Ponce, Puerto Rico facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ponce
Municipio Autónomo de Ponce
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
City and municipality
|
|||
| Autonomous Municipality of Ponce | |||
|
|||
| Nicknames:
"La Perla del Sur",
"Ciudad Señorial", "Ciudad de los Leones", "Ciudad de las Quenepas" |
|||
| Motto(s):
Ponce es Ponce
|
|||
| Anthem: "La Perla del Sur" | |||
Map of Puerto Rico highlighting Ponce Municipality
|
|||
| Sovereign state | |||
| Commonwealth | |||
| Settled | c.1500 BC (Non-Europeans) | ||
| Re-settled | 1582 (Europeans) | ||
| Sitio | 1646 (Dispersed settlement) | ||
| Partido | 1670 (Hamlet) | ||
| Founded | August 12, 1692 (Village) | ||
| † Villa | July 29, 1848 | ||
| † Ciudad | August 13, 1877 | ||
| Named for | Juan Ponce de Leon y Loayza | ||
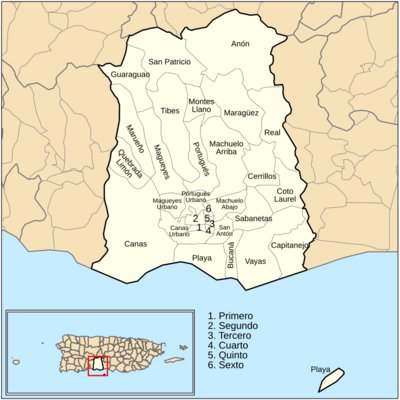
| Barrios |
31 barrios
Anón
Bucaná Canas Canas Urbano Capitanejo Cerrillos Coto Laurel Cuarto Guaraguao Machuelo Abajo Machuelo Arriba Magueyes Magueyes Urbano Maragüez Marueño Montes Llanos Playa Portugués Rural Portugués Urbano Primero Quebrada Limón Quinto Real Sabanetas San Antón San Patricio Segundo Sexto Tercero Tibes Vayas |
||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Mayor–council | ||
| Area | |||
| • City and municipality | 193.6 sq mi (501 km2) | ||
| • Land | 114.8 sq mi (297 km2) | ||
| • Water | 78.8 sq mi (204 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 52 ft (16 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • City and municipality | 137,491 | ||
| • Rank | 4th in Puerto Rico | ||
| • Density | 710.18/sq mi (274.20/km2) | ||
| • Metro | 224,142 (MSA) | ||
| • CSA | 365,233 | ||
| Demonym(s) | Ponceños | ||
| Time zone | UTC−4 (AST) | ||
| ZIP Codes |
00715, 00716, 00717, 00728, 00730, 00731, 00732, 00733, 00734, 00780
|
||
| Area code(s) | 787/939 | ||
| Major routes |  |
||
| GNIS feature ID | 1611718 | ||
| Website | http://visitponce.com/ | ||
| † = Date of the Villa and Ciudad charters | |||
Ponce is a vibrant city and municipality located on the southern coast of Puerto Rico. It is the most populated city outside the San Juan area. Ponce was founded on August 12, 1692. It is named after Juan Ponce de León y Loayza, who was the great-grandson of the famous Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León.
Ponce is known by several cool nicknames. People often call it La Perla del Sur (The Pearl of the South). It's also known as La Ciudad Señorial (The Manorial City) and La Ciudad de las Quenepas (Genip City). This last name comes from the many genip fruits that grow there!
The city is a major center for the government of Puerto Rico. It also serves as a regional hub for many U.S. Federal Government offices. As of 2020, Ponce and its surrounding areas have a population of over 278,000 people.
The municipality of Ponce is located on the southern coast of the island. It is south of Adjuntas, Utuado, and Jayuya. To its east is Juana Díaz, and to its west is Peñuelas. The Caribbean Sea borders it to the south.
Ponce has 31 different areas called barrios. Some of these are in the city, and others are in the countryside. It is the second largest municipality in Puerto Rico by land area. In 1992, Ponce became the first municipality in Puerto Rico to gain its autonomy. This means it has more control over its own local affairs.
The historic downtown area of Ponce is called Ponce Pueblo. It is about three miles inland from the coast. This historic district is famous for its unique Art Deco, Neoclásico Isabelino, and Ponce Creole buildings.
Contents
- History of Ponce: From Ancient Times to Today
- Geography of Ponce: Mountains, Rivers, and Coastlines
- Cityscape: Exploring Ponce's Unique Look
- Tourism in Ponce: Fun Places to Visit
- Culture in Ponce: Music, Arts, and Traditions
- Economy of Ponce: Industry, Agriculture, and Trade
- Demographics: Who Lives in Ponce?
- Symbols of Ponce: Flag and Coat of Arms
- Municipal Services: Keeping Ponce Safe and Educated
- Education in Ponce: Learning and Growing
- Transportation in Ponce: Getting Around the City
- Notable People from Ponce
- International Connections
- Commemorative Dates: Remembering Important Moments
- See also
History of Ponce: From Ancient Times to Today
Ponce has a long and interesting history, starting even before Europeans arrived.
Early Settlers and Spanish Beginnings
The area where Ponce is today was once home to the Taíno tribe. Their region was called Guaynia. Agüeybaná, a Taíno chief, met the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León in 1508.
Archaeologists have found four important ancient sites in Ponce. These are Canas, Tibes, Caracoles, and El Bronce.
Spanish families began settling near the Jacaguas River in the early 1500s. For safety, they later moved to the banks of the Rio Portugués. By 1646, the whole area was known as Ponce. In 1670, a small church was built and named after Our Lady of Guadalupe.
On September 17, 1692, the King of Spain, Carlos II, officially recognized the settlement as a small village. This is considered the founding date of Ponce. The city is named after Juan Ponce de León y Loayza, a descendant of the famous explorer.
In 1712, the village was formally named El Poblado de Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Ponce.
Growth in the 1800s: New People Arrive
In the early 1800s, Ponce was still a small village. People mostly farmed, raised cattle, and traded goods.
However, three big changes helped Ponce grow a lot in the 1820s:
- Many French-speaking people came to Ponce. They were escaping the Haitian Revolution (1791–1804). These new settlers brought money and skills. They helped Ponce grow its sugarcane farms and trade.
- Landowners and merchants also moved from other Latin American countries. They were looking for better opportunities after their own countries gained independence from Spain.
- The Spanish Royal Decree of Graces of 1815 encouraged Europeans to move to Puerto Rico. They just needed to become Catholic and work in farming.
These new groups of people changed Ponce a lot. The town grew quickly. Because of this fast growth, Ponce was declared a villa (village) by Queen Isabella II on July 29, 1848. Then, in 1877, it officially became a city.

Many immigrants became very rich from coffee, corn, and sugarcane farming. They also made money from rum production, banking, and other businesses. By 1898, Ponce was a busy and successful city. It had the island's main financial center and even its own money! It also had offices for other countries like England and Germany.
In 1882, Ponce held its first big fair, showing off new industrial and agricultural inventions.
Ponce in the 20th Century: Challenges and Changes
U.S. Arrival and Economic Shifts

When the U.S. arrived in Puerto Rico in 1898 during the Spanish–American War, Ponce was the largest city on the island. It had a population of 22,000 people. Ponce also had the best road, connecting it to San Juan.
On July 27, American troops landed at Playa de Ponce. The next day, General Nelson Miles took control of the city. There were small fights, but no big battles. The American flag was raised, and U.S. Army headquarters were set up in Ponce.
After the U.S. took over, they decided to manage the island mostly from San Juan. This led to a period where Ponce's economy faced challenges. Several things made this worse:
- The Hurricane San Ciriaco in 1899 caused a lot of damage.
- New sugar mills opened in other towns, taking business away from Ponce.
- Coffee farms struggled in the 1920s.
- Trade with Spain and Cuba was lost after the war.
Despite these challenges, Ponce began to build strong manufacturing industries. Companies like Ponce Cement, Vassallo Industries, and Destilería Serrallés (which makes rum) started up.
The Ponce Massacre
On March 21, 1937, a peaceful march was planned by the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party. They wanted to celebrate the end of slavery and protest the jailing of their leader, Dr. Pedro Albizu Campos.
However, the march turned into a sad event. The Insular Police, who reported to the U.S.-appointed governor, opened fire on the unarmed marchers and people watching. Many people were hurt or killed. This event is remembered as a very important moment in Puerto Rican history.
You can learn more about this event at the Ponce Massacre Museum on Marina Street. There is also a park, the Pedro Albizu Campos Park, named after the Nationalist Party leader. Many people believe this event helped shape Puerto Rican national identity.
Economic Changes in the 1970s
The 1970s brought more economic changes to Ponce. Some big businesses and banks moved their main offices to San Juan. Also, the sugar cane industry, which was very important to Ponce, stopped growing sugar cane in the area in 1976. These changes caused many people in Ponce to lose their jobs.
The Mameyes Landslide
On October 7, 1985, a terrible mudslide happened in a part of Ponce called Mameyes. More than 129 people died. Countries from all over the world sent help. The government moved hundreds of people to a new, safer community. This landslide was one of the worst in North America at the time.
Ponce Today: A City on the Rise
Ponce became the first municipality in Puerto Rico to gain its autonomy on October 27, 1992. This gave the local government more power to make decisions for the city.
In recent years, Ponce has worked hard to improve its economy. It is now considered the second most important city in Puerto Rico, after San Juan. Its economy is growing, and its population is increasing.
Ponce is still known by its nicknames: La Perla del Sur (The Pearl of the South) and La Ciudad Señorial (The Noble City). It's also called La Ciudad de las Quenepas (Genip City) because of the many genip fruits that grow there.
You can explore the full history of Ponce at the Museo de la Historia de Ponce. This museum shows the city's story from its early days until the end of the 20th century.
On September 20, 2017, Hurricane Maria hit Puerto Rico. Ponce suffered a lot of damage, with many homes destroyed or partly damaged. The hurricane also caused many landslides in the area.
Geography of Ponce: Mountains, Rivers, and Coastlines
The Municipality of Ponce is located on the southern coast of Puerto Rico, right by the Caribbean Sea. It shares borders with Adjuntas, Utuado, Jayuya, Peñuelas, and Juana Díaz.
Ponce is a very large municipality. Only Arecibo has more land area in Puerto Rico. The northern part of Ponce is mountainous, while the southern part has flat coastal plains.
Ponce's land stretches from the central mountain range in the north to the Caribbean Sea in the south. The southern area is mostly flat plains, while the central area is semi-dry hills. The northern part is rainy mountains. Cerro Maravilla, one of Puerto Rico's highest peaks, is located in Barrio Anón.
The municipality has 19 rural barrios (areas). Their land varies from flat to hilly to steep mountains. The remaining barrios are part of the city's urban area. The historic district is found within six of these urban barrios.
A special sensor that detects earthquakes is located in Barrio Cerrillos.
Land Features: Peaks and Promontories
Ponce is home to some impressive land features. Cerro de Punta, the highest peak in Puerto Rico, is located in Barrio Anón. Mount Jayuya is also nearby. Cerro Maravilla is another tall peak, almost 3,970 feet above sea level.
There are many other mountains and hills in Ponce, like Montes Llanos and Mount Diablo. Along the coast, you'll find points like Cuchara, Peñoncillo, Carnero, and Cabullón. More than half of Ponce's land has slopes of 10 degrees or more.

Water Features: Rivers, Lakes, and Beaches
Ponce has a rich system of 14 rivers. Some of the main rivers are Matilde, Inabón, Bucaná, Jacaguas, and Portugués. These rivers flow from the mountains down to the Caribbean Sea.
Lakes in Ponce include Bronce and Ponceña. There are also several smaller lakes and the Salinas Lagoon. Popular beaches include La Guancha and El Tuque. You can also find a beautiful beach on Caja de Muertos Island. Lake Cerrillos is another important water body in the municipality.
Coastal areas in Ponce feature Bahía de Ponce (Ponce Bay) and several small islands called cays. These include Jueyes, Ratones, Cardona, Gatas, and Isla del Frio. Caja de Muertos Island is also nearby. These areas have important mangrove forests.
Climate: Tropical Weather in Ponce
Ponce has a tropical savanna climate. This means it's warm all year round. In summer, highs average around 92°F, and in winter, they are about 87°F. Lows are around 67°F in winter and 74°F in summer.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Ponce was 100°F. The lowest was 49°F. The average yearly temperature is about 79°F.
| Climate data for Ponce, Puerto Rico (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1898–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 98 (37) |
95 (35) |
96 (36) |
96 (36) |
96 (36) |
99 (37) |
100 (38) |
100 (38) |
99 (37) |
98 (37) |
100 (38) |
98 (37) |
100 (38) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 87.8 (31.0) |
87.7 (30.9) |
87.6 (30.9) |
88.8 (31.6) |
89.5 (31.9) |
91.2 (32.9) |
91.5 (33.1) |
91.8 (33.2) |
91.4 (33.0) |
90.8 (32.7) |
89.8 (32.1) |
88.4 (31.3) |
89.7 (32.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 75.1 (23.9) |
74.9 (23.8) |
75.0 (23.9) |
76.7 (24.8) |
78.3 (25.7) |
80.2 (26.8) |
80.3 (26.8) |
80.5 (26.9) |
80.0 (26.7) |
79.4 (26.3) |
77.9 (25.5) |
75.9 (24.4) |
77.8 (25.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 62.5 (16.9) |
62.1 (16.7) |
62.5 (16.9) |
64.6 (18.1) |
67.0 (19.4) |
69.2 (20.7) |
69.1 (20.6) |
69.3 (20.7) |
68.7 (20.4) |
67.9 (19.9) |
66.0 (18.9) |
63.5 (17.5) |
66.0 (18.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 49 (9) |
51 (11) |
50 (10) |
53 (12) |
55 (13) |
60 (16) |
58 (14) |
60 (16) |
58 (14) |
61 (16) |
56 (13) |
52 (11) |
49 (9) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.73 (19) |
1.21 (31) |
1.87 (47) |
2.26 (57) |
4.18 (106) |
2.16 (55) |
2.84 (72) |
4.56 (116) |
6.94 (176) |
5.38 (137) |
3.94 (100) |
1.45 (37) |
37.52 (953) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 10.1 | 7.8 | 8.2 | 10.3 | 12.1 | 12.7 | 10.1 | 7.4 | 106.9 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Cityscape: Exploring Ponce's Unique Look
Architecture: A Blend of Styles

In the 1800s, Ponce became famous for its beautiful buildings. A new style, called Ponce Creole, was even created here. Architects used a mix of Art Nouveau and neoclassic styles. This gave the city a very special look, which you can see in places like the Teatro La Perla.
To show off its amazing buildings, Ponce opened the Museum of Puerto Rican Architecture. Many of Ponce's buildings, from house fronts to street corners, are inspired by the architecture of Barcelona, Spain. This is because many people from Catalonia, Spain, settled here.
Barrios: The Many Neighborhoods of Ponce
Ponce has 31 barrios, which are like neighborhoods or districts. This is the most of any municipality in Puerto Rico. Twelve of these barrios are in the city's urban area. The other 19 are outside the city, some being suburban and others rural.
The U.S. Census Bureau has detailed information about each of Ponce's barrios. For example, Montes Llanos is the least populated barrio. Canas is the most populated because it's a very large area.
Ponce has nine barrios that touch neighboring municipalities. Five barrios are along the coast: Canas, Capitanejo, Playa, Bucaná, and Vayas.
The city's urban zone includes 11 barrios. The historic downtown area is found within the original six core city barrios: Primero, Segundo, Tercero, Cuarto, Quinto, and Sexto.
The remaining eight barrios are in the interior of the municipality. They are outside the city limits and are not coastal or bordering other towns.
Here is a summary of Ponce's barrios, their population, and land area:
| No. | Barrio | Population (Census 2000) |
Density (/sq mi) |
Total Area (sq mi) |
Land Area (sq mi) |
Water Area (sq mi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anón | 1669 | 129.9 | 12.85 | 12.85 | 0.00 |
| 2 | Bucaná | 3963 | 2957.5 | 2.16 | 1.34 | 0.81 |
| 3 | Canas | 34065 | 2349.3 | 22.82 | 14.50 | 8.32 |
| 4 | Canas Urbano | 21482 | 9299.6 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 0.00 |
| 5 | Capitanejo | 1401 | 355.4 | 4.82 | 3.95 | 0.88 |
| 6 | Cerrillos | 4284 | 1377.5 | 3.31 | 3.11 | 0.20 |
| 7 | Coto Laurel | 5285 | 1492.9 | 3.60 | 3.54 | 0.06 |
| 8 | Cuarto | 3011 | 18818.8 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
| 9 | Guaraguao | 1017 | 247.4 | 4.11 | 4.11 | 0.00 |
| 10 | Machuelo Abajo | 13302 | 7515.3 | 1.86 | 1.77 | 0.90 |
| 11 | Machuelo Arriba | 13727 | 2124.9 | 6.61 | 6.46 | 0.15 |
| 12 | Magueyes | 6134 | 1345.2 | 4.56 | 4.56 | 0.00 |
| 13 | Magueyes Urbano | 1332 | 1074.2 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 0.00 |
| 14 | Maragüez | 754 | 142.0 | 6.42 | 5.31 | 1.11 |
| 15 | Marueño | 1474 | 350.1 | 4.21 | 4.21 | 0.00 |
| 16 | Montes Llanos | 462 | 214.9 | 2.15 | 2.15 | 0.00 |
| 17 | Playa | 16926 | 3864.4 | 14.98 | 4.38 | 10.60 |
| 18 | Portugués | 4882 | 1386.9 | 3.56 | 3.52 | 0.04 |
| 19 | Portugués Urbano | 5886 | 5163.2 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 0.00 |
| 20 | Primero | 3550 | 14200.0 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.00 |
| 21 | Quebrada Limón | 804 | 301.1 | 2.67 | 2.67 | 0.00 |
| 22 | Quinto | 724 | 6581.8 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.00 |
| 23 | Real | 3139 | 595.6 | 5.28 | 5.27 | 0.01 |
| 24 | Sabanetas | 6420 | 2351.6 | 2.79 | 2.73 | 0.06 |
| 25 | San Antón | 11271 | 10063.4 | 1.17 | 1.12 | 0.04 |
| 26 | San Patricio | 465 | 67.8 | 6.86 | 6.86 | 0.00 |
| 27 | Segundo | 11321 | 17416.9 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.00 |
| 28 | Sexto | 4745 | 18250.0 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.01 |
| 29 | Tercero | 773 | 9662.5 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| 30 | Tibes | 866 | 123.5 | 7.01 | 7.01 | 0.00 |
| 31 | Vayas | 1338 | 187.9 | 10.47 | 7.12 | 3.35 |
| Ponce | 186475 | 1625.5 | 193.6 | 114.7 | 78.9 |
Tourism in Ponce: Fun Places to Visit


Ponce has many interesting places for tourists to visit because of its rich history. The downtown area has most of the city's attractions. Tourism has grown a lot in recent years.
Many hotels have been built to support the growing tourism. These include the Ponce Hilton Golf & Casino Resort and the historic Hotel Meliá. The Ponce Ramada also opened in 2009. Ponce is part of Puerto Rico's Porta Caribe tourist region.
'Ponce en Marcha': A City's Revival
A big project called "Ponce en Marcha" ("Ponce on the Move") has helped to restore the city's historic area. This project started in 1985 and has revitalized many buildings.
The historic downtown area of Ponce is recognized as one of the "60 of the World's Great Places." This is because it has beautifully preserved its Caribbean culture. This revitalized area is known as "Ponce Centro" or "Historic Ponce."
Landmarks: Must-See Sights in Ponce
Ponce is often called the Museum City because it has so many great museums. All museums in Ponce are managed by the local government.

Plaza Las Delicias is the city's main square. It features the famous "Lions Fountain," the Ponce Cathedral, and Parque de Bombas. The Parque de Bombas is an old fire station that is now a museum. It is a symbol of the city and honors its brave firefighters. The Ponce City Hall is also in the plaza. It's the oldest colonial building in the city, built in the 1840s.
Just north of downtown Ponce, you'll find the Castillo Serrallés and the Cruceta del Vigía. The Cruceta del Vigía is a 100-foot observation tower that offers amazing views of the city. This hill was once used by scouts to watch for ships approaching the harbor.
Ponce is home to Puerto Rico's oldest cemetery. The Tibes Indigenous Ceremonial Center was discovered in 1975. It is the site of the oldest cemetery found in the Caribbean, with about 200 skeletons from the year 300 AD.

The Paseo Tablado La Guancha is located on the city's waterfront. It has food kiosks, a stage for events, and a marina. From its observation tower, you can see the Cardona Island Light. You can also take a boat ride to Isla de Caja de Muertos (Coffin Island). This small island has beautiful beaches and an old lighthouse.
Culture in Ponce: Music, Arts, and Traditions
Ponce is rich in cultural assets. It has libraries, museums, galleries, and parks. Hundreds of its buildings are historically valuable. The city also hosts many festivals and carnivals throughout the year. Ponce opened its first library in 1894.
Many cultural events happen in Ponce every year:
- February – Ponce Carnival
- March – Feria de Artesanías de Ponce (Ponce Crafts Fair)
- April – Ponce Jazz Festival
- May – Fiesta Nacional de la Danza; Barrio Playa Festival
- July – Barrio San Anton's Bomba Festival
- August – Festival Nacional de la Quenepa (National Genip Festival)
- September – Día Mundial de Ponce
- November – Discovering Our Indian Roots
- December – Patron Saint's Day Festival (Fiestas Patronales); Las Mañanitas; Children's Christmas Concert
Ponce is proud of its cultural traditions. This is clear from the "Ponce en Marcha" project, which helps preserve its heritage. The city has a deep love for art, architecture, and music.
Music: Rhythms and Famous Artists

Ponce is known for being the birthplace of popular music styles like Bomba and Plena. Barrio San Antón is especially famous for this. Every July, Ponce celebrates an annual Bomba and Plena festival with musicians and parades.
Ponce's culture is a mix of influences from Spain, Italy, France, Germany, England, and especially Taíno and African heritage. The African influences add a colorful rhythm to Ponce's music, especially in Bomba and Plena.
Many famous singers and musicians come from Ponce. These include opera singer Antonio Paoli and Salsa stars like Héctor Lavoe, Cheo Feliciano, and Ismael Quintana.
The Ponce's Carnival, which started in 1858, is the oldest in Puerto Rico. It features parades with masked characters.
The Museum of Puerto Rican Music in downtown Ponce shows the history of music on the island. Much of this music started and grew in Ponce.
The city honors its musical heroes. There is a statue of danza master Juan Morel Campos in Plaza Las Delicias. The home where Antonio Paoli was born is now a research center for Puerto Rican culture. Ponce also has a municipal band and a Youth Symphony Orchestra.
Arts: Museums and Theaters

Ponce has a long history of loving the arts, dating back to 1864 when the Teatro La Perla was built. Many famous artists in painting and sculpture were born in Ponce. The city is one of only seven cities in the Western Hemisphere that is part of the Ruta Europea del Modernisme, which promotes Art Nouveau heritage.
Today, Ponce has more museums (nine) than any other municipality in Puerto Rico. The most famous is the Museo de Arte de Ponce (MAP). It was founded in 1959 by Luis A. Ferré, a native of Ponce. The museum has the largest art collection in the Caribbean, with 4,500 pieces. It is also the only museum on the island accredited by the American Alliance of Museums.
Sports: Home of the Lions
Most of Ponce's professional sports teams are called the Leones de Ponce (Ponce Lions). The Leones de Ponce basketball team is one of the best on the island, winning 12 championships. They play at the Juan Pachín Vicéns Auditorium. The Leones de Ponce (men's) and Leonas de Ponce (women's) baseball teams have also been very successful. They play at the Francisco Montaner Stadium.
In 1993, Ponce hosted the 1993 Central American and Caribbean Games.
The city also hosts two international sports events every year. In May, it has the Ponce Grand Prix, a track and field event. In September, during Memorial Day Weekend, it hosts Cruce a Nado Internacional, a swimming competition. The Ponce Marathon also takes place every December.
The Francisco "Pancho" Coimbre Sports Museum honors Puerto Rico's great athletes. It is named after the famous baseball player.
The main annual sports events are:
- April – Las Justas – intercollegiate sports competition
- May – Ponce Grand Prix – international track and field competition
- August – Cruce a Nado Internacional – international swimming competition
- December – Maratón La Guadalupe – a 26-mile national marathon
Recreation: Parks and Beaches

Ponce has many parks and beaches for fun and relaxation. Popular parks include the Julio Enrique Monagas Family Park and the Dora Colón Clavell Urban Park. There are also many public tennis and basketball courts.
The municipality has 40 beaches! Twenty-eight are on the mainland, and 12 are on Caja de Muertos Island. Some of the most popular are El Tuque Beach and La Guancha Beach. You can take a ferry from La Guancha to reach the beautiful beaches on Caja de Muertos.
Religion: A Mix of Faiths
During and after the Spanish colonization, the Roman Catholic Church was the main religion. African slaves were converted to Christianity, but they also kept many of their own traditions. The Ponce Cathedral, built in 1839, is a historic Catholic church.
The Royal Decree of Graces of 1815 allowed non-Catholics to move to Puerto Rico. However, they had to promise to support the Catholic Church. Ponce was the first city in Puerto Rico where Protestant churches were built.

When the U.S. took over in 1898, the religious landscape changed a lot. Protestant missionaries arrived, and many new churches were built. Today, Ponce is home to many different faiths, including Protestants, Catholics, and Muslims. Catholicism is still the most common faith among ponceños.
Economy of Ponce: Industry, Agriculture, and Trade
For a long time, Ponce's economy relied mostly on the sugarcane industry. But since the 1950s, the city's economy has become more diverse. Today, it focuses on manufacturing, retail, and tourism.
A huge new port, called the mega port, is being built. It is expected to create many jobs and boost the economy. Farming, retail sales, and services are also important parts of Ponce's economy. The city is a center for agriculture, trade, and distribution. Its factories make electronics, communication equipment, food products, medicines, and rum.
Manufacturing: Making Products in Ponce
Ponce is one of the most developed municipalities in Puerto Rico. Its factories produce many different goods. These include electronic and electrical equipment, communication devices, and processed foods. They also make medicines, concrete, and scientific tools.
Ponce is home to the Destilería Serrallés rum distillery, which makes Don Q rum. Industrias Vassallo is another important local company that makes PVC products. Other major manufacturers include Ponce Cement and Rovira Biscuits Corporation.
Agriculture: From Coffee to Fruits
In farming, coffee is the most important product in Ponce. Other important crops include plantains, bananas, oranges, and grapefruits. Cafe Rico, a coffee company, has its headquarters in Ponce.
Retail: Shopping in the City
For many years, shopping in Ponce happened mostly around Paseo Atocha. Today, most shopping takes place in one of Ponce's many malls. Plaza del Caribe is a very popular shopping center. Centro del Sur Mall and Ponce Mall are also important retail areas.
Mega Port: A Hub for Shipping
Ponce has Puerto Rico's main Caribbean port, the Port of Ponce. This port is being expanded to become a huge international shipping center called the Port of the Americas. When it's fully ready, it is expected to create 100,000 jobs.
Demographics: Who Lives in Ponce?
| Population During Spanish Colonial Times | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1765 | 3,314 | — |
| 1776 | 5,674 | +71.2% |
| 1800 | 7,234 | +27.5% |
| 1824 | 9,878 | +36.5% |
| 1828 | 14,927 | +51.1% |
| 1836 | 16,970 | +13.7% |
| 1846 | 21,799 | +28.5% |
| 1857 | 20,205 | −7.3% |
| 1860 | 28,156 | +39.4% |
| 1876 | 33,514 | +19.0% |
| 1887 | 42,388 | +26.5% |
| 1897 | 49,000 | +15.6% |
| Sources: Govt of Ponce and Freepages | ||
| Population During U.S. Colonial Times | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1900 | 55,477 | — |
| 1910 | 63,444 | +14.4% |
| 1920 | 71,426 | +12.6% |
| 1930 | 87,604 | +22.7% |
| 1940 | 105,116 | +20.0% |
| 1950 | 126,810 | +20.6% |
| 1960 | 145,586 | +14.8% |
| 1970 | 158,891 | +9.1% |
| 1980 | 189,046 | +19.0% |
| 1990 | 187,749 | −0.7% |
| 2000 | 186,475 | −0.7% |
| 2010 | 166,327 | −10.8% |
| 2020 | 137,491 | −17.3% |
| Source: | ||
| Race - Ponce, Puerto Rico - 2020 Census | ||
|---|---|---|
| Race | Population | % of Total |
| White | 26,148 | 19.0% |
| Black/Afro Puerto Rican | 18,325 | 13.3% |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 4,129 | 3.0% |
| Asian | 365 | 0.3% |
| Two or more races/Some other race | 88,524 | 64.4% |
Ponce has always been one of the most populated cities in Puerto Rico. According to the 2010 census, Ponce had 166,327 people. This makes it the third most populated municipality in Puerto Rico.
Symbols of Ponce: Flag and Coat of Arms
The municipality of Ponce has its own official flag and coat of arms.
Coat of Arms: A Symbol of History
The coat of arms for Ponce is based on an old design from 1844. It features a shield with red and black colors, like the city's flag. In the middle, there is a lion standing on a bridge. The lion represents Juan Ponce de Leon, and the waves under the bridge symbolize the Rio Portugues, where the city began.
Above the shield is a golden wall with five towers. This represents the Spanish crown that gave Ponce its city status. On the sides, there's a coffee tree branch and a sugarcane stalk. These show the important role of agriculture in Ponce's early economy.
Flag: Two Designs for the City
Ponce has two official flags. The first, called "the 1692 flag," was adopted in 1967. It has a diagonal line dividing it into a black top triangle and a red bottom triangle. It shows a lion over a bridge and the words "Ponce 1692." The last Sunday in April is "Ponce Flag Day."
Ten years later, in 1977, a new flag was created to celebrate 100 years since Ponce became a city. This "1877 city flag" also has a diagonal line, but the top triangle is red and the bottom is black. In the center, it has the city's shield with "PONCE" above it and "1877" below.
Municipal Services: Keeping Ponce Safe and Educated
Fire Protection: Brave Firefighters

Ponce has a long history of fire protection. It had the first organized fire department in Puerto Rico. The first fire station, Parque de Bombas, still stands today as a museum.
After a big fire in 1845, a new volunteer fire fighting group was created. In 1883, the Ponce Fire Corps was reorganized with 400 firefighters. The Ponce Fire Corps Municipal Band was also formed then by Juan Morel Campos.
Major Fires and Heroes
Ponce has faced several large fires throughout its history. One major fire in 1820 almost destroyed the early settlement. Another in 1845 badly damaged the port area.

On January 25, 1899, another big fire happened. A group of firefighters, including Pedro Sabater and Rafael Rivera Esbrí, bravely fought the fire. They are remembered as heroes for saving the city. Monuments honor them in the city square and on their tombs. As a thank you, special red and black houses were built for the firefighters and their families on a street called Calle 25 de Enero (January 25th Street). These houses are still there today!
Police: Keeping the City Secure
The Ponce Municipal Police has about 500 officers. They work together with the Puerto Rico Police force to keep the city safe. The Municipal Police has its main office and several smaller stations around the city.
The Puerto Rico Police also has a regional headquarters in Ponce. They cover different areas of the city, including the historic district and coastal barrios.
There is also an FBI office in Ponce.
Education in Ponce: Learning and Growing
Ponce's first school for boys opened in 1820. Today, the city has over a hundred public and private schools. The local government is becoming more involved in public education. They are working to create the city's first free bilingual school.
Colleges and Universities: Higher Learning Opportunities
Ponce is home to several colleges and universities. These institutions offer higher education, including degrees in architecture, medicine, law, and pharmacy. Some of these include:
- Caribbean University - Ponce
- Interamerican University of Puerto Rico at Ponce
- Ponce School of Medicine
- Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico
- Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico School of Law
- Pontifical Catholic University of Puerto Rico School of Architecture
- Universidad Ana G. Méndez - Ponce
- University of Puerto Rico at Ponce
There are also technical schools like the Instituto de Banca y Comercio. Nova Southeastern University also has a pharmacy school campus in Ponce.
Transportation in Ponce: Getting Around the City
Ponce has always been an important transportation hub for Puerto Rico.
Major highways connect Ponce to other parts of the island. Puerto Rico Highway 52 goes to San Juan. PR-2 connects to the southwestern and western towns. PR-10 goes to the center and north of the island.
The city also has its own network of local highways. PR-12 runs from the Port of Ponce north through the city. PR-9 is a highway that will eventually go around most of the eastern and northern parts of the city. Ponce has 115 bridges.
Ponce's public transportation includes taxis and shared vans called públicos. Most públicos leave from the Terminal de Carros Públicos Carlos Garay downtown. In 2012, a new bus system called SITRAS started operating.
Mercedita Airport is about 3 miles east of downtown Ponce. It handles flights within Puerto Rico and international flights to the United States. It used to be a private airfield for a rum distillery.
Since 1804, Ponce has had its own port for large cargo ships. The Port of Ponce is Puerto Rico's main Caribbean port. It is being expanded to become the Port of the Americas, a major international shipping hub.
Notable People from Ponce
You can find a list of famous people from Ponce here: List of people from Ponce, Puerto Rico.
International Connections
The Dominican Republic has a consular office in Ponce.
Twin Towns – Sister Cities
Ponce is connected with:
 Zaragoza, Spain
Zaragoza, Spain
Commemorative Dates: Remembering Important Moments
These dates are special for the people of Ponce and are celebrated or remembered every year:
- January 25: El Polvorín fire. This fire is remembered with a service at the mausoleum of the Ponce firefighters.
- March 21: Ponce massacre. This event is remembered with a gathering and service at the victims' tomb.
- March 22: Abolition of slavery in Puerto Rico. This day is remembered with a memorial service at the Monumento a la abolición de la esclavitud.
- April 26 (or, last Sunday of April): Día de la Bandera Ponceña (Ponce Flag Day).
- August 12: Día de la Fundación de Ponce (Founding Date). This is often celebrated on the first Sunday of September.
- October 7: Mameyes Landslide. This tragedy is remembered with a gathering and service at the landslide site.
- December 12: Las Mañanitas. This is celebrated yearly with a pre-dawn parade, a Catholic Mass, and a town breakfast.
See also
 In Spanish: Ponce para niños
In Spanish: Ponce para niños