Lebanon facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Lebanon
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
|
|
Location of Lebanon (in green)
|
|
 |
|
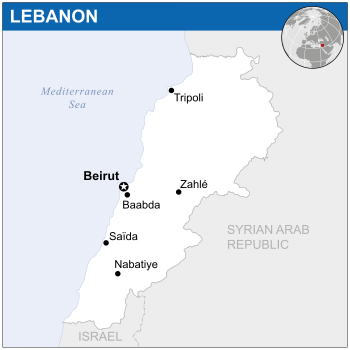
| Capital and largest city
|
Beirut 33°54′N 35°32′E / 33.900°N 35.533°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Local vernacular | Lebanese Arabic |
| Recognised minority language | French |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Lebanese |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic that includes confessionalism |
| Joseph Aoun | |
| Nawaf Salam | |
|
• Speaker of the Parliament
|
Nabih Berri |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Establishment | |
|
• Emirate of Mount Lebanon
|
1516 |
|
• Double Qaim-Maqamate of Mount Lebanon
|
1 December 1843 |
|
• Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate
|
9 June 1861 |
|
• Greater Lebanon
|
1 September 1920 |
|
• Constitution
|
23 May 1926 |
|
• Independence declared
|
22 November 1943 |
|
• French mandate ended
|
24 October 1945 |
|
• Withdrawal of French forces
|
17 April 1946 |
|
• Israeli troops withdrawn
|
24 May 2000 |
| 30 April 2005 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
10,452 km2 (4,036 sq mi) (161st) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.8 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
5,364,482 (117th) |
|
• Density
|
513/km2 (1,328.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2011) | ▼ 31.8 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 109th |
| Currency | Lebanese pound (LBP) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +961 |
| ISO 3166 code | LB |
| Internet TLD |
|
Lebanon, officially known as the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in West Asia. It is located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. Syria borders it to the north and east, and Israel to the south. The island of Cyprus is also close by.
Lebanon's special location, where the Mediterranean Basin meets the Arabian Peninsula, has given it a very interesting and long history. The country is part of the Levant region in the Eastern Mediterranean. It has over five million people and covers an area of about 10,452 square kilometers (4,036 sq mi). Its capital and largest city is Beirut, followed by Tripoli and Jounieh. While Arabic is the official language, French is also widely used.
Lebanon is a developing country, meaning it is still working to improve its economy and living standards. It is ranked 112th on the Human Development Index, which measures things like life expectancy, education, and income. It used to be considered an upper-middle-income country. However, recent problems like a money crisis, corruption, and big events like the 2020 Beirut explosion have caused its currency to lose value. This has led to political problems, shortages of basic goods, and high unemployment and poverty. The World Bank has called Lebanon's economic crisis one of the worst since the 1800s.
Despite its small size, Lebanese culture is well-known around the world, especially thanks to Lebanese people living in other countries. Lebanon is a founding member of the United Nations and the Arab League. It is also part of other important groups like the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Contents
What Does the Name Lebanon Mean?
The name of Mount Lebanon comes from an old Phoenician word, lbn, which means "white." This likely refers to the snow-covered peaks of the mountains.
The name Lebanon was first used for an official area (not just the mountain) during the Ottoman reforms in 1861. It was called the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate. Later, in 1920, it became the State of Greater Lebanon, and finally, the independent Republic of Lebanon in 1943.
A Look at Lebanon's Past
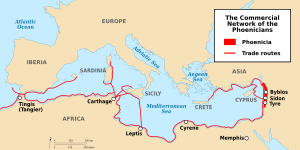
The first signs of people living in Lebanon go back about 7,000 years. For a long time, from 3200 BC to 539 BC, Lebanon was home to Phoenicia. This was a powerful trading empire that sailed all over the Mediterranean Sea.
In 64 BC, the Roman Empire took over the region. Lebanon then became an important center for Christianity under the Byzantine Empire. In the 600s AD, the Muslim conquest of the Levant brought the area under Muslim rule.
Later, in the 1000s, the Crusades began, and Christian states were set up. But these eventually fell to Muslim rulers, who then lost the land to the Ottoman Turks in 1517. Under the Ottomans, the first Lebanese "proto-state" (an early form of a state) was created in the 1800s. It was called the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate and was a special home for Maronite Christians.
After World War I, the Ottoman Empire broke apart. Lebanon then came under the control of France as part of the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon. France created Greater Lebanon, which was the start of modern-day Lebanon. However, French control weakened during World War II. By 1943, Lebanon gained independence from France. It then set up a unique government system where different religious groups share political power.
Lebanon was quite stable for a while after independence. But this peace ended with the Lebanese Civil War (1975–1990), a big conflict between different groups. Since the war ended, there have been many efforts to rebuild the economy and the country's infrastructure.
Ancient Times in Lebanon
Very old evidence of human settlements has been found in Byblos, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. This evidence dates back to before 5000 BC. Archaeologists found remains of ancient huts, simple weapons, and burial jars from fishing communities that lived on the Mediterranean coast over 7,000 years ago.
Lebanon was part of northern Canaan. It became the home of the Phoenicians, who were skilled sailors and traders. They traveled all over the Mediterranean in the first millennium BC. Important Phoenician cities included Byblos, Sidon, and Tyre. Their most famous colonies were Carthage (in modern-day Tunisia) and Cádiz (in modern-day Spain). The Phoenicians are famous for inventing the Phoenician alphabet, which later inspired the Greek and Latin alphabets.
In 539 BC, the Phoenician cities became part of the Persian Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great. Later, in 332 BC, they were taken over by Alexander the Great after the siege of Tyre. In 64 BC, the Roman general Pompey the Great added the region of Syria to the Roman Republic. The land of present-day Lebanon became part of a Roman province called Phoenice.
Lebanon in the Middle Ages
The area that is now Lebanon became a major center for Christianity in the Roman Empire as the faith spread. In the late 300s and early 400s AD, a hermit named Maron started a special monastic tradition near Mount Lebanon. His followers, known as Maronites, moved into the mountains to avoid being persecuted by Roman authorities. From 619 to 629, the Sassanid Persians occupied what is now Lebanon.
In the 600s, Muslim Arabs conquered Syria, replacing the Byzantines. Although Islam and Arabic became official, people slowly converted from Christianity and the Syriac language. The Maronite community kept a lot of their independence despite new rulers.
The mountains of Lebanon offered a safe place during times of religious and political trouble. This led to many different religious groups living there, including Maronites, Druze, Shiite Muslims, Ismailis, Alawites, and Jacobites.

In the 1000s, the Druze religion began from a branch of Shia Islam. It gained followers in southern Mount Lebanon. Maronite people grew in number in Northern Mount Lebanon, while the Druze stayed in Southern Mount Lebanon. Coastal cities like Sidon, Tyre, and Beirut were directly ruled by Muslim leaders and became more Arab in culture.
When the Muslim Turks took over Roman Anatolia, the Byzantines asked the Pope in Rome for help. This led to the Crusades, a series of wars by Europeans to take back Christian lands in the Levant. The First Crusade set up temporary Christian states along the coast, like the Kingdom of Jerusalem. These states had a lasting impact, but the region returned to full Muslim control after two centuries.
One important effect of the Crusades was the connection between the Franks (French) and the Maronites. Unlike most other Christian groups in the Eastern Mediterranean, the Maronites were loyal to the Pope in Rome. This made the Franks see them as fellow Roman Catholics. This connection led to centuries of support for the Maronites from France and Italy.
The Ottoman Empire's Rule
During the Ottoman period, Lebanon was divided into several areas. In southern Mount Lebanon, Fakhr al-Din II became a powerful prince in 1590. He expanded his control over much of Mount Lebanon and its coast. However, this became too much for the Ottoman Sultan, who had him captured and executed in 1635. His family continued to rule a smaller area under Ottoman control until the late 1600s.
After the last Maan emir died, the Shihab family ruled Mount Lebanon until 1830. The Druze and Christians in Lebanon generally lived together peacefully. However, there were some conflicts, including the 1860 Mount Lebanon civil war. After this, the Emirate of Mount Lebanon was replaced by the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate in 1861. This new system created an autonomous (self-governing) Mount Lebanon with a Christian governor, designed as a homeland for Maronites. The Maronite Catholics and the Druze are seen as founders of modern Lebanon through this "Maronite-Druze dualism" system.
Around 100,000 people in Beirut and Mount Lebanon died from starvation during World War I.
French Mandate Period
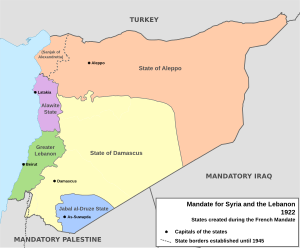
After World War I in 1920, the area of the Mutasarrifate, along with some surrounding areas with mostly Shia and Sunni populations, became part of Greater Lebanon. This was under the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, meaning France was in charge.
On September 1, 1920, France officially re-established Greater Lebanon. Lebanon was mainly Christian, but it also included areas with many Muslims and Druze. On September 1, 1926, France created the Lebanese Republic. A constitution was adopted in 1926, setting up a democratic republic with a parliament.
How Lebanon Gained Independence
Lebanon gained some independence while France was occupied by Germany during World War II. In 1941, the French authorities in Lebanon (who were allied with Germany) allowed Germany to move planes and supplies through Syria to Iraq. The United Kingdom worried that Nazi Germany might take full control of Lebanon and Syria. So, the UK sent its army into Syria and Lebanon.
After the fighting ended, General Charles de Gaulle visited the area. Due to pressure from inside and outside Lebanon, de Gaulle recognized Lebanon's independence. On November 26, 1941, General Georges Catroux announced that Lebanon would become independent under the Free French government.
Elections were held in 1943. On November 8, 1943, the new Lebanese government declared an end to the French mandate on its own. The French reacted by putting the new government officials in prison. But because of international pressure, the French released them on November 22, 1943. This day is now Lebanon's Independence Day. The Allies occupied the region until the end of World War II.
Independence and Challenges
After World War II ended in Europe, the French mandate in Lebanon officially ended. The last French troops left in December 1946.
Lebanon has an unwritten agreement from 1943 called the National Pact. It says that the country's president must be a Maronite Christian. The speaker of the parliament must be a Shia Muslim. The prime minister must be a Sunni Muslim. The Deputy Speaker of Parliament and the Deputy Prime Minister must be Greek Orthodox. This system helps different religious groups share power and avoid conflict.
Since independence, Lebanon has had times of political stability and prosperity. Beirut became an important center for finance and trade in the region.
In May 1948, Lebanon supported its Arab neighbors in a war against Israel. While some unofficial fighters crossed the border, Lebanese troops did not officially invade. Lebanon helped with artillery fire and supplies. On June 5–6, 1948, the Lebanese army captured Al-Malkiyya, which was their only success in the war.
About 100,000 Palestinians came to Lebanon because of the war. As of 2017, between 174,000 and 450,000 Palestinian refugees live in Lebanon. About half of them live in refugee camps, which often look like regular neighborhoods. Palestinians often cannot get Lebanese citizenship or even identity cards. They are also legally prevented from owning property or working in certain jobs like law or medicine.
In 1958, during President Camille Chamoun's last months in office, a small uprising happened. It was started by Lebanese Muslims who wanted Lebanon to join the United Arab Republic. Chamoun asked for help, and 5,000 United States Marines were sent to Beirut briefly on July 15. After this, a new government was formed.
Until the early 1970s, Lebanon was known as "the Switzerland of the Middle East." This was because it was a popular holiday spot with snow-capped mountains and a safe place for banking for people from Gulf Arab countries.
In 1970, the PLO was defeated in Jordan. Many Palestinian fighters moved to Lebanon, increasing their armed actions against Israel. This also caused more tension between Palestinians and Maronites and other Lebanese groups.
Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War (1975–1990) was a conflict that lasted for 15 years. About 120,000 people died. The war started because of the country's many different religious groups. Lebanon has 18 officially recognized religious groups.
Before the war, different groups lived in different parts of Lebanon. Sunni Muslims and Christians were the main groups in coastal cities. Shia Muslims lived in the south and the Beqaa Valley to the east. The mountain areas were mostly home to Druze and Christians.
The creation of Israel and the arrival of thousands of Palestinian refugees in Lebanon in 1948 and 1967 changed the population balance. This led to more Muslims in the country.
Fighting began in 1975 between Lebanese Christian militias and Palestinian fighters. This led to an alliance between Palestinians and Lebanese Muslims, Arab nationalists, and left-wing groups. However, alliances changed quickly during the war. Other countries like Syria, Israel, and Iran also got involved, supporting or fighting alongside different groups. Peacekeeping forces, like the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, were also in the country.
In 1989, the Taif Agreement helped end the fighting. It set up a committee to find solutions to the conflict. In March 1991, the Parliament of Lebanon passed a law that pardoned all political crimes committed before the law. In May 1991, most armed groups in Lebanon were disbanded. However, Hezbollah, a Shia Islamist group supported by Iran, remained armed.
Even though the Lebanese Armed Forces slowly rebuilt, the government could not fully control Hezbollah's military power. Religious tensions, especially between Shias and Sunnis, continued in Lebanon after the war ended in 1990.
Recent National Crisis (2019–Present)
On October 17, 2019, large public protests began. They started because of planned taxes on things like gasoline and online phone calls. But they quickly grew into a country-wide protest against widespread corruption in the government.

Because of these protests, Lebanon entered a political crisis. Prime Minister Saad Hariri resigned. Protests and acts of civil disobedience have continued since then. Lebanon is currently facing its worst economic crisis in decades.
On February 1, 2023, Lebanon's central bank reduced the value of the Lebanese pound by 90%. This was due to the ongoing financial crisis and was the first time Lebanon had officially devalued its currency in 25 years.
Lebanon's Geography
Lebanon is located in West Asia. It covers about 10,452 square kilometers (4,036 sq mi) of land. It has a 225 km (140 mi) coastline on the Mediterranean Sea to the west. It shares a 375 km (233 mi) border with Syria to the north and east. To the south, it has a 79 km (49 mi) border with Israel. There is a small disputed area called Shebaa Farms near the border with the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights.
Lebanon has four main natural regions:
- The coastal plain: This narrow strip of land runs along the Mediterranean Sea. It has fertile soil, sandy bays, and rocky beaches.
- The Lebanon mountain range: These mountains rise steeply from the coast. They are made of limestone and sandstone and have deep gorges. The highest peak is Qurnat as Sawda' at 3,088 meters (10,131 ft) above sea level.
- The Beqaa Valley: This valley sits between the Lebanon mountains and the Anti-Lebanon range. It is 180 km (112 mi) long and 10 to 26 km (6 to 16 mi) wide. Its soil is very fertile.
- The Anti-Lebanon Mountains: This range runs parallel to the Lebanon mountains. Its highest peak is Mount Hermon at 2,814 meters (9,232 ft).
Many seasonal streams and rivers flow from Lebanon's mountains. The most important river is the Leontes, which is 145 km (90 mi) long. It starts in the Beqaa Valley and flows into the Mediterranean Sea. Lebanon has 16 rivers in total, but none of them are navigable (meaning boats cannot travel on them).
Lebanon's Climate
Lebanon has a mild Mediterranean climate. In coastal areas, winters are cool and rainy, while summers are hot and humid. In higher mountain areas, winter temperatures often drop below freezing, and there is heavy snow that can last until early summer. Most of Lebanon gets a good amount of rainfall. However, some areas in the northeast get less rain because of the rain shadow created by the high western mountains.
Lebanon's Environment

In ancient times, Lebanon was covered with huge forests of cedar trees. The cedar tree is now the national symbol of the country. Over thousands of years, much of these forests were cut down. This changed the water flow in Mount Lebanon and negatively affected the local climate. As of 2012, forests covered about 13.4% of Lebanon's land. These forests are always at risk from wildfires during the long, dry summer.
Because of past logging, only a few old cedar trees remain in small forest areas. However, there are active programs to protect and regrow these forests. Lebanon focuses on natural regeneration, creating the right conditions for seeds to sprout and grow. The government has created several nature reserves to protect cedars, such as the Shouf Biosphere Reserve and the Forest of the Cedars of God.
In 2010, the Environment Ministry started a 10-year plan to increase forest cover by 20%. This means planting two million new trees each year. This plan, supported by the United States, has planted over 600,000 trees since 2011, including cedars and other native species.
Beirut and Mount Lebanon have faced a serious garbage problem. In 2015, a main dumpsite was forced to close, leading to piles of garbage in the streets. The government has tried to manage this crisis, but it has been difficult. In 2017, Human Rights Watch reported that Lebanon's garbage crisis, especially the open burning of waste, was harming people's health.
In September 2018, Lebanon's parliament passed a law banning open dumping and burning of waste. However, some areas still burn waste openly, which is dangerous. In October 2019, about 100 forest fires broke out across Lebanon. Countries like Cyprus, Jordan, Turkey, and Greece sent help to fight the fires. Rain later helped to put out many of them.
Government and Politics
Lebanon is a parliamentary democracy. This means people elect representatives to make laws. The country has a unique system called confessionalism. This system shares political power among the 18 recognized religious groups.
Here's how it works:
- The President must be a Maronite Christian.
- The Prime Minister must be a Sunni Muslim.
- The Speaker of the Parliament must be a Shi’a Muslim.
- The Deputy Prime Minister and the Deputy Speaker of Parliament must be Eastern Orthodox.
This system aims to prevent conflict between different religious groups and ensure everyone is fairly represented in government.
Lebanon's national legislature is the unicameral Parliament of Lebanon. It has 128 seats, which are divided equally between Christians and Muslims. These seats are also divided fairly among the 18 different religious groups and the country's 26 regions. Before 1990, Christians had more seats, but the Taif Agreement after the civil war made the number of seats equal for both religions.
The Parliament is elected every four years by popular vote. The executive branch includes the President, who is the head of state, and the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. The parliament elects the president for a six-year term. The president then appoints the Prime Minister after talking with the parliament. The president and prime minister form a cabinet, which also follows the religious power-sharing rules.
Administrative Divisions
Lebanon is divided into nine governorates. These are called muḥāfaẓāt in Arabic. Each governorate is then divided into smaller areas called districts (aqdyah). The districts are further divided into municipalities, which include groups of cities or villages.
Here are the governorates and their districts:
- Beirut Governorate: This governorate is just the city of Beirut and has no districts.
- Akkar Governorate: Includes Akkar.
- Baalbek-Hermel Governorate: Includes Baalbek and Hermel.
- Beqaa Governorate: Includes Rashaya, Western Beqaa, and Zahle.
- Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate: Includes Byblos (Jbeil) and Keserwan.
- Mount Lebanon Governorate: Includes Aley, Baabda, Chouf, and Matn.
- Nabatieh Governorate: Includes Bint Jbeil, Hasbaya, Marjeyoun, and Nabatieh.
- North Governorate: Includes Batroun, Bsharri, Koura, Miniyeh-Danniyeh, Tripoli, and Zgharta.
- South Governorate: Includes Jezzine, Sidon (Saida), and Tyre (Sur).
Lebanon's Economy
Lebanon's constitution says that its economic system is free. This means it supports private businesses and the right to own private property. Lebanon's economy generally follows a laissez-faire model, which means the government has very little control over businesses. Most of the economy uses the US dollar, and there are no limits on money moving in or out of the country.
Lebanon's economy grew a lot after the war in 2006, with an average growth of 9.1% between 2007 and 2010. However, after 2011, the Syrian civil war affected Lebanon's economy, slowing its growth. Between 2019 and 2021, the economy shrank by a lot, one of the biggest drops in the world. Since 2020, the International Monetary Fund no longer publishes data on Lebanon's economy.
Lebanon has a very high amount of public debt. In 2010, its public debt was more than 150.7% of its GDP (Gross Domestic Product), which was the fourth highest in the world. This high debt has slowed down the economy and reduced how much the government can spend on important projects.
People in Lebanon's cities are known for their business skills. Many Lebanese people have moved to other countries, creating "commercial networks" around the world. Money sent back by Lebanese people living abroad totals $8.2 billion, making up one-fifth of the country's economy. Lebanon also has a high percentage of skilled workers among Arab countries.
The Investment Development Authority of Lebanon was created to encourage investment in Lebanon. In 2001, a law was passed to help this organization.
The agricultural sector employs 12% of all workers and contributed 5.9% to the country's GDP in 2011. Lebanon has the most cultivable land in the Arab world. Major crops include apples, peaches, oranges, and lemons.
Oil has recently been found inland and under the sea between Lebanon, Cyprus, Israel, and Egypt. Talks are happening to explore these resources. The seabed between Lebanon and Cyprus is thought to have large amounts of oil and natural gas.
Industry in Lebanon mostly involves small businesses that put together and package imported parts. In 2004, industry was the second largest employer, with 26% of the workforce, and contributed 21% to Lebanon's GDP.
Almost 65% of Lebanese workers are employed in the services sector, which includes tourism and banking. This sector contributes about 67.3% of Lebanon's annual GDP. However, relying heavily on tourism and banking makes the economy sensitive to political problems.
Lebanese banks are known for being secure and having a lot of money. In 2008, Lebanon was one of only seven countries where the value of stock markets increased.
The Syrian crisis has greatly affected Lebanon's economy. Many Syrian refugees now live in Lebanon, leading to more competition for jobs. As a result, unemployment doubled in three years, reaching 20% in 2014. The poverty rate also increased, with 170,000 more Lebanese people falling below the poverty line.
Tourism in Lebanon

The tourism industry makes up about 10% of Lebanon's GDP. In 2008, Lebanon attracted about 1,333,000 tourists. In 2009, The New York Times named Beirut the number one travel destination worldwide because of its nightlife and friendly people. In 2010, tourist arrivals reached two million, but they dropped by 37% in 2012 due to the war in neighboring Syria.
Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Japan are the top three countries from which tourists visit Lebanon. The recent increase in Japanese tourists has made Japanese cuisine more popular in Lebanon.
Infrastructure
Education in Lebanon
According to surveys from 2013, Lebanon was ranked globally as the fourth best country for math and science education. It was also ranked tenth best overall for the quality of education. For the quality of management schools, Lebanon was ranked 13th worldwide.

The United Nations gave Lebanon an education index of 0.871 in 2008. This index measures things like adult literacy and school enrollment rates. Lebanon was ranked 88th out of 177 countries.
All schools in Lebanon must follow a specific curriculum set by the Ministry of Education. Some of the 1,400 private schools offer IB programs and can add more courses with approval from the Ministry. The first eight years of school are required by law.
Lebanon has 41 nationally recognized universities, and several are known internationally. The American University of Beirut (AUB) was the first English-speaking university, and the Saint Joseph University of Beirut (USJ) was the first French-speaking university in Lebanon. Universities in Lebanon mainly teach in French or English.
Some of the top universities in the country include the American University of Beirut, University of Balamand, Lebanese American University, Université Saint Joseph de Beyrouth, Université Libanaise, and Holy Spirit University of Kaslik.
Healthcare in Lebanon
In 2010, spending on healthcare made up 7.03% of the country's GDP. In 2009, there were about 31 doctors and 20 nurses for every 10,000 people. The average life expectancy at birth was 72.59 years in 2011.
After the civil war, only one-third of Lebanon's public hospitals were working. By 2009, the country had 28 public hospitals with 2,550 beds. At public hospitals, uninsured patients pay 5% of their bill, while at private hospitals, they pay 15%. The Ministry of Public Health pays the rest. The Ministry works with 138 private hospitals and 25 public hospitals.
In 2011, over 236,000 hospital admissions were subsidized (meaning the government helped pay). More patients go to private hospitals because there are more beds available there.
Recently, there has been an increase in illnesses caused by food in Lebanon. This has made people more aware of how important food safety is, including how food is stored, preserved, and prepared. More restaurants are now trying to follow international standards for food safety.
People and Culture
Population and Diversity
Lebanon's population was estimated to be around 5.3 million in 2024. However, no official census has been done since 1932. This is because of the sensitive balance of power between Lebanon's many religious groups. While most Lebanese are considered ethnically Arab, they actually come from many different groups who have lived in, invaded, or settled in this region over time. This makes Lebanon a mix of closely related cultures.
The birth rate in Lebanon has fallen over the years. It also varies among different religious groups. For example, in 2004, the birth rate was higher for Shiites than for Maronites.
Lebanon has seen many people move away. Over 1.8 million people left the country between 1975 and 2011. Millions of people of Lebanese descent live all over the world, especially in Latin America. Brazil and Argentina have large Lebanese communities. Many Lebanese also moved to West Africa, like the Ivory Coast and Senegal. Australia, Canada, and the United States also have large Lebanese populations. More than half of the Lebanese living abroad are Christian, partly because many Christians left before 1943.
As of 2012, Lebanon hosted over 1.6 million refugees and asylum seekers. This included people from Palestine, Iraq, Syria, and Sudan. Among Syrian refugees, 71% live in poverty.
Many Lebanese people have been affected by armed conflicts. About 75% of the population has direct personal experience with conflict, and almost everyone (96%) has been affected in some way.
Religion in Lebanon

Lebanon is the most religiously diverse country in West Asia and the Mediterranean. The government officially recognizes 18 religious groups: four Muslim, 12 Christian, one Druze, and one Jewish. The government counts Druze citizens as part of the Muslim population, even though most Druze today do not identify as Muslims.
It is believed that the number of Christians compared to Muslims has decreased over the past 60 years. This is due to more Christians moving away and a higher birth rate among Muslims. In the last census in 1932, Christians made up 53% of Lebanon's population.
A study in 2009 found that about 27% of the population was Sunni, 27% Shia, 21% Maronite, 8% Greek Orthodox, 5% Druze, 5% Melkite, and 1% Protestant. The remaining 6% belonged to smaller Christian groups. The CIA World Factbook (2020) estimates that Muslims are 67.8% (Sunni 31.9%, Shia 31.2%, with smaller numbers of Alawites and Ismailis). Christians are estimated at 32.4% (Maronite Catholics are the largest Christian group). Druze are 4.5%. There are also very small numbers of Jews, Baha'is, Buddhists, and Hindus.
Sunni residents mainly live in Tripoli, Western Beirut, and Northern Lebanon. Shi'a residents mostly live in Southern Beirut, the Beqaa Valley, and Southern Lebanon. Maronite Catholic residents primarily live in Eastern Beirut and the mountains of Lebanon. They are the largest Christian group. The Greek Orthodox, the second largest Christian group, live in areas like Koura, Beirut, and Akkar.
Languages Spoken in Lebanon
Article 11 of Lebanon's Constitution states that "Arabic is the official national language." A law decides when French can be used. Most Lebanese people speak Lebanese Arabic, which is a type of Levantine Arabic. Modern Standard Arabic is mostly used in formal settings like newspapers and TV news. Lebanese Sign Language is used by the Deaf community.
French and English are also widely spoken. Almost 40% of Lebanese people are considered French-speaking, and another 15% speak some French. About 70% of Lebanon's high schools use French as a second language. English is used as a second language in 30% of high schools. The use of French is a result of France's historical ties to the region. As of 2005, about 20% of the population used French daily. The use of Arabic by educated young people is decreasing, as they often prefer to speak French or English, which are seen as more modern.
English is increasingly used in science and business. Lebanese citizens of Armenian, Greek, or Assyrian descent often speak their family's languages. As of 2009, there were about 150,000 Armenians in Lebanon, making up about 5% of the population.
Lebanese Culture
Lebanon's culture shows the influence of many civilizations over thousands of years. It was originally home to the Canaanite-Phoenicians. Then, it was conquered and occupied by the Assyrians, Persians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, Crusaders, Ottoman Turks, and most recently the French. Lebanese culture has borrowed from all these groups. Lebanon's diverse population, with different ethnic and religious groups, has also added to its festivals, music, literature, and food. Despite this diversity, Lebanese people "share an almost common culture." Lebanese Arabic is spoken by everyone, and their food, music, and literature are deeply rooted in the wider Mediterranean and Levantine traditions.
Arts in Lebanon
In visual arts, Moustafa Farroukh was one of Lebanon's most famous painters in the 20th century. He studied in Rome and Paris and showed his art in many cities around the world. Many modern artists are active today, like Walid Raad. In photography, the Arab Image Foundation has a collection of over 400,000 photos from Lebanon and the Middle East. These photos can be seen in a research center, and events are held to promote the collection.
Lebanese Literature
In literature, Kahlil Gibran is one of the best-selling poets of all time. He is especially known for his book The Prophet (1923), which has been translated into over twenty languages. Ameen Rihani was an important writer in a literary movement started by Arab immigrants in North America. Mikhail Naimy is also recognized as a very important figure in modern Arabic writing. Several modern Lebanese writers have also become famous internationally, including Elias Khoury and Amin Maalouf.
Music in Lebanon

While traditional folk music is still popular in Lebanon, modern music that mixes Western and traditional Arabic styles, pop, and fusion music are quickly gaining popularity. Lebanese artists like Fairuz, Majida El Roumi, Wadih El Safi, and Sabah are well-known and loved in Lebanon and across the Arab world. Radio stations play a variety of music, including traditional Lebanese, classical Arabic, Armenian, and modern French, English, American, and Latin songs.
Media and Cinema
The cinema of Lebanon is considered one of the most important in the Arabic-speaking region, after Egyptian cinema. Lebanese cinema has existed since the 1920s, and the country has produced over 500 films. The media of Lebanon is not only a regional center for producing content but also the most open and free in the Arab world. According to Reporters Without Borders, "the media have more freedom in Lebanon than in any other Arab country." Despite its small size, Lebanon plays an important role in creating information for the Arab world.
Holidays and Festivals
Lebanon celebrates national holidays and both Christian and Muslim holidays. Christian holidays follow both the Gregorian calendar and Julian calendar. Most Christians celebrate Christmas on December 25. Armenian Apostolic Christians celebrate Christmas on January 6. Muslim holidays follow the Islamic lunar calendar. These include Eid al-Fitr (the feast at the end of Ramadan) and Eid al-Adha (the Feast of Sacrifice).
Lebanon's national holidays include Workers Day, Independence Day, and Martyrs Day. Music festivals, often held at historical sites, are a common part of Lebanese culture. Some of the most famous are the Baalbeck International Festival, Byblos International Festival, and Beiteddine International Festival. These festivals are promoted by Lebanon's Ministry of Tourism. Lebanon hosts about 15 concerts by international performers each year. It is ranked first for nightlife in the Middle East and sixth worldwide.
Lebanese Cuisine
Lebanese food is similar to the food in many other countries in the Eastern Mediterranean, like Syria, Turkey, Greece, and Cyprus. The national dishes of Lebanon are kibbe, a meat pie made from minced lamb and burghul (cracked wheat), and tabbouleh, a salad made from parsley, tomatoes, and burghul wheat.
Lebanese restaurant meals often start with many small savory dishes called mezze. These include dips, salads, and pastries. After the mezze, people usually eat grilled meat or fish. Meals usually end with Arabic coffee and fresh fruit, but sometimes traditional sweets are also offered.
Sports in Lebanon
Lebanon has six ski resorts. Because of Lebanon's unique geography, you can go skiing in the morning and swim in the Mediterranean Sea in the afternoon! At a competitive level, basketball and football are among Lebanon's most popular sports. Other common leisure sports include Canoeing, cycling, rafting, climbing, swimming, sailing, and caving. The Beirut Marathon is held every fall, attracting runners from Lebanon and other countries.
Rugby league is a newer but growing sport in Lebanon. The Lebanon national rugby league team played in the 2000 Rugby League World Cup. Hazem El Masri, born in Tripoli, is considered one of the greatest Lebanese rugby league players. He moved to Australia in 1988 and became the top point-scorer in National Rugby League history in 2009.

Lebanon also does well in basketball. The Lebanese National Team has qualified for the FIBA World Championship three times in a row. Top basketball teams in Lebanon include Sporting Al Riyadi Beirut and Club Sagesse. Fadi El Khatib is a very successful player in the Lebanese National Basketball League.
Football is also very popular. The top league is the Lebanese Premier League, with successful clubs like Al Ansar FC and Nejmeh SC. Famous Lebanese football players include Roda Antar and Hassan Maatouk.
In recent years, Lebanon has hosted big sports events like the AFC Asian Cup and the Pan Arab Games. Lebanon hosted the 2009 Jeux de la Francophonie and has participated in every Olympic Games since its independence, winning four medals in total.
Water sports have also become very popular in Lebanon. Since 2012, the Lebanon Water Festival NGO has promoted these sports, making Lebanon known as a water sport destination internationally.
Science and Technology

Lebanon was ranked 92nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2023. Important scientists from Lebanon include Hassan Kamel Al-Sabbah and Edgar Choueiri.
In 1960, a science club from a university in Beirut started a Lebanese space program called "the Lebanese Rocket Society." They had great success until 1966, when the program stopped due to war and outside pressure.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Líbano para niños
In Spanish: Líbano para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |