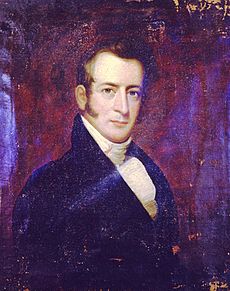North Carolina Constitutional Convention of 1835 facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Constitution of North Carolina Convention of 1835 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||

Journal of the Convention
|
|||||
| Overview | |||||
| Legislative body | State Convention | ||||
| Jurisdiction | North Carolina, United States | ||||
| Meeting place | Raleigh, North Carolina | ||||
| Term | 1835 | ||||
| Members | 130 Delegates (65 counties) | ||||
| President | Nathaniel Macon | ||||
| Chairman pro tempore | David Lowry Swain | ||||
| Secretary | Edmund B. Freeman | ||||
| Assistant Secretary | Joseph D. Ward | ||||
| Sessions | |||||
|
|||||
The North Carolina Constitutional Convention of 1835 was a meeting of delegates elected by eligible voters in counties in the United States state of North Carolina to amend the Constitution of North Carolina written in 1776 by the Fifth North Carolina Provincial Congress. They met in Raleigh, North Carolina from June 4, 1835, to July 11, 1835, and approved several amendments to the constitution that were voted on and approved by the voters of North Carolina on November 9, 1835. These amendments improved the representation of the more populous counties in the Piedmont and western regions of the state and, for the first time, provided for the election of the governor by popular vote rather than election by the members of the General Assembly.
Demand for a new constitution
The population distribution had changed since the time of the original constitution was written in 1776. The number of counties had increased from 38 at the time of the first general assembly in 1777 to 68 in 1835. Many new counties had been created in the central Piedmont and Western regions of the state. The population of the 23 counties in the Piedmont region (344,184) and eight counties in the Western region (80,592) combined exceeded that of the 34 counties in the Eastern region (313,211) in 1830. This created a greater demand for roads, schools, and infrastructure in the faster growing counties, especially the Piedmont region. The 1776 constitution had spelled out one senator for each county, at least two delegates to the house of commons for each county, and one senator from each of eight large towns, also called districts or boroughs. The governor was also chosen by the general assembly vice the voters in each county.
The 1776 Constitution was worded with restrictions on who could and who could not vote, as follows:
- "That all freemen of the age of twenty-one Years, who have been inhabitants of any one county within this State twelve months immediately preceding the day of any election, and shall have paid public taxes shall be entitled to vote for members of the House of Commons for the county in which he resides."
- "That no clergyman, or preacher of the gospels of any denomination shall be capable of being a member of either the Senate, House of Commons, or Council of State, while he continues in the exercise of the pastoral function."
- "That no person, who shall deny the being of God or the truth of the Protestant religion, or the divine authority either of the Old or New Testaments, or who shall hold religious principles incompatible with the freedom and safety of the State, shall be capable of holding any office or place of trust or profit in the civil department within this State."
Freemen included former slaves, so they were allowed to vote in North Carolina from 1777 to 1835.
Amendments to the constitution
Out of the convention came many amendments. Among those changes was fixing the membership of the Senate and House at their present levels, 50 senators and 120 representatives. Each county received at least one representative in the House and the remainder of the 120 representatives were assigned based on population of the counties. Senators were elected from districts that were laid out based on the amount of taxes paid to the state for each county. Also, the office of Governor became popularly elected. These changes gave the more populous western counties more of a say in government but still favored those who owned property, since this was required to vote and hold office. The vote was taken away from freed slaves in this convention. The convention approved the changes on July 11, 1835. The convention's proposed changes were adopted by vote of the people on November 9, 1835 with 26,771 in favor and 21,606 against. These changes remained in effect until 1868 when the Constitution was next changed.
The convention also provided amendments that eliminated private acts that granted divorces, changed names, and legitimizing persons; provided procedures to impeach of state officers; procedures to remove judges for disability; established biannual legislative sessions; and provides provisions for amending the constitution.
Officers
The following officers were chosen by the delegates to the convention:
- President Nathaniel Macon
- Chairman pro tempore: David Lowry Swain
- Secretary: Edmund B. Freeman
- Assistant Secretary: Joseph D. Ward
- Doorkeepers: Green Hill and John Cooper
- Printers: Gales & Son
Delegates
In 1835, the counties of North Carolina were characterized as either eastern or western counties. The more sparsely populated counties were in the west. The voters from the counties elected two delegates for each county in elections held in April 1835. In 1835, there were 38 Eastern counties and 27 Western counties (Western and Piedmont Regions, see table). The following delegates were elected by the eligible voters of North Carolina:
| County | Member 1 | Member 2 | Region | 1830 County Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anson | William A. Morris | Joseph White | Piedmont | 14,095 |
| Ashe | Alexander B. McMillan | George Bower | Western | 6,987 |
| Beaufort | Joshua Tayloe | Richard H. Bonner | Eastern | 10,969 |
| Bertie | David Outlaw | Joseph B. G. Roulhac | Eastern | 12,262 |
| Bladen | John Owen | Samuel B. Andres | Eastern | 7,811 |
| Brunswick | Frederick J. Hill | William R. Hall | Eastern | 6,516 |
| Buncombe | David Lowry Swain | James Gudger, Sr. | Western | 16,281 |
| Burke | Burges S. Gaither | Samuel Price Carson | Western | 17,888 |
| Cabarrus | Daniel Moreau Barringer | Christopher Melchor | Piedmont | 8,810 |
| Camden | Willie McPherson | George Ferebee | Eastern | 6,733 |
| Carteret | Wallace H. Styron | James W. Bryan | Eastern | 6,597 |
| Caswell | William A. Lea | Calvin Graves | Piedmont | 15,185 |
| Chatham | Joseph Ramsay | Hugh McQueen | Piedmont | 15,405 |
| Chowan | Joseph B. Skinner | Samuel Tredwell Sawyer | Eastern | 6,697 |
| Columbus | Alexander Troy | Absalom Powell | Eastern | 4,141 |
| Craven | William J. Gaston | Richard Dobbs Spaight, Jr. | Eastern | 13,734 |
| Cumberland | John D. Toomer | Archibald McDiarmid | Eastern | 14,834 |
| Currituck | Gideon C. Marchant | Isaac Baxter | Eastern | 7,655 |
| Davidson | John A. Hogan | John L. Hargrave | Piedmont | 13,389 |
| Duplin | Jeremiah Pearsall | John E. Hussey | Eastern | 11,291 |
| Edgecombe | Louis Dicken Wilson | Phesanton S. Sugg | Eastern | 14,935 |
| Franklin | Henry J. G. Ruffin | William P. Williams | Piedmont | 10,665 |
| Gates | Riddick Gatling | Whitmel Stallings | Eastern | 7,866 |
| Granville | Robert B. Gilliam | Josiah Crudup | Piedmont | 19,355 |
| Greene | Jesse Speight | Thomas Hooker | Eastern | 6,413 |
| Guilford | John Motley Morehead | Jonathan Parker | Piedmont | 18,737 |
| Halifax | John Branch | Joseph J. Daniel | Eastern | 17,739 |
| Haywood | William Welch | Joseph Cathey | Western | 4,578 |
| Hertford | Isaac Pipkin | Kenneth Rayner | Eastern | 8,537 |
| Hyde | Wilson B. Hodges | Alexander F. Gaston | Eastern | 6,184 |
| Iredell | Samuel King | John M. Young | Piedmont | 14,918 |
| Johnston | Jesse Adams | Hillory Wilder | Eastern | 10,938 |
| Jones | William Huggins | James W. Howard | Eastern | 5,608 |
| Lenoir | James Cox | Council Wooten | Eastern | 7,723 |
| Lincoln | Bartlett Shipp | Henry Cansler | Piedmont | 22,455 |
| Macon | Benjamin S. Brittain | James W. Guinn | Western | 5,333 |
| Martin | Jesse Cooper | Asa Biggs | Eastern | 8,539 |
| Mecklenburg | James M. Hutcheson | Isaac Grier | Piedmont | 20,073 |
| Montgomery | John B. Martin | James L. Gaines | Piedmont | 10,919 |
| Moore | John B. Kelly | Charles Chalmers | Piedmont | 7,745 |
| Nash | John Arrington | William W. Boddie | Eastern | 8,490 |
| New-Hanover | Lewis H. Marsteller | Owen Holmes | Eastern | 10,959 |
| Northampton | Roderick B. Gary | Samuel Calvert | Eastern | 13,391 |
| Onslow | David W. Saunders | John A. Averitt | Eastern | 7,814 |
| Orange | James Strudwick Smith | William Montgomery | Piedmont | 23,908 |
| Pasquotank | Richard H. Ramsay | John L. Bailey | Eastern | 8,641 |
| Perquimans | Jonathan H. Jacocks | Jesse Wilson | Eastern | 7,419 |
| Person | Moses Chambers | John W. Williams | Piedmont | 10,027 |
| Pitt | Robert Williams, Sr. | John Joiner | Eastern | 12,093 |
| Randolph | Alexander Gray | Benjamin Elliott | Piedmont | 12,406 |
| Richmond | Alfred Dockery | Henry W. Harrington | Piedmont | 9,396 |
| Robeson | John W. Powell | Richard C. Bunting | Eastern | 9,433 |
| Rockingham | Edward T. Brodnax | John L. Lesueur | Piedmont | 12,935 |
| Rowan | Charles Fisher | John Giles | Piedmont | 20,786 |
| Rutherford | Joseph Carson, MD | Theodorick F. Birchett | Western | 17,557 |
| Sampson | William B. Meares | Thomas I. Faison | Eastern | 11,634 |
| Stokes | Matthew R. Moore | Emanuel Shober | Piedmont | 16,196 |
| Surry | Meshack Franklin | William P. Dobson | Piedmont | 14,504 |
| Tyrrell | Hezekiah G. Spruill | Joseph Halsey | Eastern | 4,732 |
| Wake | Henry Seawell | Kimbrough Jones | Piedmont | 20,398 |
| Warren | Nathaniel Macon | Weldon Nathaniel Edwards | Piedmont | 11,877 |
| Washington | Joseph C. Norcom | Josiah Collins, Jr. | Eastern | 4,552 |
| Wayne | Gabriel Sherard | Lemuel H. Whitfield | Eastern | 10,331 |
| Wilkes | Edmund Jones | James Wellborn | Western | 11,968 |
| Yancey | Abner Jervis | Bacchus J. Smith | Western | 5,962 (1840) |