.
Religions of India
India is the birthplace of four major religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. These are also known as Dharmic religions. Today, Hinduism and Buddhism are among the world's largest religions.
Religion has always been a key part of India's culture. The country has a long history of religious tolerance. The Constitution of India protects the right to freedom of religion.
While most Indians (about 80%) are Hindus, there are also many Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, and Jains. India has the largest number of Zoroastrians and Baháʼís in the world.
Family Life in India
Historically, India had a strong tradition of the joint family system. This is where an extended family lives together. The oldest male, called the patriarch, leads the family. He makes decisions about money and social matters.
However, as India has modernized, more families are becoming nuclear families. This means parents and their children live together. The traditional joint family is now a smaller part of Indian households.
Arranged marriages have been a tradition in India. Marriage is seen as a union of two families, not just two people. Today, most arranged marriages happen with the consent of the people getting married. This shows that Indian culture is changing.
Traditional Indian Clothing
India's clothing styles have changed a lot over time. Cotton was first grown in India around 5000 BC. Silk was woven as early as 2450 BC. Ancient texts describe detailed garments.
Traditional Indian clothing varies greatly by region. It depends on local culture, geography, and climate. Women often wear a Sari, Gagra Choli, or Shalwar Kameez. Men traditionally wear an Angarkha, Kurta, or Sherwani. They might wear a Dhoti or Lungi on the bottom. A Pagri (turban) is often worn on the head. In cities, people also wear modern Western clothes.
Delicious Indian Cuisine
Indian food is different in each region. Common foods include various lentils (dal), whole-wheat flour (aṭṭa), rice, and millet. Millet has been grown in India since 6200 BC.
Over time, some people became vegetarians. India's climate allows many fruits, vegetables, and grains to grow all year. Indian cuisines use many ingredients and cooking styles.
Performing Arts of India
Indian music has a long history. The oldest examples are from the Samaveda (1000 BC). India's classical music has two main styles: Hindustani music and Carnatic music. Both are based on melodic patterns called Rāga and rhythmic cycles called Tāla.
The Natyashastra is an ancient Indian book about the performing arts. It covers theatre, dance, and music. It was written around 200 BC and covers everything from stage design to makeup.
Indian drama and theatre also have a rich history. Some early plays include Mṛcchakatika and Abhijñānaśākuntala. Famous fable stories like Panchatantra were performed in folk theatres. These stories even influenced One Thousand and One Nights.
Indian Contributions and Discoveries
Indian people have made huge contributions to philosophy, sciences, mathematics, arts, architecture, and astronomy.
- In mathematics, India developed the Hindu–Arabic numeral system with a symbol for zero. They also worked on quadratic equations and trigonometric functions.
- Important military inventions include war elephants and Mysorean rockets.
- Other notable inventions include chess, cotton, sugar, carbon pigment ink, and Wootz steel. Many everyday items like shampoo and the games Snakes and Ladders and ludo also came from India.
Indian culture, religions, and architecture have spread peacefully across much of Asia. Famous Indian buildings like the Taj Mahal are now UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
In modern times, Indians continue to contribute to science. Notable scientists include Satyendra Nath Bose and Srinivasa Ramanujan. Nobel Prize winners include C. V. Raman and Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, who studied black holes.
Mother India: A National Symbol
Bharat Mata (Mother India) is the national personification of India. She is seen as a mother goddess.
The image of Bharat Mata became popular during the Indian independence movement in the late 1800s. She is often shown wearing an orange or saffron sari and holding a flag. Sometimes, a lion is with her.
Popular Sports in India
Sports in India fall into two main groups: traditional and global. Traditional sports like gilli danda, kho kho, and kabaddi are quite popular.
However, cricket is extremely popular in India. Many people see it almost like a religion. Other popular sports include hockey, volleyball, and football. Polo, golf, and tennis are enjoyed by wealthier people. Recently, Olympic sports like shooting, archery, and wrestling have also become more popular.
Indians Living Abroad (Diaspora)
Many people of Indian origin live outside India. This group is called the Indian diaspora. While Indians have migrated for centuries, the term often refers to those who moved after the British Empire was established in India. There are an estimated 12 to 20 million people in the Indian diaspora.
Many Indians have moved to countries like the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and the Arab states of the Persian Gulf. In the Caribbean, many Indians came as laborers in the 1800s after slavery ended. They worked on farms and helped build new communities. Today, people of Indian descent are large ethnic groups in places like Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, and Suriname.
Images for kids
-
Priest-King, Indus Valley civilisation
-
The Mauryan Empire at its peak during the reign of Ashoka the Great.
-
The Mughal Empire during the reign of Akbar the Great.
Error: no page names specified (help).
- Lists of Indian people
- South Asian ethnic groups
- Ethnic groups in Asia
- Romani people
See also
 In Spanish: Pueblo indio para niños
In Spanish: Pueblo indio para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |