World War I facts for kids
Quick facts for kids World War I |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Clockwise from the top:
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
Allied Powers:
|
Central Powers:
|
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Total: 42,950,000 | Total: 25,248,000 | ||||||||
| 68,208,000 (Total all) | |||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
Military deaths by country: |
Military deaths by country: |
||||||||
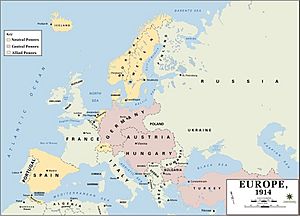
World War I (also called WWI or the Great War) was a huge global conflict that lasted from July 28, 1914, to November 11, 1918. Most of the fighting happened in Europe, but soldiers from many other countries joined in. This war changed the colonial empires of European nations. Before World War II started in 1939, people called World War I the Great War because it was so big. About 135 countries were involved, and nearly 10 million people died fighting.
Before the war, European countries formed alliances to protect themselves. This divided them into two main groups. When Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was killed on June 28, 1914, Austria-Hungary blamed Serbia and declared war. Serbia's ally, Russia, then declared war on Austria-Hungary. This started a chain reaction, with countries on both sides declaring war on each other. The two main sides were the Allied Powers (including Russia, France, and the British Empire) and the Central Powers (mainly Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire).
Fighting took place in many different areas. The French and British fought the Germans on the Western Front in France and Belgium. Germany tried to defeat France quickly but was stopped at the First Battle of the Marne. After that, much of the fighting there was trench warfare. The Russians fought the Germans and Austro-Hungarians on the Eastern Front in Central and Eastern Europe. This fighting was more about moving armies, not just trenches. Other major battle areas included the Middle East, the Gallipoli region of Turkey, and between Italy and Austria-Hungary. Battles also happened in Africa, China, at sea, and in the air. World War I was the first major war where tanks, airplanes, and submarines (called U-boats) were important weapons.
In 1917, the Russians had a revolution and left the war in March 1918. Also in 1917, the United States joined the war, though it took a year for their main army to arrive. After Russia left and before the Americans fully arrived, Germany launched a huge attack in March 1918 to try and win the war. But it wasn't enough. From August to November 1918, the Allied Powers won a big victory against the Germans in the Hundred Days Offensive. Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire then agreed to stop fighting. The German government fell, and a new government agreed to end the war on November 11.
The war ended with several treaties, the most important being the Treaty of Versailles. The war also led to the creation of the League of Nations, an organization meant to prevent future wars. People were shocked by how many people died and how much damage the war caused. They hoped it would be the war to end all wars. Instead, it led to another, even bigger world war 21 years later.
Contents
How Did World War I Start?
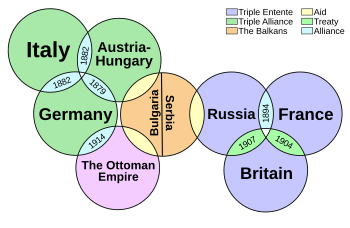
By 1914, Europe was full of tension. Many countries worried about being invaded by others. For example, Germany was becoming very powerful, which the British saw as a threat to their British Empire. To protect themselves, countries formed alliances, which ended up dividing Europe into two large groups. Germany and Austria-Hungary had been allies since 1879. They later formed the Triple Alliance with Italy in 1882. France and Russia became allies in 1894. They then joined with Britain to form the Triple Entente.
In 1908, Austria-Hungary took control of Bosnia, a region next to Serbia. Some people in Bosnia were Serbian and wanted Bosnia to be part of Serbia. A group called the Black Hand wanted to kill Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria when he visited Sarajevo, Bosnia's capital. They tried to kill him with grenades, but failed. However, a Serbian student named Gavrilo Princip shot and killed the Archduke and his pregnant wife with a pistol.
Austria-Hungary blamed Serbia for the assassination. Germany supported Austria-Hungary and promised to help if war started. Austria-Hungary sent a very strict list of 10 rules, called the July Ultimatum, to Serbia. Many historians believe Austria-Hungary already wanted a war with Serbia. Serbia agreed to most of the rules, but not all. Because of this, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. This quickly pulled both countries' allies into the war within days.
Russia joined the war to help Serbia because many Serbians were Slavic, and Slavic countries had agreed to help each other if attacked. Russia, being a large country, started moving its soldiers. Germany worried that Russia's soldiers might also attack Germany. Germany and Russia had not been friendly in the past. Germany declared war on Russia. Germany then put into action a plan made long ago to fight a war in Europe. Germany is in the middle of Europe, so it couldn't attack Russia in the east without weakening its forces in the west, towards France. Germany's plan was to quickly defeat France in the west before Russia was ready to fight. Then, Germany would move its armies east to fight Russia. Germany couldn't invade France directly because France had many forts on their border. So, Germany invaded the nearby country of Belgium to get into France through an undefended border. Great Britain then joined the war, saying it wanted to protect Belgium. Some historians think Britain would have joined to help France even if Germany hadn't gone through Belgium.
Soon, most of Europe was involved. The Ottoman Empire (now Turkey) joined Germany and Austria-Hungary. It's not fully clear why they joined or chose that side, but they had become friendly with Germany. Although Italy was allied with Germany and Austria-Hungary, they had only agreed to fight if those countries were attacked first. Italy argued that since Austria-Hungary attacked Serbia first, Italy didn't have to fight. Italy also didn't like Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Allied Powers in 1915.
Major Events and Battles
Most people thought the war would be short. They believed armies would move quickly, attack, and one side would win without many deaths. They thought it would be a war of brave soldiers, not understanding how warfare had changed. Only a few, like Lord Kitchener, predicted the war would last a long time.
German generals decided the best way to defeat France was to go through Belgium, using a plan called the Schlieffen Plan. This plan was created by German Army Chief of Staff, Alfred Von Schlieffen. They aimed to attack the French army from both the north and south at the same time. The German Army entered Belgium on August 4th. On the same day, Great Britain declared war on Germany. Britain had promised in 1839 to protect Belgium's neutrality, and they kept their word.
When the Germans reached the Belgian city of Liège, the Belgians fought fiercely to stop them. The Germans eventually pushed the Belgians out, but it took longer than planned. Then, the Germans attacked the northern part of the French army. The French and British moved troops to fight the Germans. They could do this because the Belgians had held out for so long at Liège. The Germans pushed the French back at the borders. The British held the Germans back at Mons but then also retreated to join the French army. They finally stopped the Germans at the River Marne. This was called the First Battle of the Marne or the Miracle of the Marne.
In the East, the Russians attacked the Germans. The Russians pushed the Germans back, but then the Germans defeated the Russians at the Battle of Tannenberg.
What Was Trench Warfare Like?
Trench warfare caused huge numbers of soldier deaths. New weapons like machine guns and long-range artillery fired much faster. They killed many soldiers during mass charges, which was an old battle tactic. Soldiers on both sides dug holes, which then connected to form long trenches. These lines of trenches stretched all the way from Switzerland to the North Sea. In front of the trenches, there was barbed wire to cut anyone trying to cross, and land mines that exploded. Later in the war, poison gas also became an important weapon.
The new machine guns, artillery, trenches, and mines made attacking very hard. Generals, used to older wars, ordered their armies to attack in old ways, marching in rows. This made soldiers easy targets. At the Battle of the Somme in 1916, 60,000 British men died in a single day. It was one of the deadliest days for the British army. Later in the war, the British and French invented tanks. They used them to attack German trenches, but they couldn't make enough to make a huge difference. The Germans developed special tactics to sneak into enemy positions, but these were also too little, too late.
The British used whistles to signal other soldiers. Before shelling German trenches, they would blow the whistle. Germans soon learned this tactic. After the shelling, when British soldiers came to attack, the Germans were ready with their machine guns because they knew they were coming.
How Airplanes Changed Warfare

Airplanes were used a lot for the first time in World War I. Before this war, airplanes weren't used much in fighting. This was the first war to use them as weapons. At first, airplanes were used for reconnaissance, meaning they took pictures of enemy land and helped direct artillery. By the end of the war, generals saw airplanes as a key part of their attack plans. World War I showed that airplanes could be very important war weapons.
Airplanes in World War I were made of wood and canvas, a strong fabric. They didn't last very long. At the start of the war, they couldn't fly very fast, only up to 116 kilometers per hour (72 miles per hour). By the end of the war, they could fly up to 222 kilometres per hour (138 miles per hour). But they were still much slower than planes today. Guns were put on planes for the first time during the war. Pilots, who fly the planes, used these guns to shoot enemy planes. One pilot used metal sheets to armor his airplane. Other pilots started doing this too. Pilots also improved their planes with machine guns, which shoot bullets much faster. Machine guns made fighting between airplanes much harder and more dangerous.
Pilots had to wear special clothes when flying in World War I. They flew high where the air is cold. Their clothes kept them warm and protected them from wind and cold. Pilots wore a leather coat to protect their bodies. They wore a padded helmet and goggles, which are large glasses with special lenses, to protect their head and face. They also wore a scarf around their neck. The scarf stopped the wind from blowing against their neck when they turned their head.
Why Did the USA Join the War?
The German leaders decided to use submarines, called U-boats (from the German word Unterseeboot, meaning underwater boat). These U-boats attacked passenger ships, like the RMS Lusitania, carrying civilians to Great Britain. They didn't follow the laws of war because the British could destroy them if they did. America was selling weapons to Germany's enemies but not to Germany, which meant they weren't truly "neutral" (not involved in the war). Many American and British civilians were killed by these submarines.
Germany also sent a secret telegram to Mexico in code. This note, called the Zimmermann Telegram, suggested that Mexico and Germany work together to attack the United States. It offered Mexico land in the southwestern United States that the United States had taken in earlier wars. Spies from the United Kingdom found out about the note and told the United States. American people became very angry. Many decided they wanted their country to join the war against Germany. For these reasons, on April 6, 1917, the United States declared war against Germany and joined the Allies.
Russia Leaves the War
By the end of 1916, nearly five million Russian soldiers were killed, wounded, or captured. Major cities faced food shortages and high prices. In March 1917, Tsar Nicholas ordered the military to stop strikes in Petrograd, but the troops refused to fire on the crowds. Revolutionaries formed the Petrograd Soviet. Fearing a takeover, the State Duma forced Nicholas to step down and set up the Russian Provisional Government. This government said Russia would keep fighting the war. However, the Petrograd Soviet refused to stop, creating two competing power centers. This caused confusion and chaos, and soldiers at the front became very discouraged.
After the Tsar stepped down, Vladimir Lenin, with help from the German government, was brought from Switzerland to Russia on April 16, 1917. Unhappiness and the weakness of the Provisional Government made the Bolshevik Party, led by Lenin, very popular. They demanded an immediate end to the war. The November Revolution was followed in December by a ceasefire and talks with Germany. At first, the Bolsheviks refused Germany's terms. But when German troops started marching through Ukraine without resistance, they agreed to the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk on March 3, 1918. This treaty gave huge areas, including Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and parts of Poland and Ukraine, to the Central Powers.
With the Russian Empire out of the war, Romania was left alone on the Eastern Front. It signed the Treaty of Bucharest with the Central Powers in May 1918. Under this treaty, Romania gave land to Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria and leased its oil to Germany. However, the treaty also meant the Central Powers recognized the joining of Bessarabia with Romania.
What Happened After the War?
After the war, Germany had to agree to the Treaty of Versailles. Germany had to pay about $31.5 billion in reparations (payments for damages). They also had to take responsibility for starting the war. Part of the treaty suggested that countries should form an international organization to prevent future wars. This organization was called the League of Nations. The United States Senate did not agree with this, even though it was the idea of the US president, Woodrow Wilson. Woodrow Wilson tried to convince the American people to agree, but the United States never joined the League of Nations. Problems with the Treaty in Germany later contributed to World War II.
Images for kids
-
Military recruitment near Tiberias, Ottoman Empire, 1914
-
Royal Irish Rifles in a communications trench, first day on the Somme, 1916
-
King George V (front left) and a group of officials inspect a British munitions factory in 1917
-
Refugee transport from Serbia in Leibnitz, Styria, 1914
-
Mehmed V greeting Wilhelm II on his arrival at Constantinople
-
A pro-war demonstration in Bologna, 1914.
-
Marshal Joffre inspecting Romanian troops, 1916
-
"They shall not pass", a phrase typically associated with the defense of Verdun.
-
French Army lookout at his observation post, Haut-Rhin, France, 1917.
-
Ottoman troops during Mesopotamian campaign.
-
British artillery battery on Mount Scopus in the Battle of Jerusalem, 1917.
-
British troops on the march during Mesopotamian campaign, 1917
-
President Wilson before Congress, announcing the break in official relations with Germany on 3 February 1917
-
British 55th Division soldiers, blinded by tear gas during the Battle of Estaires, 10 April 1918
-
French soldiers under General Gouraud, with machine guns amongst the ruins of a cathedral near the Marne, 1918.
-
Canadian Scottish, advancing during the Battle of the Canal du Nord, 1918
-
The New York Times of 11 November 1918
-
Greek prime minister Eleftherios Venizelos signing the Treaty of Sèvres
-
The Signing of Peace in the Hall of Mirrors, Versailles, 28 June 1919
-
British Vickers machine gun, 1917
-
The First Contingent of the Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps to the 1 Lincolns, training in Bermuda for the Western Front, winter 1914–1915. The two BVRC contingents suffered 75% casualties.
-
British prisoners guarded by Ottoman forces after the First Battle of Gaza in 1917.
-
Poster urging women to join the British war effort, published by the Young Women's Christian Association
-
Sackville Street (now O'Connell Street) after the 1916 Easter Rising in Dublin
-
Young men registering for conscription, New York City, 5 June 1917
-
A 1919 book for veterans, from the US War Department
See also
 In Spanish: Primera Guerra Mundial para niños
In Spanish: Primera Guerra Mundial para niños