Soviet Union facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
Союз Советских Социалистических Республик
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1922–1991 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Flag
(1955–1991) State Emblem
(1956–1991) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Motto: Пролетарии всех стран, соединяйтесь!
"Workers of the world, unite!" |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: Интернационал
"The Internationale" (1922–1944) Государственный гимн СССР "State Anthem of the USSR" (1944–1991) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
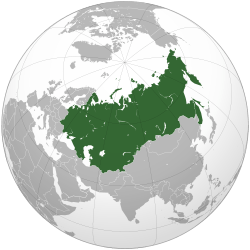
The Soviet Union after World War II
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city
|
Moscow 55°45′N 37°37′E / 55.750°N 37.617°E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | Russian (1990–1991) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognised regional languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ethnic groups
(1989)
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Secular state (de jure) State atheism (de facto) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Soviet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | ----
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leader | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1922–1924
|
Vladimir Lenin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1924–1953
|
Joseph Stalin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1953
|
Georgy Malenkov | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head of state | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1922–1946 (first)
|
Mikhail Kalinin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1988–1991 (last)
|
Mikhail Gorbachev | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head of government | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1922–1924 (first)
|
Vladimir Lenin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1991 (last)
|
Ivan Silayev | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Congress of Soviets (1922–1936) Supreme Soviet (1936–1991) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soviet of Nationalities (1936–1991) Soviet of Republics (1991) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soviet of the Union (1936–1991) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period • World War II • Cold War | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 November 1917 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Treaty of Creation
|
30 December 1922 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Civil War ended
|
16 June 1923 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• First constitution
|
31 January 1924 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Second constitution
|
5 December 1936 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Westward expansion
|
1939–1940 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1941–1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 October 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 February 1956 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Last constitution
|
9 October 1977 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• First republic secedes
|
11 March 1990 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• August Coup
|
19–22 August 1991 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Belovezh Accords
|
8 December 1991 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 December 1991 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
22,402,200 km2 (8,649,500 sq mi) (1st) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1989 census
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Density
|
12.7/km2 (32.9/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 1990 estimate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
$2.7 trillion (2nd) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Per capita
|
$9,000 (28th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 1990 estimate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
$2.7 trillion (2nd) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Per capita
|
$9,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gini (1989) | 0.275 low |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDI (1989) | 0.920 very high |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Soviet ruble (руб) (SUR) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | (UTC+2 to +12) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calling code | +7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | SU | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .su | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Soviet Union (also known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or USSR) was a very large country. It existed for 69 years, from 1922 until 1991. It was the first country to say it was socialist and aimed to build a communist society. This meant that the government controlled almost everything.
The Soviet Union was formed after the Russian Revolution. Vladimir Lenin became the leader. The government worked hard to build up its industry. Over time, the Soviet Union became a major world power. The largest part of the Union was Russia, and Kazakhstan was the second largest. The capital city was Moscow.
After World War II, the Soviet Union grew even more powerful. It gained a lot of political control over Eastern Europe. These countries, like Poland and East Germany, were not officially part of the Soviet Union. However, they were strongly influenced and controlled by it. They were often called satellite states.
The main law-making group was the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. But the most important person was the General Secretary of the Communist Party. This leader made most of the big decisions.
The Soviet Union's constitution said that its member republics could leave. But in reality, the government was very centralized. The smaller republics had little power. The Union was supposed to give everyone equal social and economic rights. There was almost no private property. Everything belonged to the state. Workers' councils, called 'Soviets', were meant to lead the country. But they lost power when Stalinism became strong.
The Soviet Union achieved many things. It put the first satellite and the first person into space. It also helped win World War II alongside the United States and the United Kingdom. However, its centralized government found it hard to adapt and change. The Union finally broke apart in 1991. This was partly due to the reform efforts of its last leader, Mikhail Gorbachev.
Contents
Important Holidays
The Soviet Union had several important holidays. These days were celebrated across the country.
| Date | English Name | Local Name | What it Celebrated |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year | Новый Год | A new year beginning |
| March 8 | International Women's Day | Международный Женский День | Women's rights and achievements |
| May 1-May 2 | Day of International Solidarity of Labor people | Первое Мая - День Международной Солидарности Трудящихся | Workers' rights and unity |
| May 9 | Victory Day | День Победы | The defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II in 1945 |
| October 7 | Constitution Day | День Конституции | The country's laws (since 1978) |
| November 7 | Great October Socialist Revolution | Седьмое Ноября | The October Revolution of 1917 |
Republics of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was made up of 15 different republics. These were called Soviet Socialist Republics or Soviet Socialist Federal Republics. Each republic was supposed to manage its own culture. They also had the right to leave the Union. They all did so in 1991.
The Federal Republics had more independence. They were made up of smaller states called Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics. Many of these still exist today as republics within independent countries. For example, the Tatar ASSR is now the Republic of Tatarstan.
The 15 Soviet Republics
- Armenian SSR
- Azerbaijan SSR
- Byelorussian SSR
- Estonian SSR
- Georgian SSR
- Kazakh SSR
- Kyrgyz SSR
- Latvian SSR
- Lithuanian SSR
- Moldavian SSR
- Russian SFSR (This was a Soviet Federal Socialist Republic)
- Tajik SSR
- Turkmen SSR
- Ukrainian SSR
- Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
Countries After the Union Dissolved
After the Soviet Union broke apart, these 15 republics became independent countries:
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Moldova
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Ukraine
- Uzbekistan
Geography and Climate
The Soviet Union was the world's largest country in 1991. It covered about 22,400,000 square kilometres (8,600,000 sq mi). This was one-sixth of all the land where people lived. Its size was similar to North America.
The western part of the country was in Europe. It made up about a quarter of the total area. This part was the main cultural and economic center. The eastern part was in Asia. It stretched all the way to the Pacific Ocean in the east. This area was much less populated than the western part.
The Soviet Union was over 10,000 kilometres (6,200 mi) wide. This meant it covered 11 different time zones. It was almost 7,200 kilometres (4,500 mi) from north to south. The country had five main climate zones. These included tundra, taiga (forests), steppes (grasslands), deserts, and mountains.
The Soviet Union had the longest border in the world. In 1991, it was over 60,000 kilometres (37,000 mi) long. Two-thirds of this border was along the Arctic Ocean coastline. The United States was across the Bering Strait. At the end of World War II, the Soviet Union shared borders with many countries. These included Afghanistan, China, Finland, Poland, and Turkey.
The longest river in the Soviet Union was the Irtysh. The highest mountain was Communism Peak. It is now called the Ismail Samani Peak in Tajikistan. It is 7,495 metres (24,590 ft) tall. The world's largest lake, the Caspian Sea, was mostly in the Soviet Union. The world's deepest lake, Lake Baikal, was also located there.
History of the Soviet Union
The last Russian Tsar (emperor), Nicholas II, ruled Russia until March 1917. His empire was then replaced by a temporary government. This government was led by Alexander Kerensky. But in November, a group called the Bolsheviks took over.
From 1917 to 1922, the country before the Soviet Union was the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR). Other Soviet republics also existed as separate countries. The Soviet Union was officially formed in December 1922. It was a union of the Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Transcaucasian Soviet republics. These were all ruled by the communist Bolshevik parties.
Revolution and the Start of the USSR
Big changes began in the Russian Empire with the Decembrist Revolt in 1825. Later, serfdom (a system where peasants were tied to the land) was ended in 1861. But this change did not help the poor farmers much. This led to more calls for revolution.
A parliament called the State Duma was created in 1906. This happened after the Russian Revolution of 1905. However, the Tsar did not want to give up his absolute power. World War I made things worse. There were many failures and food shortages in cities.
In March 1917, a rebellion in Saint Petersburg led to the "February Revolution". The Tsar's rule ended. A "Provisional government" took over. Its leaders wanted to hold elections and continue fighting in World War I.
At the same time, workers' councils called Soviets appeared everywhere. The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, wanted a socialist revolution. They gained power in the Soviets and on the streets. In November 1917, during the "October Revolution", they took control from the Provisional Government.
In December, the Bolsheviks signed a peace agreement with the Central Powers. In March, after more fighting, the Soviets left World War I for good. They signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
The new Soviet government then fought a long and bloody Russian Civil War. This war was between the Reds (Bolsheviks) and the Whites (anti-Bolsheviks). It lasted from 1917 to 1923. During this time, Nicholas II and his family were killed. A terrible famine in 1921 killed about 5 million people.
In March 1921, the Peace of Riga was signed. This treaty divided land in Belarus and Ukraine between Poland and Soviet Russia. The Soviet Union also had to deal with new independent countries. These included Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. They had all broken away from the Russian Empire during the civil war.
Forming the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
On December 28, 1922, representatives from four republics agreed to form the Soviet Union. These were the Russian SFSR, the Transcaucasian SFSR, the Ukrainian SSR, and the Byelorussian SSR. They approved the Treaty of Creation of the USSR. This officially created the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.
On February 1, 1924, the British Empire recognized the USSR as a country. Later in 1924, the first Soviet Constitution was approved. This set of laws confirmed the union of the republics.
The Soviet government started making big changes to the economy and industry in 1917. One important plan was the GOELRO plan. This plan aimed to bring electricity to the entire country. It was developed in 1920 and lasted 10 to 15 years. It included building 30 power stations, including ten large hydroelectric plants. This plan was a model for the later Five-Year Plans. It was mostly finished by 1931.
Stalin's Time in Power

From its early days, the Soviet Union was a one-party state. It was ruled by the Communist Party. After a policy called War Communism during the Civil War, the government allowed some private businesses in the 1920s. This was part of the New Economic Policy.
Soviet leaders said that one-party rule was needed. They believed it would stop "capitalist exploitation" and represent the people's will. After Lenin died in 1924, leaders started to gain more power. Joseph Stalin became the most powerful.
Stalin led the country through World War II and into the Cold War. During his rule, many Gulag camps were built. Millions of prisoners were sent to these camps. After Stalin died in 1953, Georgy Malenkov briefly continued his policies.
Nikita Khrushchev later changed some of Stalin's policies. This was called de-Stalinization. However, Leonid Brezhnev and Alexei Kosygin kept things mostly the same. After a new constitution in 1936, the Soviet Union acted more like one big country. It was less like a union of independent republics.
The Khrushchev Era
Stalin died on March 5, 1953. Nikita Khrushchev became the new leader by the mid-1950s. In 1956, he spoke out against Stalin's harsh rule. He also loosened some controls over the party and society. This period was known as de-Stalinization.
Moscow saw Eastern Europe as a very important area. It was a "buffer zone" to protect its western borders. So, the USSR worked to control this region more strongly. It turned Eastern European countries into satellite states. These countries depended on and obeyed the Soviet leadership. Soviet military force was used to stop uprisings in Hungary and Poland in 1956.
In the late 1950s, the USSR had disagreements with China. This led to the Sino–Soviet split. It caused a break in the global Marxist–Leninist movement. Governments in Albania, Cambodia, and Somalia chose to side with China instead of the USSR.
During the late 1950s and early 1960s, the Soviet Union made great progress in the Space Race. It was competing with the United States. The USSR launched the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957. They also sent a dog named Laika into space in 1957. In 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space. Valentina Tereshkova was the first woman in space in 1963. Alexei Leonov was the first person to walk in space in 1965. The USSR also achieved the first soft landing on the Moon with Luna 9 in 1966. They also sent the first Moon rovers, Lunokhod 1 and Lunokhod 2.
Leonid Brezhnev's Leadership
Leonid Brezhnev led the Soviet Union from 1964 until he died in 1982. He became leader after convincing the government to remove Nikita Khrushchev. Brezhnev's time in power is often linked to a decline in the Soviet economy. This started a chain of events that led to the Union's collapse.
Brezhnev gave himself many medals. He received the Hero of the Soviet Union award three times. After he died, Yuri Andropov took over. Andropov died a few years later. Then, Konstantin Chernenko became leader. Chernenko was old and frail. He died just one year after taking office.
In 1980, the Soviet Union hosted the Summer Olympics. Brezhnev opened and closed the games. Many Western countries, especially the United States, boycotted the games. During the closing ceremony, the flag of Los Angeles was raised instead of the US flag. This was a response to the boycott.
Brezhnev was the second longest-serving Soviet leader after Stalin. Here is a list of the main leaders (General Secretary of the Communist Party) and how long they led:
- Vladimir Lenin (1922-1924) - 2 years
- Joseph Stalin (1924-1953) - 29 years
- Nikita Khrushchev (1953-1964) - 11 years
- Leonid Brezhnev (1964-1982) - 18 years
- Yuri Andropov (1982-1984) - 2 years
- Konstantin Chernenko (1984-1985) - 1 year
- Mikhail Gorbachev (1985-1991) - 6 years
Khrushchev and Gorbachev were the only Soviet leaders who did not die while in office.
Gorbachev's Rule and Reforms

Mikhail Gorbachev was the last leader of the Soviet Union. He was the only Soviet leader born after the October Revolution. This meant he grew up entirely within the Soviet system. He and US President Ronald Reagan signed a treaty to reduce nuclear weapons.
Gorbachev started big social and economic changes. These changes gave people more freedom of speech. This allowed them to criticize the government and its policies. The ruling Communist Party lost its tight control over the media and the people. Newspapers began to print stories about the many problems the Soviet Union had hidden in the past. The Soviet Union's economy was struggling. The government was spending a lot of money competing with Western countries.
The Dissolution of the Soviet Union
By the 1980s, the Soviet economy was facing difficulties. Gorbachev's new ideas, meant to fix things, led to the Communist Party losing control. Boris Yeltsin was democratically elected President of the Russian SFSR. This happened even though Gorbachev did not want him to gain power.
Lithuania then announced its independence from the Union. The Soviet government demanded that Lithuania give up its independence. It threatened to send the Red Army to keep order. Gorbachev tried to keep the Soviet Union together. He suggested that each republic could be more independent but still under the same leader. He wanted to call it the 'Union of Soviet Sovereign Republics'. This would keep the Russian initials as CCCP (USSR in English).
A group of communist leaders were unhappy with Gorbachev's plan. They tried to take over Moscow to stop the Soviet Union from collapsing. This event, known as the August Coup, only made people want independence even more. Although Gorbachev survived the attempted takeover, he lost most of his power outside of Moscow.
Russia declared its independence in December 1991. Later that month, leaders from Russia, Byelorussia, and Ukraine signed a treaty. This treaty, called the Belavezha Agreement, officially dissolved the USSR. Gorbachev was very angry, but he had no choice but to accept it. He resigned on Christmas Day 1991. The Soviet Union's parliament, the Supreme Soviet, then made the Belavezha Agreement law. This formally marked the end of the Soviet Union. The next day, the Soviet flag was lowered from the Kremlin for the last time.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
Lenin, Trotsky and Kamenev celebrating the second anniversary of the October Revolution
-
The Battle of Stalingrad, a key moment in World War II.
-
From left to right: Soviet General Secretary Joseph Stalin, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt, and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill at the Tehran Conference in 1943.
-
Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev (left) with US President John F. Kennedy in Vienna, 1961.
-
Nikolai Podgorny visiting Tampere, Finland in 1969.
-
Soviet General Secretary Leonid Brezhnev and US President Jimmy Carter signing the SALT II arms treaty in Vienna in 1979.
-
Mikhail Gorbachev talking with US President Ronald Reagan.
-
The Paneuropean Picnic happened in August 1989 on the Hungarian-Austrian border.
-
A T-80 tank in Red Square during the 1991 August Coup.
-
Changes in country borders after the Cold War ended.
-
Sukarno and Voroshilov at a meeting in 1958.
-
A 1960s poster showing friendship between Cuba and the Soviet Union, with Fidel Castro and Nikita Khrushchev.
-
Gerald Ford, Andrei Gromyko, Leonid Brezhnev, and Henry Kissinger at the Vladivostok Summit in 1974.
-
Mikhail Gorbachev and George H. W. Bush signing documents in 1990.
-
A Soyuz rocket at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
-
People picking cotton in Armenia in the 1930s.
-
Workers at the Salihorsk potash plant in Belarus, 1968.
-
A Soviet stamp from 1987, marking 30 years of the International Atomic Energy Agency.
-
A Soviet stamp showing the orbit of Sputnik 1.
-
Valentina Tereshkova, the first woman in space, visiting a candy factory in Ukraine, 1967.
-
People in Samarkand, Uzbek SSR, 1981.
-
A ceremony in the Uzbek SSR where women burned their traditional veils.
-
A 2001 stamp from Moldova showing Yuri Gagarin.
-
People in Donetsk celebrating the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany in 2018.
-
Soviet singer, songwriter, poet, and actor Vladimir Vysotsky in 1979.
-
Valeri Kharlamov played for the Soviet Union in 11 Ice Hockey World Championships, winning many medals.
-
The Aral Sea in 1989 and 2014, showing the impact of environmental changes.
See also
 In Spanish: Unión Soviética para niños
In Spanish: Unión Soviética para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |