Vietnam facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Cộng hòa Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam (Vietnamese)
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: Độc lập – Tự do – Hạnh phúc
"Independence – Freedom – Happiness"
|
|
|
Anthem: Tiến Quân Ca
"The Song of the Marching Troops" |
|
|
Location of Vietnam (green)
in ASEAN (dark grey) |
|
| Capital | Hanoi 21°2′N 105°51′E / 21.033°N 105.850°E |
| Largest city | Ho Chi Minh City 10°48′N 106°39′E / 10.800°N 106.650°E |
| Official language | Vietnamese |
| Ethnic groups
(2019)
|
|
| Religion
(2019)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Vietnamese Viet (colloquial) |
| Government | Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic |
| Tô Lâm | |
| Lương Cường | |
| Phạm Minh Chính | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation | |
|
• Văn Lang
|
7th century BC |
|
• Âu Lạc
|
3rd century BC |
| 111 BC | |
|
• Independence from China
|
939 |
| 1428 | |
|
• Nguyễn's unification
|
1802 |
|
• Protectorate Treaty
|
25 August 1883 |
|
• Declaration of Independence
|
2 September 1945 |
|
• North–South division
|
21 July 1954 |
| 30 April 1975 | |
|
• Reunification
|
2 July 1976 |
|
• Đổi Mới
|
18 December 1986 |
|
• Current constitution
|
28 November 2013 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
331,344.82 km2 (127,932.95 sq mi) (66th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
6.38 |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
100,300,000 (15th) |
|
• 2019 census
|
96,208,984 |
|
• Density
|
298/km2 (771.8/sq mi) (49th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2020) | ▲ 36.8 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 107th |
| Currency | Vietnamese đồng (₫) (VND) |
| Time zone | UTC+07:00 (Vietnam Standard Time) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +84 |
| ISO 3166 code | VN |
| Internet TLD | .vn |
Vietnam is a country in Southeast Asia. Its full name is the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It also has sea borders with Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia. The capital city is Hanoi, and the largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (also known as Saigon).
Contents
- Exploring Vietnam's Past: A Brief History
- Vietnam's Diverse Geography
- Vietnam's Climate and Weather
- Amazing Biodiversity in Vietnam
- Understanding Vietnam's Government and Politics
- How Vietnam is Divided: Administrative Divisions
- Vietnam's Growing Economy
- Education in Vietnam
- Understanding Vietnam's Population
- Religion and Beliefs in Vietnam
- Languages Spoken in Vietnam
- Vietnamese Culture and Traditions
- Delicious Vietnamese Cuisine
- Holidays and Festivals in Vietnam
- Popular Sports in Vietnam
- Related pages
- Images for kids
- See also
Exploring Vietnam's Past: A Brief History
People have lived in Vietnam since the Paleolithic age. Early states formed around the Red River Delta in northern Vietnam over 2,000 years ago. From 111 BC, parts of Vietnam were ruled by China. The first independent Vietnamese dynasty, the Ngô dynasty, appeared in 939 AD.
Later Vietnamese kingdoms adopted ideas from China, like Confucianism and Buddhism. They also expanded their land southward to the Mekong Delta. In 1883, the last imperial family, the Nguyễn dynasty, was taken over by France. Vietnam became part of French Indochina in 1887.
After World War II, a group called the Viet Minh, led by Ho Chi Minh, declared Vietnam's independence in 1945. However, France tried to regain control, leading to the First Indochina War. Vietnam won this war in 1954.
Vietnam's Modern History and Reunification
After the war, Vietnam was divided into two parts: North Vietnam (communist) and South Vietnam (anti-communist). This led to the Vietnam War, with the Soviet Union and China supporting the North, and the United States supporting the South. The war ended in 1975 with North Vietnam's victory.
In 1976, Vietnam became one united socialist state under the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV). After the war, the country faced economic challenges. In 1986, the CPV started economic and political changes called Đổi Mới. These changes helped Vietnam join the global economy and improve its situation.
Vietnam's Diverse Geography

Vietnam is located on the eastern Indochinese Peninsula. It covers about 331,210 square kilometers (127,880 square miles). The country has a long coastline of 3,444 kilometers (2,140 miles). At its narrowest point, Vietnam is only about 50 kilometers (31 miles) wide.
Most of Vietnam's land is hilly and covered in forests. Mountains make up 40% of the country's area. The Red River Delta in the north is a flat, fertile region. The Mekong River Delta in the south is also a low-lying plain, crisscrossed by many rivers and canals.

Southern Vietnam has coastal lowlands and mountains from the Annamite Range. The highlands here have rich basalt soil. Fansipan is Vietnam's highest mountain, standing 3,143 meters (10,312 feet) tall. Vietnam also has many islands, with Phú Quốc being the largest. The Hang Sơn Đoòng Cave is known as the world's largest cave passage. The Ba Bể Lake and Mekong River are the largest lake and longest river in Vietnam.
Vietnam's Climate and Weather
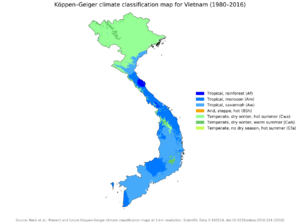
Vietnam's climate changes a lot from one region to another. This is because of its long shape and varied landscape. From November to April, during the dry season, winds blow from the northeast. These winds pick up moisture over the Gulf of Tonkin.
Temperatures are generally higher in the plains than in the mountains. Southern Vietnam, around Ho Chi Minh City, has temperatures between 21 and 35 °C (70 and 95 °F) all year. In Hanoi, temperatures are lower, ranging from 15 to 33 °C (59 to 91 °F). In the northern mountains, temperatures can drop to 3 °C (37 °F) in winter and reach 37 °C (99 °F) in summer. Snow can even fall on the highest peaks near the Chinese border in winter.

Vietnam gets a lot of rain, especially during the monsoon seasons. This often causes flooding. The country is also affected by tropical storms and typhoons. Vietnam is very vulnerable to climate change, with many people living in low-lying coastal areas.
Amazing Biodiversity in Vietnam

Vietnam is one of the top 25 countries in the world for its amazing variety of life, known as biodiversity. It ranks 16th globally, being home to about 16% of the world's species. Over 15,986 types of plants have been found here, with 10% found nowhere else.
Vietnam's animals include many insects, reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 100 bird species and 78 mammal species are unique to Vietnam. The country has two World Natural Heritage Sites: Hạ Long Bay and Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park. It also has nine biosphere reserves.
In recent years, many new species of plants and animals have been discovered in Vietnam. These include six new mammal species like the saola and Tonkin snub-nosed monkey. Sadly, the last Javan rhinoceros in Vietnam was reportedly lost in 2010.
Protecting wildlife is a big concern in Vietnam. Organizations like Education for Nature – Vietnam and GreenViet work to raise awareness and stop poaching. However, the illegal trade of animal parts, like rhinoceros horns, remains a challenge.
Understanding Vietnam's Government and Politics
Vietnam is a united one-party socialist republic. It is one of two communist states in Southeast Asia (the other being Laos). The Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV) plays a central role in all parts of the country's government and society, as stated in the constitution.
The president is the head of state and the leader of the military. This person also handles executive duties and sets policies. The general secretary of the CPV manages the party's national organization.
The prime minister is the head of government. The prime minister leads a group of ministers who manage different government departments. Only political groups connected to or approved by the CPV can participate in elections.
The National Assembly of Vietnam is the country's main law-making body, with 500 members. It is more powerful than the executive and judicial branches. All government ministers are chosen from its members. The Supreme People's Court of Vietnam is the highest court, but it also answers to the National Assembly.
How Vietnam is Divided: Administrative Divisions
Vietnam is divided into 58 provinces. There are also five major municipalities (large cities) that are treated like provinces. These include Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
|
|

Provinces are further divided into cities, townships, and counties. These are then split into smaller towns or communes. The main municipalities are divided into districts and counties, which are then split into wards.
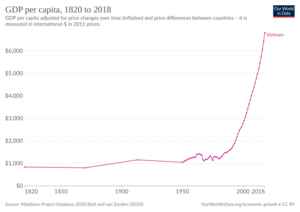
Vietnam's Growing Economy
| Share of world GDP (PPP) | |
|---|---|
| Year | Share |
| 1980 | 0.21% |
| 1990 | 0.28% |
| 2000 | 0.39% |
| 2010 | 0.52% |
| 2020 | 0.80% |
For a long time, Vietnam's economy was mostly based on agriculture, especially growing rice. The country also has bauxite, which is used to make aluminium. After the country was reunified, the government, led by the CPV, planned the economy using "Five Year Plans."
Many businesses were owned by the state, but this led to problems like inefficiency. When economic aid from the Soviet Union decreased, Vietnam started to change its economy. In 1986, the CPV began economic reforms called Đổi Mới.

These reforms encouraged private businesses in farming, industry, and trade. This helped Vietnam's economy grow quickly, with about 8% growth each year between 1990 and 1997. The United States also ended its trade restrictions against Vietnam in 1994.
Even with a global economic slowdown in the late 1990s, Vietnam's economy recovered and grew around 7% per year from 2000 to 2005. In 2007, Vietnam joined the World Trade Organization (WTO). The country has significantly reduced poverty, with fewer people living on less than $1 a day.
Agriculture: Farming and Fishing
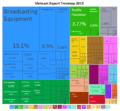
Thanks to land reforms, Vietnam has become a major exporter of farm products. It is the world's largest producer of cashew nuts and black pepper. Since the 1990s, it has been the second-largest rice exporter after Thailand. Vietnam is also the world's second-largest exporter of coffee. Other important exports include tea, rubber, and fish products.
The share of agriculture in Vietnam's economy has decreased over the years. This is because other parts of the economy have grown.
Seafood Production
Vietnam's fishing industry has grown a lot. In 2011, it produced 5.6 million metric tons of fish and seafood. By 2016, this increased to 6.7 million metric tons. This growth is largely due to the expansion of aquaculture (fish farming).
Science and Technology Advances
In 2010, Vietnam spent about 0.45% of its GDP on science and technology. Vietnamese scientists have made important contributions, especially in mathematics. For example, Hoàng Tụy was a pioneer in applied mathematics. Ngô Bảo Châu won the 2010 Fields Medal for his work in mathematics.
Vietnam is also working on its first national space flight program. The country has made progress in developing robots, like the TOPIO humanoid robot. Zalo, a popular Vietnamese messaging app, was created by a Vietnamese developer.

Vietnam's ranking in the Global Innovation Index has improved a lot, from 76th in 2012 to 46th in 2023. The number of scientific publications from Vietnam has also increased. These publications often focus on life sciences, physics, and engineering.
Tourism: Exploring Vietnam's Beauty
Tourism is a very important part of Vietnam's economy, making up 7.5% of its total GDP. In 2017, Vietnam welcomed about 13 million tourists, making it one of the fastest-growing tourist spots in the world. Most visitors come from Asia, especially China, South Korea, and Japan. Many also come from Europe, the United States, and Australia.
The most popular places to visit are Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, and Hạ Long, which includes Hạ Long Bay. All three are among the top 100 most visited cities globally. Vietnam is home to eight UNESCO World Heritage Sites. In 2018, Travel + Leisure magazine named Hội An one of the world's best destinations.
Education in Vietnam
Vietnam has a large system of schools, colleges, and universities controlled by the state. There are also more private schools now. Education is divided into kindergarten, elementary, middle, high school, and university. Many public schools have been built to improve the country's literacy rate, which was 90% in 2008.
Most universities are in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. The government is always working to improve the education system. Basic education is mostly free for poorer families. Vietnam has one of the highest school enrollment rates in the world.
The number of colleges and universities grew a lot in the 2000s. Enrollment in higher education has increased tenfold since 1995. Some foreign universities also have campuses in Vietnam. The government is committed to investing in education, especially for those who are less fortunate.
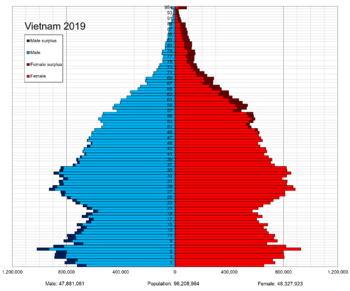
Understanding Vietnam's Population
Ethnic groups of Vietnam Vietnamese (85.32%) Other (14.68%)
As of 2023, Vietnam has about 100.3 million people. The main ethnic group is the Viet or Kinh, who make up about 85.32% of the population. Most of them live in the country's river deltas and coastal plains.
Religion and Beliefs in Vietnam
Religion in Vietnam (2019) Vietnamese folk religion or no religion (86.32%) Buddhism (4.79%) Catholicism (6.1%) Protestantism (1.0%) Hoahaoism (1.02%) Caodaism (0.58%) Islam (0.07%) Others (0.12%)
The 1992 Constitution of Vietnam states that all citizens have freedom of belief and religion. All religions are treated equally under the law, and places of worship are protected. However, religious beliefs cannot be used to go against state laws.
Most Vietnamese people do not follow an organized religion. However, many practice some form of Vietnamese folk religion. Confucianism, a system of social and ethical ideas, still influences modern Vietnam. Mahāyāna Buddhism is the main type of Buddhism practiced. About 8-9% of the population is Christian, including Roman Catholics and Protestants.
Languages Spoken in Vietnam
The national language of Vietnam is Vietnamese. It is a tonal language from the Austroasiatic family. Most people in Vietnam speak it. Minority groups in Vietnam speak many different languages. These include Tày, Mường, Cham, Khmer, Chinese, Nùng, and Hmong.
French is spoken by some educated older Vietnamese people. This is a legacy of colonial rule. Vietnam is still a member of the International Organisation of the Francophonie. Russian, German, Czech, and Polish are known by some northern Vietnamese. This is due to historical ties with Eastern European countries.
With better relations with Western countries, English is now widely used as a second language. Learning English is required in most schools. The popularity of Japanese, Korean, and Mandarin Chinese has also grown. Students in third grade can choose one of seven foreign languages to study.
Vietnamese Culture and Traditions
Vietnamese culture is part of the Sinosphere. It has developed over centuries from ancient traditions, with wet rice farming as its base. Some parts of the culture come from China, including ideas from Confucianism, Mahāyāna Buddhism, and Taoism. Vietnamese society is built around ancestral villages (làng). All Vietnamese celebrate a common ancestral anniversary on the tenth day of the third lunar month.
In central and southern Vietnam, you can still see traces of Champa and Khmer culture. In recent times, Western cultures have become popular among younger Vietnamese people.

Vietnamese culture values humanity (nhân nghĩa) and harmony (hòa). Family and community are very important. Key cultural symbols include the Vietnamese dragon, which comes from crocodile and snake images. Other important symbols are the turtle, buffalo, and horse. Many Vietnamese also believe in the supernatural and spiritualism.
The main traditional Vietnamese dress is the áo dài. It is worn for special events like weddings and festivals. White áo dài is the uniform for girls in many high schools. Other traditional clothes include the áo tứ thân (a four-piece dress) and the áo bà ba (rural working clothes). Traditional hats include the conical nón lá. Popular cultural tourist spots include the former Imperial City of Huế and the World Heritage Sites of Phong Nha-Kẻ Bàng National Park, Hội An, and Mỹ Sơn.
Delicious Vietnamese Cuisine
Traditional Vietnamese food is based on five main tastes: spicy, sour, bitter, salty, and sweet. Common ingredients are fish sauce, shrimp paste, soy sauce, rice, fresh herbs, fruits, and vegetables. Vietnamese recipes use lemongrass, ginger, mint, and basil leaves.
Vietnamese cooking is known for using fresh ingredients and little oil. It is considered one of the healthiest cuisines. In the past, meats like pork, beef, and chicken were used less. Instead, freshwater fish, crabs, and mollusks were common. Vietnam has a strong street food culture with many popular dishes.
Many famous Vietnamese dishes like gỏi cuốn (salad roll) and phở noodles started in the north. They were later brought to central and southern Vietnam. Northern dishes are often less spicy than southern ones. Drinks in the south are usually served cold with ice, while hot drinks are preferred in the colder north. Popular drinks include cà phê đá (iced coffee) and nước mía (sugarcane juice).
Holidays and Festivals in Vietnam
Vietnam has eleven national holidays. These include New Year's Day on January 1st and Vietnamese New Year (Tết Nguyên Đán). Tết is celebrated from the last day of the last lunar month to the fifth day of the first lunar month. Other holidays are Hùng Kings' Festival (10th day of the third lunar month), Reunification Day (April 30th), International Workers' Day (May 1st), and National Day (September 2nd).
During Tết, many Vietnamese return to their villages for family reunions. They also pray for their ancestors. Older people often give young people a lì xì (red envelope) with money. Special holiday foods like bánh chưng (rice cake) are prepared. Many other festivals are celebrated throughout the year, such as Tết Trung Thu (Mid-Autumn Festival). In the highlands, Elephant Race Festivals are held every spring.
Popular Sports in Vietnam

Traditional Vietnamese martial arts like Vovinam are popular. However, football is the most loved sport in the country. The national team has won the ASEAN Football Championship twice. The under-23 team was runner-up in the 2018 AFC U-23 Championship. The under-20 team qualified for the 2017 FIFA U-20 World Cup for the first time. The women's team often wins at the Southeast Asian Games.
Other popular sports include badminton, tennis, volleyball, ping-pong, and chess. Vietnam has participated in the Summer Olympic Games since 1952. After the country was divided, only South Vietnam competed until reunification. Since 1988, the united Socialist Republic of Vietnam has competed in every Summer Olympics. In 2016, Vietnam won its first gold medal at the Olympics. Basketball has also become very popular, especially in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
French Indochina circa 1930.
-
The Grand Palais built for the 1902–1903 world's fair as Hanoi became French Indochina's capital.
-
The pink lotus, widely regarded by the Vietnamese as the national flower of the country, symbolises beauty, commitment, health, honour and knowledge.
-
Natural fog in northwest Vietnam (Tây Bắc).
-
The port of Hai Phong is one of the largest and busiest container ports in Vietnam.
-
In rural areas of Vietnam, piped water systems are operated by a wide variety of institutions.
-
Cultural dance performed by one of 54 recognised Vietnamese ethnic groups.
See also
 In Spanish: Vietnam para niños
In Spanish: Vietnam para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |