Exploration facts for kids

Exploration is like going on an adventure to learn about places you've never seen before. It's all about discovering new things and finding out what's out there. Humans are unique because we love to explore, even when we have everything we need right where we are! We're the only mammal that does this.
Long ago, Neanderthals lived in Eurasia for thousands of years, but they didn't travel very far. Modern humans, however, explored and spread across all the continents in less than 50,000 years. A huge time for exploration was the Age of Discovery, when European explorers sailed all over the world, mapping new lands. Today, we even explore outer space! But exploration isn't just about places; it's also about new ideas, art, and even understanding life itself.
Contents
Ancient Explorers
Phoenicians: Master Sailors
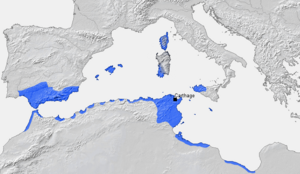
The Phoenicians were an ancient people who lived along the coast of the Levant (which is now parts of countries like Lebanon and Syria). They became very important around 1100 BC. By the 9th century BC, they were the most powerful culture in the Mediterranean Sea. They became rich through trade, not war. They made agreements and alliances to expand their colonies.
The Phoenicians were amazing sailors with the best ships in the Mediterranean. They also explored land routes and set up caravan paths to trade with faraway places. The famous city of Carthage started as a Phoenician colony in North Africa and grew to be their biggest and most successful settlement.
Carthaginians: Venturing into the Unknown
Over time, many Phoenician colonies in the western Mediterranean came under the control of Carthage. The Carthaginians were also great explorers. Ancient writers mention two big expeditions around 500 BC.
Pliny the Elder wrote that Carthage sent an explorer named Himilco to explore distant parts of Europe. His travel report, called a periplus (a sailing record), is lost, but other old writers saw it. Himilco had as many as 60 ships. He likely sailed along the Iberian Peninsula and up the coast of Gaul (modern France). A Roman writer named Avienus wrote about this trip. Himilco traveled north from Brittany to the British Isles. He was probably looking for tin, a rare metal back then. He reached an island called insula sacra, which most people believe was Ireland.
Around the same time, Hanno the Navigator explored the western coast of Africa. His periplus has survived, making it one of the oldest travel records we have! It lists landmarks, ports, and distances, like a guide for other ship captains. Hanno's 60 ships sailed south along the African coast. He might have reached an island off the coast of Sierra Leone. No other explorations of the west African coast are recorded until the time of Henry the Navigator from Portugal.
Greek Explorers: Scientific Journeys
One of the first explorers to use a scientific approach was Pytheas of Massalia. He was an ancient Greek from the Greek colony of Massalia (now Marseille, France). Around 325 BC, he sailed to northwestern Europe. He sailed all the way around Great Britain.
Pytheas was the first person to describe the Midnight Sun, where the sun stays visible all night. He was also the first known scientific visitor to the Arctic and reported on the polar ice. He even suggested that the moon caused the tides, which was the earliest known idea about this!
Chinese Exploration: Opening New Paths
During the 2nd century BC, the Han dynasty in China explored much of the eastern part of the Northern Hemisphere. In 139 BC, a Chinese diplomat named Zhang Qian traveled west. He was trying to make an alliance with a group called the Da Yuezhi, but he didn't succeed. However, he discovered countries the Chinese didn't even know existed! He traveled as far as the Indus River in northwestern India.
Medieval Adventures

Vikings: Bold Seafarers
The Viking Age saw three main groups of Vikings from Scandinavia: the Danes, the Swedes (also called the "Rus"), and the Norwegian Vikings. The 'Rus' Vikings founded the settlement of Kiev and named their land Russland, which later became Russia.
A Swedish Viking explorer named Garðar Svavarsson was the first to sail all the way around Iceland in 870 CE. He proved it was an island. Around 890 CE, Vikings led by Ohthere of Norway traveled north above the Arctic Circle to the White Sea.
Around 982 CE, the Norwegian Erik the Red explored Greenland. In 986, he returned to Iceland and convinced others to follow him. He founded the first settlement there. By the year 1000, about a thousand settlers lived in Greenland. Erik's son, Leif Erikson, was probably the first European to step foot on North America. He landed in a place he called "Vinland."
Marco Polo: Journey to the East
Marco Polo (1254-1324) was a Venetian merchant and explorer. He traveled across Asia during the time of the powerful Mongol Empire. He was one of the first Europeans to explore Eastern Asia.
He left Venice at age 17 with his father and uncle. They traveled along what later became known as the Silk Road. They reached Cathay (China), where Marco Polo joined the court of Kublai Khan. He explored China for 24 years! He brought back amazing things like ivory, jade, jewels, porcelain, and silk. He also brought back noodles from China, which Italians later called pasta.
The Age of Discovery

The Age of Discovery was a special time in European history, from the early 15th century to the early 17th century. In this short period, Europeans completely changed how they saw the world. European countries sent ships all over the globe to find new trade routes. They were looking for valuable goods like gold, silver, and spices. As they explored, Europeans discovered new people and lands they had never known about.
Here are some famous explorers from this exciting age:
- Christopher Columbus was a Genoese navigator who worked for the Queen of Spain. In 1492, he sailed three ships to find a trade route to asia. Instead, he landed in the Americas! People once thought he was the first European to discover America, but Norse explorers had been there centuries earlier. His discovery led to many more European explorations. He made four voyages in total. Sadly, his arrival had a terrible impact on the native people, many of whom died from European diseases, hunger, and conflict.
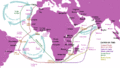
- Vasco da Gama was a Portuguese sailor. He was the first European to sail to India by going around the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa. He made three trips to India using this new trade route. In 1497, he left Lisbon with four ships. No European explorer before him had sailed further than what is now South Africa. Vasco da Gama sailed all the way around the bottom of Africa. His voyages made Portugal very powerful in trade with India, and they set up trading posts along the African coast.
- Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer who sailed for Spain. He discovered the Strait of Magellan (named after him), which connects the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. He was the first European to sail across the Pacific Ocean. He was killed in the Philippines in 1521. However, his ships, led by the Basque navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, continued sailing west to Spain. This completed the first trip around the world, proving that the Earth is round!
- Giovanni da Verrazzano was an explorer from Florence who sailed for France. He is known for being the first European (since the Norse) to explore the East Coast of the United States. In 1524, the King of France sent Verrazzano to find a “Northwest Passage” to Asia through North America. He explored the coast between Cape Fear in North Carolina and Newfoundland. He also explored what is now New York Harbor and Narragansett Bay. He wrote about the lands and people he found, some accurately, some not. His return that year gave France a claim to all of North America. He sailed to the Americas two more times. On his last trip, he was captured and killed, likely on Guadeloupe in the Caribbean Sea.
- Samuel de Champlain was a French navigator, mapmaker, and explorer. In 1608, he founded Quebec City. He discovered lake Champlain (named after him). He is known as the father of New France. Champlain explored much of western New York and the eastern Great Lakes.
- James Cook was an English explorer, navigator, and mapmaker. Captain Cook made three voyages to the Pacific Ocean. He mapped many areas and recorded several islands and coastlines on European maps for the first time. He explored the east coast of Australia and discovered the Hawaiian Islands. He was also the first to map parts of Newfoundland and New Zealand. In 1769, he received a gift from a Polynesian priest named Tupaia. It was a map of all the major islands of the South Pacific—the first any European had ever seen! It matched what Cook had already explored and included other parts of the Pacific he hadn't seen. This helped him bring back a very accurate map of the Pacific.
Modern Explorations
Exploring the Universe
There are many reasons why humans explore outer space. At first, people explored space just by looking up at the sky. Ancient people mapped the universe they could see. Then, the telescope was invented, letting us see even more! In the mid-twentieth century, humans actually started exploring space with rockets and Spacecraft. The main reasons are for scientific research and because humans are naturally curious about the universe. Space exploration has also led to new technologies, new products, and even new industries!
Related pages
For more information on exploration and explorers, check out these articles:

- Famous explorers
- Famous female explorers
- Expedition
- Age of Discovery
- Colonization
- European exploration of Africa
- Human migration
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Timeline of European exploration
- Treaty of Tordesillas
Images for kids
-
Outward and return voyages of the Portuguese India run in the Atlantic and Indian oceans. This shows the volta do mar (a sailing technique) used by Henry's navigators, and the route around South Africa discovered by Bartolomeu Dias in 1488, later used by Vasco da Gama and Pedro Alvares Cabral.
-
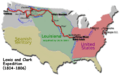
Route of the Lewis and Clark Expedition
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |