List of islands in the Pacific Ocean facts for kids
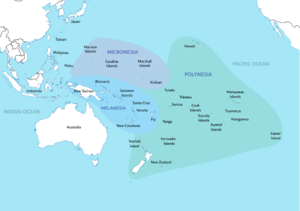
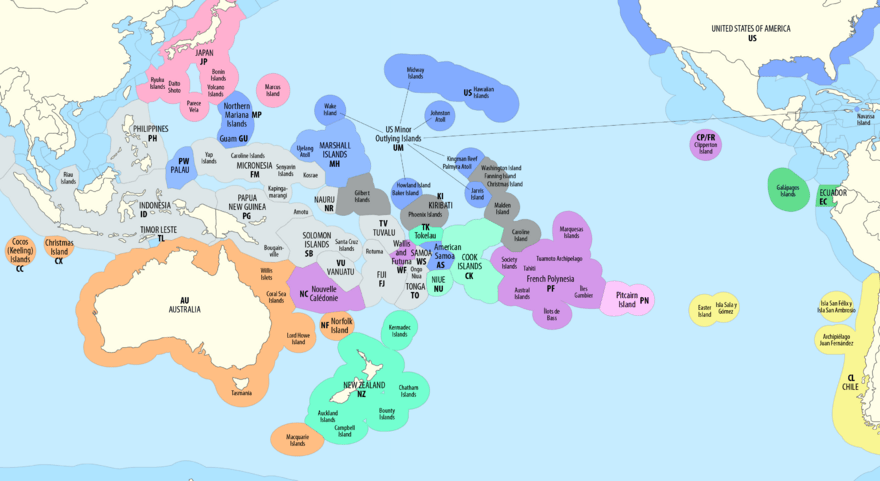
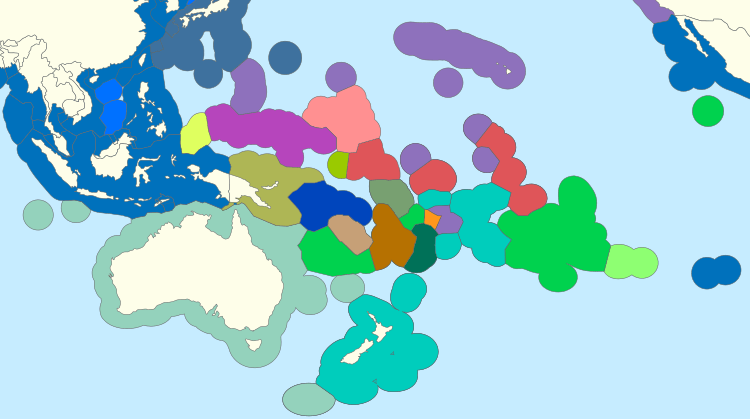
The Pacific islands are a huge group of islands found in the Pacific Ocean. They are often divided into three main groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. When people talk about the Pacific Islands, they might mean different things. Sometimes, it refers to islands with similar cultures, like those with Austronesian roots. Other times, it means islands that were once colonized by European countries. It can also simply mean the whole geographical area called Oceania.
This list of islands in the Pacific Ocean is organized by groups of islands (called archipelagos) or by political boundaries. We've kept this list to a good size. For countries with many small or uninhabited islands, you can find more complete lists by clicking the links.
Contents
Understanding Pacific Island Groups
The term Pacific Islands can mean different things. Sometimes, it only includes islands within Oceania. Other times, it refers to Pacific Ocean islands that were once ruled by countries like Britain, France, or the United States. Examples include Borneo, the Pitcairn Islands, and Taiwan.
Scientists often define the "Tropical Pacific Islands" as those with oceanic geology found in Melanesia, Micronesia, Polynesia, and the eastern Pacific. In the 1990s, ecologists Dieter Mueller-Dombois and Frederic Raymond Fosberg divided these tropical islands into several smaller areas:
- Western Melanesia
- The Bismarck Archipelago (islands east of New Guinea)
- Bougainville and Buka Island
- The Solomon Islands
- Eastern Melanesia
- Subtropical Islands (near Australia/New Zealand)
- Micronesia
- The Bonin Islands and Volcano Islands
- Marcus Island
- The Northern Marianas and The Southern Marianas
- The Caroline Islands
- Nauru and Banaba
- Wake Island
- Palau
- The Marshall Islands
- The Gilbert Islands (Kiribati)
- Central Polynesia
- Johnston Atoll
- The Phoenix Islands
- The Line Islands
- Howland Island, Baker Island, Jarvis Island, Malden Island, and Starbuck Island
- Tuvalu, Tokelau, and the Northern Cook Islands
- Western Polynesia
- Eastern Polynesia
- The rest of the Cook Islands
- The Austral Islands
- The Society Islands
- The Tuamotu Archipelago and the Pitcairn Islands
- Easter Island and Salas y Gómez
- The Marquesas Islands
- Northern Polynesia
- The Hawaiian Islands
- Oceanic Islands of the Eastern Pacific
- The Revillagigedo Islands
- Cocos Island and Malpelo Island
- Clipperton Island
- The Galápagos Islands
- The Desventuradas Islands
- The Juan Fernández Islands
Pacific Islands and Oceania: A Closer Look
In 2007, a book by Ron Crocombe, a scholar from New Zealand, looked at the term Pacific Islands politically. He included many places like American Samoa, Australia, the Cook Islands, Easter Island, Fiji, Guam, Hawaii, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu. Crocombe thought some islands, like Easter Island, could become important in the future for the Asia-Pacific region.
Another way to define "Pacific Islands" is by the islands served by the Pacific Community. This group helps with development and includes Australia and many islands that are not politically part of other countries.
Since the early 1800s, geographers have grouped Australia and the Pacific islands into a region called Oceania. The Pacific Ocean is what truly defines this area. In some countries, Oceania is even seen as a continent, like Europe or Asia. In 1879, a British scientist named Alfred Russel Wallace said that "Oceania is the word often used by continental geographers to describe the great world of islands we are now entering upon." He also noted that "Australia forms its central and most important feature."
Today, Oceania usually includes Australia and the islands of Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Islands that are geologically linked to the Asian mainland, like those in the Malay Archipelago, are usually not included. Also, non-tropical islands north of Hawaii are often left out.
Some definitions of Oceania are even stricter, only including islands that are culturally part of Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. However, the Encyclopedia Britannica sees "Pacific Islands" as mostly meaning Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. They say Oceania, in its widest sense, includes all parts of the Pacific that are not in those three groups. The The World Factbook and the United Nations consider Oceania/the Pacific area as one of the world's seven main continental divisions.
Since the 1950s, many people, especially in English-speaking countries, have seen Australia as a continent-sized landmass. However, Australia is also sometimes seen as a Pacific Island, or both. Australia is a founding member of the Pacific Islands Forum. This group is now the main governing body for the Oceania region. It works on trade and defense issues. By 2021, the Pacific Islands Forum included all independent Pacific Island nations, like Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, and Tonga. It also includes areas that are part of other nations, such as American Samoa, French Polynesia, and Guam.
In 2014, Tony deBrum, the Foreign Minister for the Marshall Islands, said, "Not only [is Australia] our big brother down south, Australia is a member of the Pacific Islands Forum and Australia is a Pacific island, a big island, but a Pacific island." Japan and some nations of the Malay Archipelago, like East Timor, Indonesia, and the Philippines, have a presence in the Pacific Islands Forum, but they are not full members. These nations have their own regional group called ASEAN.
Largest Pacific Islands
Here are some of the largest islands in the Pacific Ocean, with an area bigger than 10,000 square kilometers.
Islands by Continent
Antarctica
- List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands
Asia
- List of islands of Asia
- List of islands of China
- Japanese Archipelago (6,852 islands)
- List of islands of Indonesia
- List of islands of North Korea
- List of islands of the Philippines
- List of islands of Russia
- List of islands of South Korea
- List of islands of Vietnam
North America
- Central American Pacific Islands
- List of islands of North America
- Islands of Canada (British Columbia)
- List of islands of Mexico
- List of islands of the United States
Oceania
- List of islands of Australia
- Islands of Britain
- List of islands of Fiji
- Islands of France (Pacific Ocean)
- List of islands of Hawaii
- List of islands of Kiribati
- List of islands of the Marshall Islands
- List of islands of New Zealand
- List of islands of Papua New Guinea
- List of islands of the Solomon Islands
- Islands of Tonga
- List of islands of Tuvalu
- Islands of the United States (Insular areas)
- List of islands of Vanuatu
South America
- List of islands of South America
- List of islands of Chile
- List of islands of Colombia
- List of islands of Ecuador
- List of islands of Peru
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |