South Asia facts for kids
 |
|
| Area | 5,222,321 km2 (2,016,349 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 2.04 billion (2024) |
| Population density | 362.3/km2 (938/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | $5.04 trillion (2024) |
| GDP (PPP) | $18.05 trillion (2024) |
| GDP per capita | $2,650 (nominal) (2024) $9,470 (PPP) (2024) |
| HDI | |
| Ethnic groups | Indo-Aryan, Iranian, Dravidian, Sino-Tibetan, Austroasiatic, Turkic etc. |
| Religions | Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Buddhism, Sikhism, Jainism, Zoroastrianism, Irreligion |
| Demonym |
|
| Countries |
8 states
|
| Dependencies |
External (1)
|
| Languages |
Official languages (national level)
Other official languages (provincial/regional level)
|
| Time zones | |
| Internet TLD | .af, .bd, .bt, .in, .io, .lk, .mv, .np, .pk |
| Calling code | Zone 8 & 9 |
| Largest cities | |
| UN M49 code | 034 – Southern Asia142 – Asia001 – World |
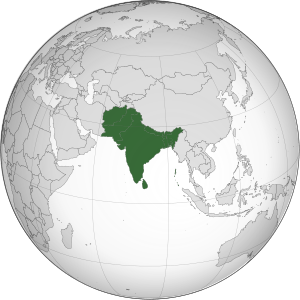
South Asia is a large area in the southern part of Asia. It's known for its unique geography and many different cultures. The countries that are usually considered part of South Asia are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
This region shares borders with East Asia to the northeast and Central Asia to the northwest. To the west is West Asia, and to the east is Southeast Asia. South Asia is mostly made up of the Indian subcontinent. It is surrounded by the Indian Ocean in the south. The huge Himalayas, Karakoram, and Pamir Mountains form its northern border.
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is a group that helps these eight countries work together. It was started in 1985. South Asia covers about 5.2 million square kilometers. This is about 10% of the entire Asian continent. The region is home to about 2.04 billion people. This means about one-fourth of the world's population lives here. It is the most populated and most crowded region on Earth.
In 2022, South Asia had the largest number of people practicing Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism, Jainism, and Zoroastrianism in the world. For example, over 90% of all Hindus live in South Asia. It also has many Christians and Buddhists.
Contents
Exploring South Asia's Past
Early Times: Pre-history
Human activity in South Asia goes back a very long time. Evidence shows Homo sapiens lived here 75,000 years ago. Even older human-like species, like Homo erectus, were here about 500,000 years ago. Some of the oldest cultures are seen in rock paintings. These paintings in Bhimbetka rock shelters are from 30,000 BCE or even earlier.
Ancient Civilizations and Empires
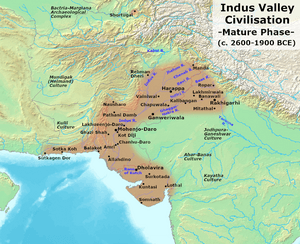
The Indus Valley civilization was the first major civilization in South Asia. It grew in the northwest, in what is now Pakistan, Northern India, and Afghanistan. This civilization had advanced cities and technology between 2600 and 1900 BCE.
After the Indus Valley civilization, the Vedic period began around 1900 BCE. This era is named after the Vedic religion of the Indo-Aryans. They were groups who moved into northern India. Their culture and farming lifestyle spread across the region. During this time, early forms of states began to appear. Important religious texts, like the Upanishads, were also created. These texts explored deeper meanings of rituals and life.
Between 800 and 400 BCE, cities in South Asia grew bigger. This led to new ways of thinking and new religious movements. Two important figures from this time were Mahavira, who started Jainism, and Buddha, who founded Buddhism.
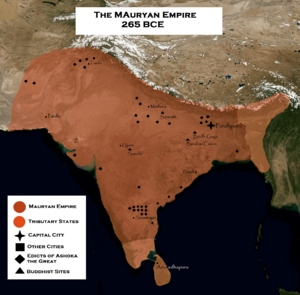
Later, Alexander the Great's Greek army came to the region. The Maurya Empire then became very powerful in the 3rd century BCE. It covered much of South Asia. Buddhism also spread widely, reaching Central Asia and Southeast Asia. The Gupta Empire followed, ruling from the 4th to 7th centuries. This was a time when many temples, monasteries, and universities were built. Famous examples include the Nalanda university and the Ajanta Caves.
Medieval Kingdoms and New Influences
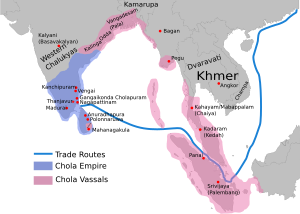
In the 8th century CE, Islam arrived in South Asia. Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim conquered Sindh. Later, Muslim armies from Central Asia began raiding kingdoms in northern India. One famous leader was Mahmud of Ghazni. He raided many times between 997 and 1030.
Around 1173, Mu'izz al-Din Muhammad started to expand Muslim rule. This led to the creation of the Delhi Sultanate. This sultanate ruled different parts of South Asia. It was led by several dynasties, like the Mamluk and Tughlaq. The Delhi Sultanate reached its largest size under Muhammad bin Tughlaq.
However, many parts of South Asia revolted against the Delhi Sultanate. The Bengal Sultanate became independent in the northeast. In South India, the Hindu Vijayanagara Empire rose to power. It lasted until the mid-16th century.
Around 1526, the Mughal Empire began. Its first ruler, Babur, defeated the Delhi Sultanate. The Mughal Empire grew to cover almost all of the Indian subcontinent. This era brought new art and architecture, like the Taj Mahal. During this time, there were also challenges for different religious groups. Some Mughal rulers, like Akbar, promoted religious tolerance.
Modern Changes and Independence
After the Mughal Empire declined in the 18th century, other local powers grew strong. These included the Marathas and Sikhs. European traders, like the British and French, also started to gain influence. They made agreements with local rulers and set up trading posts.
By the 19th century, British traders had taken control of much of South Asia. This period is known as British rule. It brought changes like railways, which helped with food distribution. However, it also led to economic difficulties and famines. Western ideas also inspired a growing movement for independence. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi pushed for full freedom from British rule.
After World War II, Britain granted independence to South Asia in 1947. This led to the partition of India. India became a Hindu-majority country, and Pakistan was created as a Muslim-majority country. This division caused a lot of violence and made religious differences stronger.
South Asia Today
India and Pakistan have had several conflicts since independence, especially over Kashmir. In 1971, eastern Pakistan became the independent country of Bangladesh. Both India and Pakistan later developed nuclear weapons, increasing tensions.
Pakistan has faced challenges with terrorism and military involvement in its government. India has grown a lot economically, reducing extreme poverty. Bangladesh is also growing fast. Afghanistan has gone through many conflicts and changes in government. Religious nationalism has also increased in the region. India and China are also competing for influence in South Asia.
South Asia's Geography
South Asia is a very diverse region. It has glaciers, rainforests, valleys, deserts, and grasslands. It is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, the Indian Ocean, and the Arabian Sea. The climate here changes a lot, from tropical in the south to cooler in the north.
The Indian Plate
Most of South Asia sits on the Indian Plate. This is a part of the Earth's crust that moved away from the ancient supercontinent Gondwana. About 50-55 million years ago, it crashed into the Eurasian Plate. This huge collision created the Himalayan mountain range and the Tibetan Plateau. The Indian Plate includes most of South Asia, extending into parts of the Indian Ocean.
Climate Zones
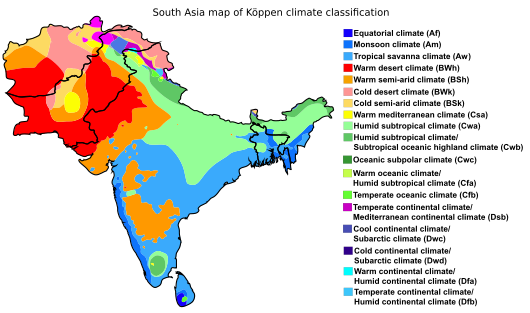
The climate in South Asia varies greatly. It ranges from tropical monsoon in the south to temperate in the north. This variety is due to altitude, closeness to the sea, and the seasonal monsoon winds. Southern areas are hot in summer and get heavy rain during monsoons. The northern plains are hot in summer but cooler in winter. The mountainous north is much colder and gets snow.
The Himalayas act like a shield, blocking cold winds from North Asia. This keeps temperatures in the plains milder. Most of the region has a monsoon climate. This means it's humid in summer and dry in winter. This climate is good for growing crops like jute, tea, rice, and vegetables.
South Asia has four main climate zones:
- A dry subtropical climate in northern India and Pakistan.
- An equatorial climate in far southern India and southwest Sri Lanka.
- A tropical climate across most of the peninsula, with different types.
- An Alpine climate in the Himalayas and Hindu Kush mountains.
Monsoon rains are very important for South Asia. The summer monsoon brings wind from the southwest. It provides 70%–90% of the yearly rainfall. The winter monsoon blows from the northeast and affects Sri Lanka and Maldives more.
Climate change in South Asia is causing new challenges. These include sea level rise, stronger storms, and changes in temperatures and rainfall.
People and Cultures
Population and Diversity
South Asia has about 1.938 billion people. This makes it the most populated region in the world. It is a very diverse place with many language groups and religions. Social customs can be very different from one area to another.
India has the largest population, making up over 73% of South Asia's total. Bangladesh and Pakistan also have very large populations. Countries like Bhutan and Maldives are much smaller. The population growth in South Asia is slowing down. Some countries, like India and Bangladesh, are reaching lower birth rates.
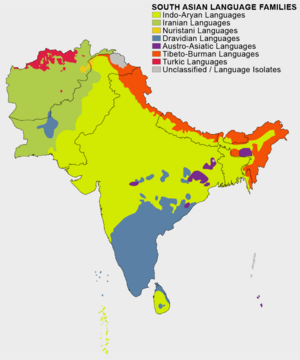
Languages Spoken in South Asia
South Asia has many languages. The spoken languages often cross religious lines. However, the written scripts are often linked to different religions. For example, Muslims in Afghanistan and Pakistan often use the Arabic alphabet. Non-Muslims use scripts like those from the Brahmi script.
The Devanagari script is used for over 120 South Asian languages. These include Hindi, Marathi, and Nepali. It is one of the most used writing systems in the world. It is also used for ancient Sanskrit texts.
The most spoken language in the region is Hindustani language. This includes Hindi and Urdu. Other major languages are Bengali, Telugu, and Tamil. New languages like Urdu developed in the modern era. They are used by Muslim communities in northern South Asia. The Punjabi language is spoken by people of different religions. However, it is written in three different scripts.
Sino-Tibetan languages are spoken in the northern Himalayan areas. These are common in Bhutan and Nepal. English is also widely used in cities. It is an important language for business and communication across South Asia.
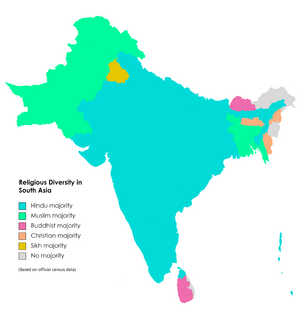
Religions of South Asia
South Asia is known for its many religions. It is one of the most religiously diverse places on Earth. In 2010, it had the world's largest number of Hindus. It also had many Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, and Buddhists.
Indian religions like Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism started in this region. These religions share some ideas and goals. Early Christianity and Islam came to coastal areas through traders. Later, Islam spread more widely under Muslim rulers. About one-third of the world's Muslims live in South Asia.
Most Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, Sikhs, and Christians live in India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan. Muslims are mostly found in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Maldives.
Major Cities of South Asia
South Asia has some of the world's most populated cities. Many of these are "megacities," meaning they have over 10 million people.
- Delhi in India is a huge urban area.
- Mumbai in India is another very large city.
- Dhaka in Bangladesh is a major city.
- Karachi in Pakistan is also a very big city.
- Kolkata in India is a large and historic city.
- Lahore in Pakistan is a significant urban center.
- Kabul in Afghanistan is a large city.
- Bangalore in India is known for its technology.
- Chennai in India is a major cultural and economic hub.
- Hyderabad in India is a growing city.
- Ahmedabad in India is also a large urban area.
South Asian Culture
South Asian culture, also called Desi culture, is a mix of many different traditions. It started with Hinduism and later included Buddhism. Over time, influences from the Muslim world and Europe also became important. South Asian culture has also spread to other parts of Asia, especially Southeast Asia.
Popular Sports
Cricket is the most popular sport in South Asia. About 90% of cricket fans worldwide live in this region. There are also traditional games like kabaddi and kho-kho. These games are played across the region and in major events like the South Asian Games. Leagues for these traditional sports are very popular.
Cinema and Movies
South Asian cinema includes movies from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Movies are very important in South Asia. Bollywood (Hindi films) and South Indian film industries are the biggest. Pakistan's Lollywood is also growing. Historically, Bengali cinema was highly praised around the world.
Music Styles
South Asian music has many different styles. Each country and region has its own unique musical traditions. These styles show the local customs, languages, and history of the area. Many South Asian musicians have put religious and spiritual ideas into their music. This led to styles like Qawwali and Hindustani classical music.
In recent times, movies and TV have made genres like Bollywood and Lollywood music very popular. Even today, traditional folk and ritual music are still loved. Many modern artists get ideas from classical South Asian music.
Delicious South Asian Food
South Asian cuisine includes traditional foods from Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Sometimes, it also includes Bhutan and Afghanistan. This food is also called Desi cuisine. It has both influenced and been influenced by other Asian cuisines.
Main Foods and Flavors
Chapati, a type of flatbread, is a common food in many parts of South Asia. Other main foods include rice, roti (another flatbread), and beans.
South Asian dishes are full of flavor. They use different types of chili, black pepper, cloves, and other strong herbs and spices. Ghee (clarified butter) is also used. Ginger is a common ingredient in both savory and sweet dishes. Turmeric and cumin are often used to make curry dishes.
Common meats are lamb, goat, fish, and chicken. Beef is less common in India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. This is because cattle are important in Dharmic religions. Pork is avoided by Muslims and many Hindus. However, it is eaten in some areas like Northeast India and Goa.
South Asia also has many very sweet desserts. These often use milk, ground almonds, and sugar. Kheer is a popular milk-based rice pudding.
South Asia's Economy
India has the largest economy in South Asia. It makes up almost 80% of the region's economy. India is the world's 5th largest economy in terms of total value. It is also one of the fastest-growing major economies.
Bangladesh has the second largest economy in the region. It has one of the fastest GDP growth rates in Asia. Pakistan is next, followed by Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka has the second highest income per person in the region.
According to the World Bank, South Asia became the fastest-growing region in the world in 2014. This was helped by India's strong growth and good oil prices. Some parts of South Asia are much richer than others. For example, certain states in India contribute a large part of India's economy.
Poverty is a challenge in South Asia. In 2011, about 24.6% of South Asians lived on less than $1.25 per day. Bhutan, Maldives, and Sri Lanka had the fewest people living in poverty. A 2023 report by the UN found that about 20% of South Asians are still considered poor. India has lifted many people out of poverty in recent years.
Education in South Asia
It's hard to compare education quality across South Asia. There are many differences between countries. In 2018, millions of children were not in school. Many others finished primary school without learning basic reading and math skills.
In 2017, UNESCO reported that 241 million children in Southern and Central Asia were not learning. Most of these children were in school but not getting a good education. Only 19% of primary and secondary students reached basic skill levels in reading and math. This poor quality leads to many students dropping out.
Classrooms in South Asia often focus on teachers giving information. Students learn by memorizing things. Children can also face physical punishment and unfair treatment. Different countries have different education systems. India and Pakistan have more developed systems. Bangladesh's system is still very centralized.
Education is usually free in most South Asian countries. However, parents often have to pay for other things, like private tutoring. This is to make up for problems in the school system. Larger, poorer countries like India and Bangladesh struggle to fund their education systems. Smaller countries like Sri Lanka and Maldives have done better. They have achieved almost full primary school enrollment.
Crises like natural disasters and political problems also affect education. Afghanistan and India have many reported disasters. The difficult security situation in Afghanistan makes it hard to run education programs.
Girls face special challenges in getting an education. In 2005, UNESCO estimated that 24 million primary-school-aged girls in the region were not in school. However, many countries have made progress in girls' education. Bangladesh has made great strides in increasing girls' secondary school enrollment.
India has one of the largest higher education systems in the world. In 2011, it had about 21 million students in universities and colleges. This was 86% of all higher education students in South Asia. Bangladesh and Pakistan also have many students in higher education. Bhutan and Maldives have very few. The number of students going to college is still lower than the global average.
Health and Nutrition
South Asia faces health challenges. For example, Pakistan and Afghanistan are two of the few countries still affected by polio. Efforts to stop polio have been difficult due to opposition from militant groups.
Many children in South Asia suffer from malnutrition. India has one of the highest rates of underweight children in the world. This can lead to serious health problems. In 2021, about 330 million people in the region were malnourished.

Most South Asians live in rural areas. Many rely on farming for their food. Nepal and Bangladesh have made progress in reducing the number of undernourished people. However, Pakistan has seen an increase in hungry people. India still has the highest number of undernourished people in any single country.
One reason for malnutrition is the low status of women in some South Asian countries. They may lack knowledge about nutrition. Corruption and lack of government action also play a role. Even with improvements in food production, there are still problems with feeding young children properly.
Governance and Politics

South Asian countries have different types of governments.
- Afghanistan is an Islamic emirate. It has faced many years of conflict and instability. This has made its economy very weak.
- Bangladesh is a parliamentary republic. It is a Muslim-majority democracy.
- Bhutan is a Buddhist state with a constitutional monarchy. It is known for being peaceful and having economic freedom.
- India is a federal parliamentary republic. It is the world's largest democracy. India has a very long written constitution. It has remained a stable democracy since 1950.
- Maldives is a presidential republic. Sunni Islam is its state religion.
- Nepal is a federal parliamentary republic. It was the last Hindu state before becoming a secular republic in 2008. Nepal has faced political instability and natural disasters.
- Pakistan is a federal parliamentary Islamic republic. It was the first country to adopt an Islamic republic system. Pakistan's government has often been unstable.
- Sri Lanka is a semi-presidential republic. It is the oldest continuous democracy in Asia. Sri Lanka experienced a long civil war. However, it has a high Human Development Index.
India leads the region in democracy. Its political system has been stable. Pakistan's government has been less stable. Many prime ministers have not finished their full terms. Sri Lanka has also faced challenges, but it has made good progress in development. Bangladesh is a Muslim-majority democracy. Nepal has also made progress in development recently.
See also
 In Spanish: Asia del Sur para niños
In Spanish: Asia del Sur para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |