Romania facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Romania
România
|
|
|---|---|
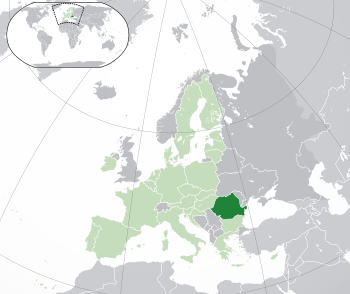 Show map of the European Union Show map of the European Union |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Bucharest 44°25′N 26°06′E / 44.417°N 26.100°E |
| Official languages | Romanian |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Romanian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Nicușor Dan | |
| Ilie Bolojan | |
| Mircea Abrudean | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Formation | |
| 1330 | |
| 1346 | |
|
• United Principalities
|
24 January 1859 |
|
• Independence from the Ottoman Empire
|
10 May 1877 |
| 13 March 1881 | |
|
• Great Union
|
1 December 1918 |
| 30 December 1947 | |
| 8 December 1991 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
238,397 km2 (92,046 sq mi) (81st) |
|
• Water (%)
|
3 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
|
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
79.9/km2 (206.9/sq mi) (136th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2024) | ▼ 28.0 low |
| HDI (2023) | very high · 55th |
| Currency | Romanian leu (RON) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +40 |
| ISO 3166 code | RO |
| Internet TLD | .ro |
Romania is a country in Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe. It shares borders with Ukraine, Hungary, Serbia, Bulgaria, Moldova, and the Black Sea. Romania has a mostly continental climate and covers about 238,397 square kilometers. Around 19 million people live there.
Romania is the 12th largest country in Europe by size. It is also the 6th most populated country in the European Union. The Danube river, Europe's second-longest, flows into the Danube Delta in Romania. The Carpathian Mountains cross the country, with Moldoveanu Peak being the highest point at 2,544 meters. Bucharest is Romania's largest city and financial hub. Other big cities include Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Iași, Constanța, and Brașov.
People have lived in Romania since ancient times. It was once the Dacian Kingdom before the Romans conquered it. The modern country of Romania was formed in 1859. This happened when Moldavia and Wallachia united under Alexandru Ioan Cuza. Romania gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1877. After World War I, more regions joined Romania, creating "Greater Romania."
Later, Romania lost some land during World War II. After the war, it became a socialist republic under Soviet influence. The 1989 Revolution ended this period. Since then, Romania has become a liberal democracy with a market economy.
Romania is now a country with a high-income economy. It is known as a middle power in global affairs. The country has 11 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also a popular place for tourists. Romania is a major exporter of car parts. It is also growing as a technology center with very fast internet speeds. Romania is a member of the European Union, NATO, and other international groups.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Romania comes from the Romanian word român. This word means "Roman" or "from Rome" in Latin. People started using this name in the 1500s. An old letter from 1521 mentions Wallachia as Țara Rumânească, which means "The Romanian Land."
A Look at History
Ancient Times: Dacia and the Roman Empire
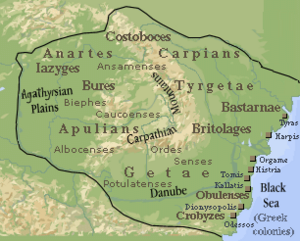
The first people in this area were likely the Thracians. The Getae and Dacians spoke similar languages. The Romans conquered Dacia. This led to a mix of cultures, forming the Daco-Romans. They are the ancestors of today's Romanians. When Dacia became a Roman Empire province, Vulgar Latin was introduced. This language later became the basis for the Romanian language.
Under King Burebista, the first Dacian state was formed. After his death, the state split into smaller kingdoms. The Dacian state became very strong under King Decebalus. But in 106 AD, the Roman emperor Trajan conquered part of Dacia. The Romans left Dacia between 271 and 275 AD.
Middle Ages: Principalities and Ottoman Influence
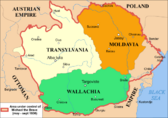
In the first thousand years, many groups like the Goths and Huns moved through Romania. In the 13th century, the first small states appeared. Wallachia was formed in 1310, and Moldova in 1359. Important rulers included Stephen the Great in Moldova and Vlad the Impaler in Wallachia.
By the late 1400s, these two states came under the Ottoman Empire's influence. Transylvania became a self-governing principality. Around 1600, Michael the Brave briefly united Wallachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania. He became a symbol for Romanian unity.
Modern Times: Unification and Independence
In the 1700s, the Habsburg monarchy took over Transylvania. Moldavia and Wallachia kept some freedom but were ruled by Greek governors chosen by the Ottomans. These rulers were called Phanariots. They often made life hard for the people.
In 1821, a revolt led by Tudor Vladimirescu started in Wallachia. This helped the principalities gain more freedom. The Treaty of Adrianople in 1829 made them even more independent.
Forming the Kingdom

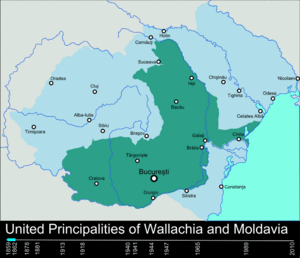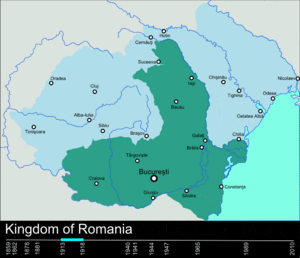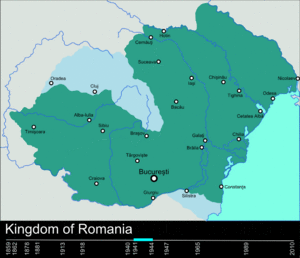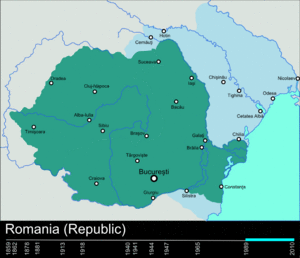
Modern Romania began in 1859. The principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia united. Alexandru Ioan Cuza was chosen as their ruler. He made many changes to modernize the country. In 1866, he had to step down.
Carol I of Romania became the new prince. On May 10, 1877, Romania declared its full independence. In 1881, Carol was crowned King of Romania. In 1913, Romania gained Southern Dobruja after a war with Bulgaria. King Carol I died in 1914, and Ferdinand I became king.
World War I and Greater Romania
In 1916, Romania joined World War I with the Entente Powers. After the war, the Austrian and Russian Empires fell apart. Transylvania, Bessarabia, and Bukovina joined Romania. This created "Greater Romania," which was the largest it had ever been. King Ferdinand I and Queen Maria were crowned rulers of all Romanians in 1922.
World War II and its Aftermath
In 1940, Romania lost some territories to the Soviet Union, Hungary, and Bulgaria. King Carol II gave up his throne. General Ion Antonescu took power. In 1941, Romania joined Nazi Germany in World War II against the Soviet Union.
On August 23, 1944, King Mihai I removed Antonescu from power. Romania then switched sides and joined the Allies. After the war, Romania regained Northern Transylvania.
Socialist Romania (1947–1989)
After World War II, the Soviet Union occupied Romania. In 1947, King Michael I was forced to step down. Romania became a socialist republic. The new communist government took strong control.
In the 1960s, Romania started to act more independently from the Soviet Union. In 1965, Nicolae Ceaușescu became the leader of the communist party. His rule became very strict in the 1980s.
Romania Since 1989
In December 1989, protests against the communist rule began in Timișoara. These quickly grew into a national uprising. Ceaușescu and his wife were executed on December 25, 1989.
A new government took over. Ion Iliescu became the temporary president. In May 1990, Romania held its first free elections since 1937. Iliescu won the presidency. He was reelected in 1992 after a new constitution was approved.
Klaus Iohannis became president in 2014 and was re-elected in 2019. In February 2025, he resigned due to political pressure. Ilie Bolojan became acting president. In the 2025 presidential election, Nicușor Dan was elected president.
Since 1989, Romania has worked to become a democratic state with a market economy. It has seen good economic growth. However, corruption has been a challenge. The National Anticorruption Directorate was formed in 2002 to fight this. In 2015, large protests led to the prime minister's resignation.
Geography and Nature
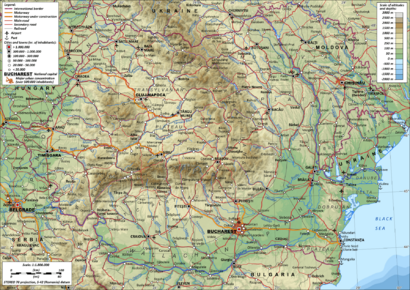
Romania is the largest country in Southeastern Europe. It covers 238,397 square kilometers. The land is split almost equally between mountains, hills, and plains. The Carpathian Mountains are in the center. They have 14 peaks over 2,000 meters high. The highest is Moldoveanu Peak at 2,544 meters.
Romania has many different natural areas. About 47% of the country's land is natural or semi-natural. There are nearly 10,000 square kilometers of protected areas. These include 13 national parks and three biosphere reserves.
The Danube river forms part of Romania's border. It flows into the Danube Delta, which is a huge wetland. It is the second-largest and best-preserved delta in Europe. It is also a World Heritage Site because of its rich plant and animal life. The Danube Delta is 5,800 square kilometers and has 1,688 different plant species.
Romania has large areas of undisturbed forest, covering almost 27% of its land. About 3,700 plant species have been found here. Many of these are rare or endangered.
The country is home to 33,792 animal species. This includes almost 400 unique types of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Romania has about 50% of Europe's brown bears and 20% of its wolves.
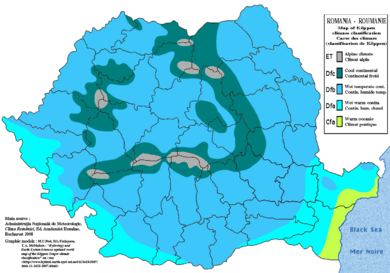
Climate
Romania has a continental climate with four clear seasons. This is because it is far from the open sea. The average yearly temperature is 11°C in the south and 8°C in the north. Summers in Bucharest can reach 28°C, and sometimes over 35°C in lower areas. Winters are cold, with average maximum temperatures below 2°C.
Rainfall is moderate. The highest western mountains get over 750 mm per year. Around Bucharest, it is about 570 mm. The western parts of Romania have a milder climate. The eastern part has a more typical continental climate. The Black Sea also affects the climate in the Dobruja region.
How Romania is Governed
Politics and Government
Romania is a unitary republic with a semi-presidential system. This means it has a president and a prime minister. The President is the head of state. They represent Romania in international matters. They also lead the Romanian Armed Forces. The president is elected by the people.
The Prime Minister is the head of government. They are chosen by the president and approved by the Parliament. The prime minister manages the government and its policies.
Romania's Parliament has two parts: the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. Members of Parliament are elected by the people. The justice system is separate from the government and Parliament. The highest court is the High Court of Cassation and Justice.
Foreign Relations
Since 1989, Romania has worked to build stronger ties with Western countries. It joined NATO in 2004 and the European Union in 2007. Romania is seen as a middle power because of its military and diplomatic efforts.
Romania supports other Eastern European countries joining NATO and the EU. It has close ties with Moldova because they share a language and history. Romania fully joined the Schengen Area in 2025.
In 2005, Romania and the United States agreed to allow a U.S. military presence in Romania. In 2011, Romania agreed to host a U.S. missile defense system. This system became active in 2016.
Military
The Romanian Armed Forces include land, air, and naval forces. They are led by a Commander-in-chief under the Ministry of National Defence. The president is the Supreme Commander during wartime. Romania has about 71,500 active military personnel.
Romania stopped requiring military service in 2007. Now, it has a volunteer army. The country spends about 2.44% of its GDP on defense. This is about $8.48 billion.
The Air Force uses F-16 fighter jets and transport planes. The Navy has frigates and corvettes. Romania sent troops to Afghanistan and Iraq. It ended its mission in Iraq in 2009.
In 2024, work began to expand the Mihail Kogălniceanu Air Base. It is planned to become the largest NATO base in Europe.
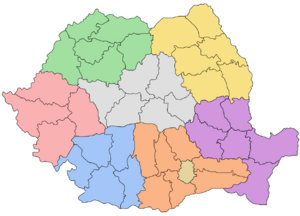
Administrative Divisions
Romania is divided into 41 counties and the city of Bucharest. Each county has a council for local matters. A prefect handles national affairs in each county. Counties are further divided into cities and communes. These have their own mayors and local councils. There are 320 cities and 2,861 communes. Bucharest is a special case, acting like a county itself.
| Development region | Area (km2) | Population (2021) | Most populous urban centre* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nord-Vest | 34,152 | 2,521,793 | Cluj-Napoca (411,379) |
| Centru | 34,097 | 2,271,067 | Brașov (369,896) |
| Nord-Est | 36,853 | 3,226,436 | Iași (382,484) |
| Sud-Est | 35,774 | 2,367,987 | Constanța (425,916) |
| Sud – Muntenia | 34,469 | 2,864,339 | Ploiești (276,279) |
| București - Ilfov | 1,803 | 2,259,665 | Bucharest (2,272,163) |
| Sud-Vest Oltenia | 29,207 | 1,873,607 | Craiova (356,544) |
| Vest | 32,042 | 1,668,921 | Timișoara (384,809) |
Economy and Development
In 2024, Romania's economy was valued at about $894 billion. Its GDP per person was $47,203. The World Bank considers Romania a high-income economy. Romania's economy has grown quickly, especially since joining the EU in 2007.
The Bucharest Stock Exchange is Romania's stock market. In 2024, it had a market value of $74 billion. Many companies are listed there.
After 1989, Romania's economy faced challenges. But from 2000 onwards, it became more stable. It saw high growth and low unemployment. In 2006, the economy grew by 7.7%, one of the highest rates in Europe. However, the Great Recession in the late 2000s caused a setback.
Romania's main exports include vehicles, software, clothing, and machinery. It trades mostly with EU countries like Germany, Italy, and France.
In 2005, Romania set a flat tax rate of 16% for personal income and company profits. This is one of the lowest rates in the EU. Services make up most of Romania's economy (56.2%). Industry accounts for 30%, and agriculture for 4.4%. About 25.8% of Romanian workers are in agriculture.
Foreign companies have invested a lot in Romania since the end of communism. Romania plans to adopt the euro currency in 2029.
Infrastructure
Romania has a large road network, estimated at 86,080 km in 2015. Its railway network is the fourth-largest in Europe, with 22,298 km of track. Rail transport has improved recently due to upgrades. The Bucharest Metro is the only underground railway system. It opened in 1979 and is 80.01 km long.
Romania has 16 international airports. Over 12.8 million passengers used Bucharest's Henri Coandă International Airport in 2017.
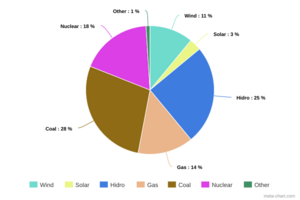
Romania exports more electricity than it imports. About a third of its energy comes from renewable sources, mainly hydroelectric power. It has large oil and natural gas reserves. Romania is also expanding its nuclear power plant at Cernavodă.
In 2014, there were almost 18.3 million internet connections. Romania is known for having some of the fastest internet speeds in the world.
Tourism
Tourism is important for Romania's economy. It makes up about 5% of the country's GDP. The number of tourists has been growing. In 2016, 9.33 million foreign tourists visited Romania.
Popular summer spots include Mamaia and other Black Sea resorts. Skiing is popular in areas like Valea Prahovei and Poiana Brașov.
Many tourists visit Romania's castles and old medieval towns. Cities like Cluj-Napoca, Sibiu, and Brașov are popular. Bran Castle, often called "Dracula's Castle," attracts many visitors. Other attractions include the Danube Delta and the sculptures of Constantin Brâncuși.
Rural tourism is also growing. Visitors can learn about local traditions. They can see the painted churches of northern Moldavia and the wooden churches of Maramureș. The Via Transilvanica is a long hiking and cycling trail. It helps promote slow tourism in rural areas.
People and Culture
Demographics
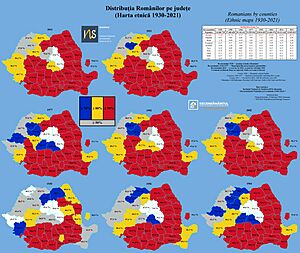
In 2021, Romania's population was 19,053,815. The population is expected to slowly decrease. Most people are Romanians (89.33%). Other groups include Hungarians (6.05%) and Roma (3.44%). Hungarians are the majority in Harghita and Covasna counties. Other minorities include Ukrainians, Germans, and Turks.
The birth rate in Romania is lower than the death rate. This means the population is shrinking and getting older. In 2015, life expectancy was about 74.92 years. Many Romanians have moved to other countries since 1989.
Languages
The official language is Romanian. It is a Romance language, similar to Italian, French, and Spanish. The Romanian alphabet has 31 letters, including five special ones.
Romanian is the first language for 91.55% of the population. Hungarian and Vlax Romani are also spoken by many people. The Constitution protects the language rights of minorities. In areas where a minority group is over 20% of the population, their language can be used in public services.
English and French are the main foreign languages taught in schools. In 2012, 31% of Romanians spoke English, and 17% spoke French.
Religion
Romania is a secular state, meaning it has no official religion. Most people are Christians. In 2021, 73.60% identified as Orthodox Christians. Most of these belong to the Romanian Orthodox Church. Other Christian groups include Protestants and Roman Catholics. There are also about 58,347 Muslims and 2,708 Jewish people.
The Romanian Orthodox Church is the third-largest Eastern Orthodox Church in the world. It uses a Romance language for its services.
Urbanization
In 2011, 54.0% of Romanians lived in urban areas. This percentage has been slowly decreasing. Bucharest is the capital and largest city, with over 1.7 million people in 2021. Its larger urban area has almost 2.2 million people.
Seventeen other cities have populations over 100,000. These include Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Constanța, and Timișoara. Many of these cities have formed metropolitan areas.
|
Largest cities in Romania
2021 Census |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Bucharest | 1,716,961 |
| 2 | Cluj-Napoca | 286,598 |
| 3 | Iași | 271,692 |
| 4 | Constanța | 263,688 |
| 5 | Timișoara | 250,849 |
| 6 | Brașov | 237,589 |
| 7 | Craiova | 234,140 |
| 8 | Galați | 217,851 |
| 9 | Oradea | 183,105 |
| 10 | Ploiești | 180,540 |
Education

Romania's education system has been changing since 1989. In 2004, about 4.4 million people were in school. This included kindergarten, primary, secondary, and university levels. In 2018, 98.8% of adults could read and write.
Schooling is required from age 5 until the twelfth grade. Primary and secondary education lasts 12 or 13 grades. Some Romanian universities are ranked among the top in the world.
Romania has a strong record in international academic competitions. It ranks fifth in medals at the International Mathematical Olympiad. It is also sixth in medals at the International Olympiad in Informatics.
Healthcare
Healthcare in Romania is mainly public. Most hospitals are run by the state. Nearly all citizens have national health insurance. In 2021, healthcare spending was about $16.7 billion.
Romania has over 65,000 health units. This includes 543 hospitals. Many of these are large hospitals with over 100 beds.
Culture and Traditions
Arts and Monuments

Romanian culture has a rich history. Famous writers from the 19th century include Mihai Eminescu, considered the greatest Romanian poet. In the 20th century, artists like Constantin Brâncuși gained international fame. Brâncuși's sculptures are very valuable.

Well-known Romanian painters include Nicolae Grigorescu. Famous classical composers include George Enescu. The annual George Enescu Festival is held in Bucharest. Modern musicians like Inna and Alexandra Stan are also known internationally.
Romanian films have won awards at major festivals. 4 Months, 3 Weeks and 2 Days won the top prize at the Cannes Film Festival in 2007.
Romania has six cultural sites on the World Heritage List. These include painted churches, wooden churches of Maramureș, and villages with fortified churches in Transylvania. The city of Sibiu was a European Capital of Culture in 2007. Many castles, like Peleș Castle and Bran Castle, are popular tourist spots.
Holidays, Traditions, and Food

Romania has 12 public holidays. Great Union Day is celebrated on December 1st. Winter holidays include Christmas and New Year. People perform special folklore dances and games during this time. Traditional Romanian clothing is often worn.
Easter traditions include painting eggs. On March 1st, people give mărțișor talismans for good luck.
Romanian food has been influenced by Austrian and German cooking. It also shares similarities with Greek and Bulgarian food. Common dishes include Ciorbă (sour soups), mititei (grilled sausages), and sarmale (cabbage rolls).
Pork, chicken, and beef are popular meats. Special dishes are made for holidays. Țuică, a strong plum brandy, is Romania's traditional alcoholic drink. Wine and beer are also popular.
Sports
Football is the most popular sport in Romania. The Romania national football team has played in seven FIFA World Cups. They had their best performance in 1994, finishing 6th.
Steaua București was the first Eastern European team to win the UEFA Champions League in 1986. Dinamo București also had success in European club competitions.
Tennis is the second most popular sport. Romania reached the Davis Cup finals three times. Handball is also very popular. The men's national team has won the world championship four times. The women's team won in 1962.
Romania has won many medals at the Summer Olympics. It ranks 12th in total medals and 14th in gold medals. Gymnastics is a major medal-winning sport for Romania.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Rumania para niños
In Spanish: Rumania para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |