Belize facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Belize
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "Land of the Free"
|
|
 Location of Belize (dark green) in the Americas Location of Belize (dark green) in the Americas |
|
| Capital | Belmopan 17°15′N 88°46′W / 17.250°N 88.767°W |
| Largest city | Belize City 17°29′N 88°11′W / 17.483°N 88.183°W |
| Official languages | English |
| Vernacular language | Belizean Creole |
| Regional and minority languages | |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion
(2022)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Belizean |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Froyla Tzalam | |
| Johnny Briceño | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
| January 1964 | |
|
• Independence
|
21 September 1981 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
22,966 km2 (8,867 sq mi) (147th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.8 |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 census
|
397,483 |
|
• Density
|
17.31/km2 (44.8/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2013) | 53.1 high |
| HDI (2023) | high · 115th |
| Currency | Belize dollar ($) (BZD) |
| Time zone | UTC−06:00 (CST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/Template:Yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +501 |
| ISO 3166 code | BZ |
| Internet TLD | .bz |
Belize is a country located on the northeastern coast of Central America. It shares borders with Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also has a sea border with Honduras to the southeast. Belize is part of the wider Caribbean region. It is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Commonwealth Caribbean, which were once part of the British West Indies.
The ancient Maya civilization spread into the area of Belize between 1500 BCE and 300 CE. This civilization thrived until about 1200 CE. Europeans first arrived between 1502 and 1504 when Christopher Columbus sailed along the Gulf of Honduras. English settlers began exploring the area in 1638. Both Spain and Britain claimed the land. Britain won control after defeating the Spanish in the Battle of St. George's Caye in 1798. The area became a British colony called British Honduras in 1840, and a Crown colony in 1862. Belize gained its independence from the United Kingdom on 21 September 1981. It is the only mainland Central American country that is a Commonwealth realm. This means King Charles III is its monarch and head of state, represented by a governor-general.
Belize has many different plants and animals, both on land and in the sea. It has various ecosystems, including large coral reefs. This makes it an important part of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor, which is a vital area for wildlife globally. Belize is seen as both a Central American and Caribbean nation, with strong connections to both regions.
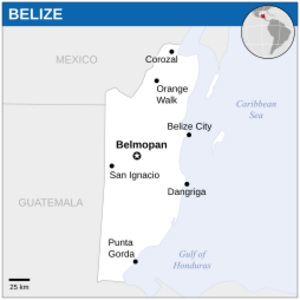
The country covers about 22,966 square kilometres (8,867 square miles). In 2022, its population was 397,483 people. The mainland is about 290 kilometres (180 miles) long and 110 kilometres (68 miles) wide. It is the least populated and least densely populated country in Central America. Its capital city is Belmopan, and its largest city is Belize City. Belize has a diverse society with many cultures and languages. It is the only Central American country where English is the official language. Belizean Creole and Spanish are also widely spoken. After these, Mayan languages and Garifuna are common. Many people in Belize speak more than one language because of the country's diverse population. Belize is known for its September Celebrations and punta music.
Contents
- What's in a Name? The Story of "Belize"
- Belize's Past: A Journey Through Time
- How Belize is Governed
- Belize's Natural World
- Belize's Economy
- People of Belize
- Belizean Culture
- Interesting Facts About Belize
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? The Story of "Belize"
The name "Belize" first appeared in a journal by a priest named Fray José Delgado in 1677. He wrote about three rivers he crossed, one of which was called Rio Balis. People think "Balis" might have come from a Mayan word belix (or beliz), meaning "muddy water," though this word isn't actually found in Mayan languages. More recently, some suggest the name comes from the Mayan phrase "bel Itza," meaning "the way to Itza."
In the 1820s, a story was made up by people in Belize that the name came from a Scottish sea adventurer named Peter Wallace. He was said to have started a settlement at the mouth of the Belize River in 1638. However, there is no proof that sea adventurers settled there, and Peter Wallace himself might be a myth. Other ideas for the name's origin include French and African roots.
Belize's Past: A Journey Through Time
Ancient Times: The Maya Civilization
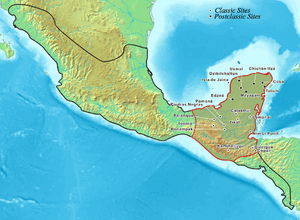
The amazing Maya civilization began over 3,000 years ago. It developed in the lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the southern highlands. This area includes parts of modern-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and western Honduras. Even after nearly 500 years of European influence, many parts of this ancient culture still exist today. Around 2500 BCE, some groups of hunters and gatherers started settling in small farming villages. They began growing crops like corn, beans, squash, and chili peppers.
Many different languages and cultures grew within the Maya civilization. Between about 2500 BCE and 250 CE, the main parts of Maya society began to form.
The Flourishing Maya in Belize
The Maya civilization spread across what is now Belize around 1500 BCE. It thrived until about 900 CE. In the central and southern parts of Belize, Caracol was a very important city. It might have been home to over 140,000 people. North of the Maya Mountains, Lamanai was the most important political center. During the late Classic Era (600–1000 CE), it's thought that between 400,000 and 1,000,000 people lived in the area of modern Belize.
When Spanish explorers arrived in the 1500s, the area of Belize had at least three different Maya territories:
- Chetumal province, near Corozal Bay.
- Dzuluinicob province, between the lower New River and the Sibun River.
- A southern territory controlled by the Manche Ch'ol Maya, between the Monkey River and the Sarstoon River.
Early European Influence (1506–1862)
Spanish explorers claimed the land as part of the Spanish Empire. However, they did not settle there because it lacked valuable resources. Also, the local tribes in Yucatán defended their land fiercely.
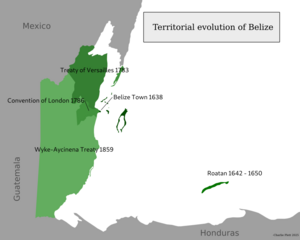
English pirates, also known as buccaneers, sometimes visited the coast of what is now Belize. They looked for a safe place to attack Spanish ships. They also came to cut logwood trees. Logwood was important because it produced a valuable dye for clothing. The first lasting British settlement was started around 1716 in the area that became the Belize District. During the 1700s, a system was set up using enslaved Africans to cut logwood trees. Spain later allowed the British settlers to stay and cut logwood if they helped stop piracy.
The British government did not officially recognize the settlement as a colony. They were afraid of making Spain angry. This lack of official control allowed the settlers to create their own laws and government. During this time, a few wealthy settlers gained control of the local government, called the Public Meeting. They also controlled most of the land and timber. Britain did not appoint its first leader for the Belize area until 1786.
Throughout the 1700s, the Spanish attacked Belize whenever they were at war with Britain. The Battle of St. George's Caye in 1798 was the last of these attacks. A Spanish fleet fought against a group of settlers, called Baymen, and their enslaved people. From September 3 to 5, the Spanish tried to get through a shallow area but were stopped. Spain's final attempt was on September 10. The Baymen pushed back the Spanish fleet in a short fight with no known deaths on either side. The anniversary of this battle is now a national holiday in Belize. It celebrates the "first Belizeans" and their defense of the territory.
British Rule (1862–1981)
In the early 1800s, the British wanted to change how the settlers lived. They threatened to stop the local government unless slavery was completely ended. After many arguments, slavery was abolished across the British Empire in 1833. Owners in British Honduras received a high amount of money for each enslaved African, but the enslaved people themselves received no compensation.
Even after slavery ended, working conditions for formerly enslaved Africans did not change much if they stayed in the timber business. Rules made it hard for them to buy land. This meant they often had to keep working in timber cutting.
In 1836, after Central American countries became free from Spanish rule, the British claimed the right to govern the region. In 1862, the United Kingdom officially declared it a British Crown Colony. It was named British Honduras and was under the control of Jamaica.
As a colony, Belize attracted British investors. One powerful British company, the Belize Estate and Produce Company, eventually owned half of all private land. This company's influence meant that the colony relied heavily on the mahogany trade for many years.
The Great Depression in the 1930s severely hurt Belize's economy. Demand for timber dropped, causing widespread unemployment. A terrible hurricane in 1931 made things even worse. People felt the government's help was not enough. The government also refused to allow labor unions or a minimum wage. Economic conditions improved during World War II as many Belizean men joined the armed forces.

After the war, the economy struggled again. Britain's decision to change the value of the British Honduras dollar in 1949 made things worse. This led to the creation of the People's Committee, which demanded independence. The People's Committee's next group, the People's United Party (PUP), pushed for changes that would allow all adults to vote. The first election where everyone could vote was held in 1954. The PUP won by a lot, and they controlled the country's politics for the next thirty years. A leader for independence, George Cadle Price, became the PUP's leader in 1956. He became the effective head of government in 1961 and held that position until 1984.
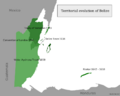
Moving towards independence was difficult because Guatemala claimed parts of Belize. In 1964, Britain gave British Honduras self-government with a new constitution. On June 1, 1973, British Honduras was officially renamed Belize.
Independent Belize (since 1981)
Belize became independent on September 21, 1981. Guatemala did not recognize the new nation because of its long-standing claim to Belizean land. After independence, about 1,500 British troops stayed in Belize to prevent any possible attacks from Guatemala.
With George Cadle Price as leader, the PUP won all national elections until 1984. In that election, the first after independence, the PUP lost to the United Democratic Party (UDP). UDP leader Manuel Esquivel became prime minister. The PUP, led by Price, returned to power after elections in 1989. The United Kingdom later announced it would end its military presence in Belize, and British soldiers left in 1994. However, the UK left a military training unit to help the new Belize Defence Force.
The UDP won power again in the 1993 national election, and Esquivel became prime minister for a second time. Border tensions with Guatemala continued into the early 2000s, though the two countries worked together in other areas.
In 1996, the Belize Barrier Reef, a beautiful natural area, was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The PUP won a big victory in the 1998 elections, and Said Musa became prime minister. He promised to improve conditions in the less developed southern part of Belize.
In 2005, there was some unrest in Belize due to unhappiness with the PUP government, including tax increases. On February 8, 2008, Dean Barrow became prime minister after his UDP won a large victory. Barrow and the UDP were re-elected in 2012 and again in November 2015.
On November 11, 2020, the People's United Party (PUP), led by Johnny Briceño, won against the United Democratic Party (UDP). Briceño became Prime Minister on November 12.
In 2023, Belize became the second Central American country to be recognized by the WHO for successfully eliminating malaria.
How Belize is Governed

Belize has a parliamentary constitutional monarchy. This means its government is based on the British system. The legal system follows the common law of England. The head of state is Charles III, the King of Belize. He lives in the United Kingdom and is represented in Belize by the governor-general. The cabinet, led by the prime minister, makes the main decisions. Cabinet ministers are usually members of the main political party in parliament.
Belize's parliament, called the National Assembly of Belize, has two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The 31 members of the House are chosen by public vote for up to five years. They create laws for Belize. The governor-general chooses the 12 members of the Senate. The Senate discusses and approves laws passed by the House.
The government and the Parliament of Belize both have the power to make laws. The constitution protects important rights like freedom of speech, press, worship, movement, and association. The courts are separate from the government and parliament.
Judges are appointed to their positions. The court system includes local Magistrates' Courts for smaller cases. The Supreme Court handles serious cases like murder. The Court of Appeal hears appeals from people who want their sentences reviewed. In some situations, cases can be appealed to the Caribbean Court of Justice.
Political Life
In 1935, elections started again, but only a small number of people could vote. In 1954, women gained the right to vote.
Since 1974, two main political parties have been strong in Belize: the People's United Party (PUP) and the United Democratic Party (UDP). Other smaller parties have also taken part in elections.
Belize's Place in the World
Belize is a full member of many international groups. These include the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organization of American States (OAS), and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). It is also part of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
The British Army has a base in Belize. It is mainly used for training soldiers in jungle warfare.
The United States (US) is a very important partner for Belize. Relations between the two countries have grown stronger since Belize's independence in 1981. The US often provides financial support to Belize. For example, in 2024, the Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC), a US government agency, helped Belize with economic growth. This program focuses on improving education and the energy sector.
The US Peace Corps also plays a big role in Belize. Since 1952, volunteers have worked in communities to improve education, economic development, and public health. These efforts help build strong connections between Belize and the US at a local level.
Belize's Military

The Belize Defence Force (BDF) is the country's military. It works with the Belize National Coast Guard and the Immigration Department. In 1997, the total strength was about 1,400 people. In 2005, the maritime part of the BDF became the Belizean Coast Guard. In 2012, Belize spent about $17 million on its military.
After Belize became independent in 1981, the United Kingdom kept a military force in the country. This was to protect Belize from any attacks by Guatemala. The main British force left in 1994, after Guatemala recognized Belize's independence. However, the UK kept a training presence until 2011.
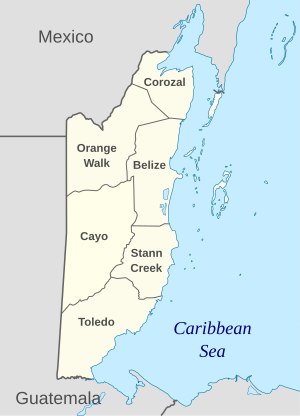
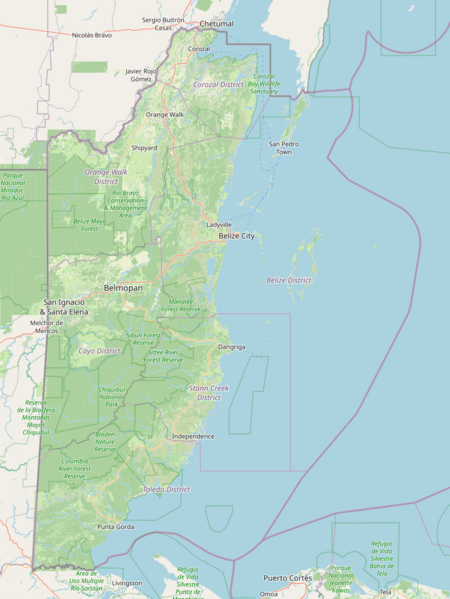
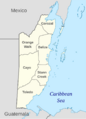
How Belize is Divided
Belize is divided into six districts. These districts are further split into 31 areas called constituencies. Local government in Belize includes city councils, town councils, village councils, and community councils. City and town councils manage urban areas, while village and community councils manage rural areas.
The Border Question with Guatemala
For a long time, Guatemala has claimed parts of Belize. Sometimes, maps made by Guatemala's government show Belize as its "twenty-third department."
Guatemala's claim covers about 53% of Belize's mainland. This includes large parts of four districts: Belize, Cayo, Stann Creek, and Toledo. About 43% of Belize's population lives in this area.
The border dispute with Guatemala is still ongoing. Guatemala's claim is partly based on a treaty from 1859. This treaty said Britain should build a road between Belize City and Guatemala. Different countries and organizations, like the United Kingdom and the Organization of American States (OAS), have tried to help solve the issue. In 2018, Guatemala held a vote to decide if the country should take its claim to the International Court of Justice (ICJ). Guatemalans voted yes. Belize held a similar vote in May 2019, and 55.4% of voters chose to send the matter to the ICJ.
Both countries have presented their cases to the ICJ. The court is now preparing for oral arguments from each country's legal teams.
Land Rights for Indigenous People
Belize supported the United Nations (UN) Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in 2007. This declaration recognized legal land rights for indigenous groups. Other court decisions have also supported these rights. For example, Belize's Supreme Court ruled in 2013 that traditional land titles are communal land for indigenous peoples. The Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ) also ordered the Belizean government in 2015 to create a land registry for Mayan lands. Despite these rulings, Belize has not made much progress in supporting the land rights of indigenous communities.
Belize's Natural World
Belize is located on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It has a border with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo to the north. To the west, it borders the Guatemalan department of Petén, and to the south, the Guatemalan department of Izabal. In the east, the Belize Barrier Reef, the second-longest barrier reef in the world, runs along much of the 386 kilometers (240 miles) of mostly marshy coastline. The total area of the country is about 22,960 square kilometers (8,860 square miles). This is a bit larger than countries like El Salvador or Wales. Many lagoons along the coasts and in the northern interior reduce the actual land area. Belize is the only Central American country without a Pacific coastline.
Belize is roughly shaped like a diamond. It stretches about 280 kilometers (170 miles) from north to south and about 100 kilometers (62 miles) from east to west. The Hondo and the Sarstoon River form much of the country's northern and southern borders. The western border does not follow natural features. It runs north-south through forests and highlands.
The north of Belize is mostly flat, swampy coastal plains, with many forests. The plants found here are very diverse for such a small area. The south has the low mountain range of the Maya Mountains. The highest point in Belize is Doyle's Delight at 1,124 meters (3,688 feet).
Protecting Nature and Wildlife
Belize has a rich variety of wildlife. This is because it is located between North and South America. It also has many different climates and habitats for plants and animals. Belize has a small human population and a lot of untouched land. This makes it a perfect home for over 5,000 species of plants and hundreds of animal species. These include armadillos, snakes, and monkeys.
The Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary is a nature reserve in south-central Belize. It was created to protect the forests, animals, and water systems of about 400 square kilometers (150 square miles) of the Maya Mountains. The reserve was started in 1990. It was the first wildlife sanctuary specifically for the jaguar. Some people consider it the best place in the world for jaguar protection.
Plants and Forests
About 56% of Belize's land is covered by forests. This was about 1,277,050 hectares in 2020. Around 20% of the country's land is used for farming and human settlements. Belize also has important mangrove ecosystems along its coast. As part of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor, Belize has rich biodiversity, both in the sea and on land.
Belize is a leader in protecting its natural resources. About 37% of Belize's land is officially protected. This gives Belize one of the largest systems of protected areas in the Americas. Also, about 13.6% of Belize's territorial waters, which include the Belize Barrier Reef, are protected. The Belize Barrier Reef is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is the second-largest barrier reef in the world, after Australia's Great Barrier Reef.
Studies have shown that Belize's forest cover has decreased over the years. However, protected areas have been very effective in saving the country's forests.
Natural Resources and Energy
Belize has some valuable minerals, but not enough to make mining a big industry. These minerals include dolomite, barite, bauxite, cassiterite, and gold. In 1990, limestone, used for building roads, was the only mineral used much.
In 2006, crude oil was found in Spanish Lookout. This brought new opportunities and challenges for the country.
Belize uses more natural resources than its land can produce. This means it has an "ecological deficit."
The Amazing Belize Barrier Reef
The Belize Barrier Reef is a chain of coral reefs along the coast of Belize. It is about 300 meters (980 feet) offshore in the north and 40 kilometers (25 miles) in the south. The Belize Barrier Reef is a 300-kilometer (190-mile) section of the larger 900-kilometer (560-mile) Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System. This makes it one of the largest coral reef systems in the world.
It is the most popular place for tourists in Belize, especially for scuba diving and snorkelling. It also plays a vital role in the country's fishing industry. In 1842, Charles Darwin called it "the most remarkable reef in the West Indies."
The Belize Barrier Reef was named a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1996. This was because it is fragile and provides important natural homes for many different living things.
Reef Life: Species
The Belize Barrier Reef is home to a huge variety of plants and animals. It is one of the most diverse ecosystems in the world:
- 70 types of hard corals
- 36 types of soft corals
- 500 species of fish
- Hundreds of invertebrate species
Scientists believe that only about 10% of all the species on the reef have been discovered so far.
Protecting the Reef
Belize was the first country in the world to completely ban bottom trawling (a type of fishing) in December 2010. In December 2015, Belize banned offshore oil drilling near the Barrier Reef and its World Heritage Sites. In 2017, Belize made history by putting an indefinite stop to offshore oil activities in its waters. This was further strengthened by a law requiring a public vote if anyone tries to lift the ban.
Despite these efforts, the reef is still threatened by ocean pollution, uncontrolled tourism, shipping, and fishing. Other dangers include hurricanes, climate change, and rising ocean temperatures, which cause coral bleaching. Scientists say that over 40% of Belize's coral reef has been damaged since 1998.
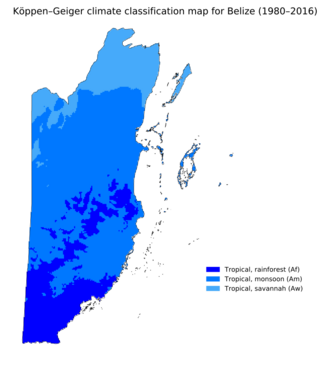
Weather and Climate
Belize has a tropical climate with clear wet and dry seasons. However, weather patterns can vary a lot by region. Temperatures change depending on how high up you are, how close you are to the coast, and the cooling effect of winds from the Caribbean. Average temperatures along the coast are around 24°C (75°F) in January and 27°C (81°F) in July. Temperatures are a bit higher inland, except in the southern highlands, where it is cooler all year. Overall, the seasons are more about differences in humidity and rainfall than in temperature.
Average rainfall varies greatly, from 1,350 millimeters (53 inches) in the north and west to over 4,500 millimeters (180 inches) in the far south. The dry season is from January to April or May in the north and central regions. It is shorter in the south, usually from February to April. A shorter, less rainy period, called the "little dry," often happens in late July or August.
Hurricanes Hurricanes have caused major damage in Belize's history. In 1931, an unnamed hurricane destroyed most of Belize City and killed over 1,000 people. In 1955, Hurricane Janet flattened the northern town of Corozal. Just six years later, Hurricane Hattie hit the central coast with very strong winds and high storm tides. Because Belize City was damaged so badly twice in 30 years, the capital was moved inland to the planned city of Belmopan.
In 1978, Hurricane Greta caused over US$25 million in damage. In 2000, Hurricane Keith caused 19 deaths and at least $280 million in damage. Soon after, in 2001, Hurricane Iris hit as a strong Category 4 storm. It destroyed most homes in the village of Monkey River Town and ruined the banana crop. In 2007, Hurricane Dean made landfall as a Category 5 storm near the Belize–Mexico border, causing widespread damage in northern Belize.
In 2010, Hurricane Richard hit Belize, causing an estimated BZ$33.8 million ($17.4 million USD) in damage, mainly to crops and homes. The most recent hurricane to hit Belize was Hurricane Lisa in 2022. Extreme weather events, like hurricanes and floods, have become more frequent and intense due to climate change.
Climate Change Belize is very vulnerable to climate change. This is because it has low-lying coastal areas, many different ecosystems, and its economy relies on tourism and farming. Belize's greenhouse gas emissions are relatively low. However, it ranks high for emissions per person. The government has promised to reach net zero emissions by 2050. It has also developed plans to become more resilient to climate change.
Belize's Economy

Belize has a small economy, mostly run by private businesses. It is mainly based on farming, industries that process farm products, and trade. Tourism and construction have become more important recently. The country also produces some industrial minerals, crude oil, and petroleum. As of 2017, oil production was about 2,000 barrels per day. In farming, sugar is still the main crop, making up almost half of all exports. The banana industry is the largest employer. In 2007, Belize became the world's third-largest exporter of papaya.
The government of Belize faces challenges to keep its economy stable. Improving tax collection has been promised. Infrastructure is a big challenge for economic growth. Belize has the most expensive electricity in the region. Trade is important, and its main trading partners are the United States, Mexico, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and CARICOM.
Belize has four main commercial banks. There are also many credit unions, which started in the 1940s.
Because of its location, Belize is a popular place for tourists. The Belize currency is linked to the US dollar. Banks in Belize allow non-residents to open accounts.
Power and Communication
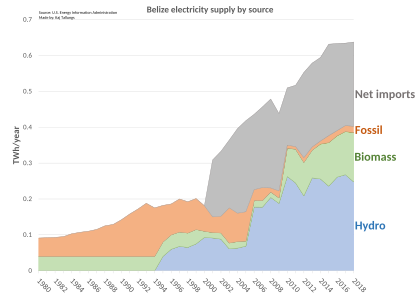
Belize Electricity Limited (BEL) is the main power company. It plans to invest $500 million to add more solar power and battery storage systems. This aims to keep electricity prices stable and reduce reliance on imported power from Mexico. The government wants 75% of electricity to come from renewable energy by 2030. As of 2022, 53% of electricity came from renewable sources.
BEL has also upgraded its power grid. In 2024, it increased the capacity of a gas turbine and installed a new one on Ambergris Caye. The World Bank is helping with a project to improve power reliability and reduce outages.
Belize Telemedia Limited (BTL), known as Digi, is the main phone and internet provider. It offers landline phones, mobile services, broadband internet, and digital television. BTL is expanding its services to improve digital connectivity across the country. It provides high-speed internet and mobile services like 4G LTE.
Tourism in Belize
Belize is a great place for tourism and ecotourism. It has a warm climate, the Belize Barrier Reef, over 450 islands (Cays), great fishing, and safe waters for boating, scuba diving, snorkelling, and freediving. There are also many rivers for rafting and kayaking. The country has many jungle and wildlife reserves for hiking, birdwatching, and helicopter tours. Plus, there are many ancient Maya sites to explore.
Developing tourism is expensive, but the government sees it as a top priority after farming. In 2012, over 917,000 tourists visited Belize.
After COVID-19 affected tourism, Belize was the first Caribbean country to allow vaccinated travelers to visit without a COVID-19 test.
People of Belize
According to the 2022 census, Belize's population is 397,483. The number of children born per woman in 2023 was 2.010. Since 1980, there has been a big change in the population. The Creole people, who used to be the majority, are now outnumbered by the Hispanic/Mestizo community. This is partly because many Creoles have moved to the United States. Also, more Mestizo babies are being born, and more people are moving to Belize from Latin America.
Different Groups of People
| Ethnic Groups in Belize | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnic Groups | percent | |||
| Hispanic/Mestizo | 51.7% | |||
| Creole | 25.2% | |||
| Maya | 9.8% | |||
| White | 4.8% | |||
| Garifuna | 4% | |||
| East Indian | 1.5% | |||
| Other | 1.2% | |||
| East Asian and Arab | 1% | |||
| Not Stated | 0.3% | |||
The Maya People
The Maya people are believed to have lived in the Yucatán region and Belize since 2000 BCE. The Classical Maya culture declined between the 7th and 9th centuries CE. This left large areas of Belize without people. Many Maya also died from internal conflicts and later from diseases brought by Europeans.
Three Maya groups live in Belize today:
- The Yucatec, who came from Yucatán, Mexico, to escape a violent war in the 1840s.
- The Mopan, who are native to Belize but were forced into Guatemala by the British. They returned to Belize to avoid being enslaved by Guatemalans in the 1800s.
- The Q'eqchi', who also fled from slavery in Guatemala in the 1800s.
These last two groups mostly live in the Toledo District. The Maya speak their native languages and Spanish. They are often also fluent in English and Belizean Creole.
Belizean Creoles
Belizean Creoles are mainly people of mixed heritage. Their ancestors include West and Central Africans brought to British Honduras (now Belize) and English and Scottish log cutters, known as the Baymen. Over time, they also mixed with people from Nicaragua, Jamaica, other Caribbean people, Mestizos, Europeans, Garifunas, and Maya.
Most Creoles can trace their family history to several of these groups. Many enslaved Africans came to British Honduras from Jamaica. It is also said that many enslaved people brought to Belize were those who caused trouble or resisted in Jamaican sugar cane plantations.
Belize Town was the center of the colony. Many enslaved people worked in the logwood and timber industries. Women and children did domestic and farm work. Enslaved people in Belize had more freedom to travel. This led to different African tribes mixing with free people of color and children of slave owners.
Some Creole communities in the Belize River Valley, like Crooked Tree and Bermudian Landings, had lighter skin and more European features.
Belizean Creoles, along with Africans and Garifuna, make up about 30% of the Afro-Belizean population. Creoles have had a big impact on Belizean history and politics. They were involved in the Battle of St. George's Caye and fought in the World Wars. They also led movements for equal rights and independence.
Creoles were the largest ethnic group in Belize until the 1980s. This changed because many Afro-Belizeans moved to the United States and other countries. Also, many Central American refugees immigrated to Belize.
The Belizean Creole Language
Creole is both an ethnic group and a language. Some people, even with light hair and eyes, identify as Creoles.
Belizean Creole or Kriol developed during the time of slavery. Historically, only formerly enslaved Africans spoke it. It has become a key part of Belizean identity. About 45% of Belizeans speak it. Belizean Creole comes mostly from English. It also has words from the Native American language Miskito, and from various West African and Bantu languages. Creoles live all over Belize, but mostly in cities like Belize City and coastal towns.
The Garinagu People

The Garinagu (one person is a Garifuna) make up about 4.5% of the population. They are a mix of West/Central African, Arawak, and Island Carib ancestors. These people were captured but were never officially recorded as slaves. One idea is that they were survivors of shipwrecks in 1635. Another is that they took over the ship they were on.
They were sometimes wrongly called "Black Caribs." When the British took over Saint Vincent and the Grenadines in 1763, they fought against French settlers and their Garinagu allies. The Garinagu eventually surrendered in 1796.
The British separated the Garifunas who looked more African from those who looked more indigenous. About 5,000 Garinagu were sent away from the island of Baliceaux. Around 2,500 of them survived the journey to Roatán, an island off Honduras. The Garifuna language is part of the Arawakan language family. It has many words borrowed from Carib languages and English.
Because Roatán was too small, the Garinagu asked the Spanish in Honduras if they could settle on the mainland coast. The Spanish used them as soldiers, and they spread along the Caribbean coast of Central America. The Garinagu settled in Seine Bight, Punta Gorda, and Punta Negra, Belize, as early as 1802. In Belize, November 19, 1832, is officially recognized as "Garifuna Settlement Day" in Dangriga.
Hispanic Belizeans
Hispanic people make up about half of Belize's population. They include two main groups: the Yucatec Mestizos and Central American refugees and migrants. Central American immigrants come from El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
The Mestizo are people of mixed Spanish and Yucatec Maya descent. They brought Catholicism and the Spanish language to Belize. They first came to Belize in 1847 to escape the Caste War in Yucatán, where many Mayas fought against the state.
The Mestizos live all over Belize, but most are in the northern districts of Corozal and Orange Walk. In the 1980s, many Central American migrants came to Belize. The Government of Belize, with help from the United Nations, welcomed neighbors fleeing civil war.
Because of the influence of Belizean Creole and English, many Mestizos speak ""Kitchen Spanish"." This is a mix of Spanish and Belize Creole. You can hear it in places like Corozal and San Pedro.
The Yucatec Mestizo culture is unique. Their food, like tamales, escabeche, and empanadas, comes from their Mexican side. Corn tortillas come from their Mayan side. Music often features the marimba. Dances at village parties include the Hog-Head and Zapateados.
Central American immigrants have greatly contributed to Belize's culture and economy. The Mestizo make up about 37% of the population, and Latin American immigrants and refugees make up about 15%. Together, Hispanic people are roughly 52% of Belize's population.
White Belizeans
White people make up about 4.8% of Belize's population. A small number are from Ireland, the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Lebanon, and other countries. Irish settlers and veterans from the Southern US states started sugar cane farms.
The largest group of White people are the German-speaking Mennonites, who make up almost four percent. They range from very traditional groups to more modern ones.

Over 13,000 Plautdietsch-speaking Mennonites live in Belize. They farm the land and live according to their religious beliefs.
These Mennonites are of German descent. They settled in the Russian Empire in the 1700s and 1800s. Many moved to Canada in the 1870s, then to Mexico in the 1920s, and to Belize after 1958. Most Russian Mennonites live in settlements like Spanish Lookout and Shipyard.
The Russian Mennonites speak Plautdietsch, a German dialect, in daily life. They use Standard German for reading the Bible and writing. Most men can also speak Spanish and English.
There are also over a thousand Pennsylvania Dutch-speaking Old Order Mennonites. They came from the United States and Canada in the late 1960s. They live mainly in Upper Barton Creek and Springfield. They look similar to Old Order Amish but are different.
East Indians
Indo-Belizeans, also called East Indian Belizeans, are citizens of Belize with Indian ancestors. In 2010, they made up 3.9% of the population. They are part of the larger Indo-Caribbean community.
East Indians started arriving in Belize after a rebellion in India in 1857. The first ship with Indians arrived in 1858 as part of a system set up by the British government after slavery ended. Many stayed to work on sugar plantations.
Indians have spread out to many villages and towns, especially in the Corozal and Toledo districts. While few descendants are of full Indian descent, many have mixed with other groups like Creoles and Mestizos.
However, they are still recognized by their appearance and are called 'Hindus' or 'East Indians'. Most of these Indians came from northern India. A smaller number came from South India. Most Indians in cities are business owners.
East Asians and Arabs
In the 1900s, more Asian settlers arrived from Mainland China, India, Syria, and Lebanon. Said Musa, whose father was from Palestine, was the Prime Minister of Belize from 1998 to 2008.
Chinese workers were brought to British Honduras in the mid-1800s as sugar cane farming grew. In 1865, 474 Chinese workers arrived. Many died or ran away, seeking safety with native peoples.
Since the 1990s, Belize has been a safe place for people of East Asian and Arab descent. Many have become part of Belizean society. Belize's program for gaining citizenship by investment was popular among Chinese migrants in the 1990s.
East Asian and Arab Belizeans mostly live in cities. They have a strong presence in retail and fast food businesses. Belizean Arabs mostly live in Belize City and on the islands. They have contributed a lot to politics and education in Belize.
Moving In and Out of Belize
Creoles and other groups are moving mostly to the United States, and also to the United Kingdom and other developed countries, looking for better opportunities. About 160,000 Belizeans live in the United States.
Because of conflicts in nearby Central American countries, many refugees from El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras have come to Belize since the 1980s. This has greatly changed the country's ethnic makeup.
The United States has given Belize aid to help fight trafficking and gang violence. Belize has also worked with the International Organization for Migration (IOM) to create a national migration policy. Most migrants entering Belize plan to cross into the US. As of 2018, migrants made up 15% of Belize's population.
Belizeans have historically moved to the US and Canada for better education, family reunions, and job opportunities. Temporary Protected Status (TPS) in the US has helped this trend. Canada's family reunion programs also help Belizean immigrants.
Belize's main economic sector is services. About 50% of migrants came from Guatemala. Most Guatemalan migrants were indigenous people like the Mopan Maya or Kekchi Maya. Many stayed in cities for jobs, while native Belizeans moved to rural areas.
Languages Spoken in Belize
| Languages in Belize | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Languages | percent | |||
| English | 80.9% | |||
| Spanish | 62.8% | |||
| Creole | 44.6% | |||
| Mayan | 10.5% | |||
| German | 4.2% | |||
| Garifuna | 2.9% | |||
| Caribbean Hindustani/Hindi | 1.9% | |||
| Chinese | 0.9% | |||
| Other | 0.9% | |||
| None | 0.2% | |||
| American Sign Language | 0.3% | |||
English is the official language of Belize. This is because it used to be a British colony. Belize is the only country in Central America with English as its official language. English is the main language used in schools, government, and most media. However, Belizean Creole is also widely spoken in many situations, from informal talks to official meetings.
When a creole language exists alongside its main language, like in Belize, they often blend together.
About 52.9% of Belizeans identify as Mestizo or Hispanic. When Belize was a British colony, Spanish was not allowed in schools. But now, it is widely spoken. ""Kitchen Spanish" is a mix of Spanish and Belize Creole. It is spoken in the northern districts, like Corozal and San Pedro.
Over half of the population speaks more than one language. This is because Belize is a small country with many different ethnic groups, surrounded by Spanish-speaking nations.
Belize is also home to three Mayan languages: Q'eqchi', Mopan (which is an endangered language), and Yucatec Maya. About 16,100 people speak the Arawakan-based Garifuna language. In the mid-1990s, about 6,900 Mennonites in Belize spoke Plautdietsch. A smaller number of Mennonites spoke Pennsylvania Dutch.
Major Cities
|
Largest cities or towns in Belize
Belize Population and Housing Census 2010 |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Belize City | 57,169 |
| 2 | San Ignacio | 17,878 |
| 3 | Belmopan | 13,939 |
| 4 | Orange Walk Town | 13,708 |
| 5 | San Pedro Town | 11,767 |
| 6 | Corozal Town | 10,287 |
| 7 | Dangriga | 9,593 |
| 8 | Benque Viejo del Carmen | 6,140 |
| 9 | Ladyville | 5,458 |
| 10 | Punta Gorda | 5,351 |
Religion in Belize
According to the 2010 census, 40.1% of Belizeans were Catholics. 31.8% were Protestants, including Pentecostals, Adventists, Anglicans, Mennonites, Baptists, Methodists, and Nazarenes. 1.7% were Jehovah's Witnesses. 10.3% followed other religions, and 15.5% said they had no religion.
Until the late 1990s, most people in Belize were Catholic. The percentage of Catholics has been decreasing as Protestant churches and other religions have grown.
There has always been a large Protestant group in Belize. It was brought by British, German, and other settlers. The Protestant community has seen a big increase in Pentecostal and Seventh-Day Adventist groups. German Mennonites mostly live in the rural areas of Cayo and Orange Walk.
The Greek Orthodox Church also has a presence in Santa Elena.
The Association of Religion Data Archives estimated that in 2005, 2.5% of Belize's population were Baháʼís. This might be the highest percentage of Baháʼís in any country. Hinduism is followed by most Indian immigrants. Belize's Muslim population started in the 1980s.
Health and Education
Belize has a number of schools, from kindergartens to universities. Most are funded by the government. Belize has about a dozen higher education institutions. The most well-known is the University of Belize. Before that, St. John's College, founded in 1877, was the main place for higher education.
Education in Belize is required for children between the ages of six and 14. As of 2010, about 79.7% of people in Belize could read and write. This is one of the lowest rates in the Western Hemisphere.
The current education plan aims to improve access, quality, and management of the education system. It also focuses on providing technical and vocational education and training.
Social Life
Belize's society has lasting differences in how wealth, power, and respect are shared. However, because Belize has a small population, the gap between rich and poor is not as wide as in some other Caribbean and Central American countries. Belize does not have the same level of class and racial conflict seen in its neighbors.
Political and economic power is held by a small group of wealthy people. The large middle group includes people from different backgrounds. This group is made up of middle-class and working-class people. They often share beliefs about education, cultural respect, and opportunities to move up in society. These beliefs help set them apart from the majority of the Belizean people.
Women in Belize
In 2021, the World Economic Forum ranked Belize 90th out of 156 countries in its Global Gender Gap Report. This report looks at how equal men and women are. Belize ranked higher in "economic participation and opportunity" and "health and survival." However, it ranked very low in "political empowerment." As of 2019, about 49.9% of women in Belize work, compared to 80.6% of men. Also, 11.1% of the seats in Belize's National Assembly are held by women.
Belizean Culture
Belizean folklore includes legends like Lang Bobi Suzi, La Llorona, La Sucia, Tata Duende, Anansi, Xtabay, Sisimite, and the cadejo.
Most of Belize's public holidays in Belize are traditional Commonwealth and Christian holidays. However, some are unique to Belizean culture, like Garifuna Settlement Day and Heroes and Benefactors' Day. The month of September is a special time of national celebration called September Celebrations. It has many events. Besides Independence Day and St. George's Caye Day, Belizeans also celebrate Carnival in September. This usually includes several events over multiple days, with the main event being the Carnival Road March. In some areas, Carnival is celebrated before Lent (in February).
Delicious Belizean Food
Belizean food is a lively mix that shows the country's many cultures. It includes flavors from Mestizo, Creole, Garifuna, Maya, and even Chinese and Indian traditions. This unique blend creates dishes that feel familiar to Central America and the Caribbean, but are also distinctly Belizean.
Breakfast is often big, with foods like bread, flour tortillas, or fry jacks (fried dough). These are usually eaten with cheese, refried beans, and eggs, along with coffee or tea. Street vendors often sell breakfast items like tacos and meat pies. The midday meal, called "dinner," is the main meal of the day. Traditional midday dishes include rice and beans (sometimes with coconut milk), stewed chicken, tamales, escabeche (an onion soup), and panades (fried corn shells with beans or fish).
In rural areas, meals often focus on local maize, beans, and squash, especially in Maya communities. Garifuna cuisine is known for its African and Caribbean roots. It uses a lot of seafood and dishes made from cassava, like ereba (cassava bread). These local ingredients and cooking styles connect deeply to the land and traditions. Belize's rich agriculture supports this food variety, offering many fresh ingredients from tropical fruits to seafood.
Belize has many affordable restaurants and fast food places. Local fruits are common, but fresh vegetables from markets are less so. Mealtime is a special time for families. Some schools and businesses close at midday for lunch.
Music and Sounds of Belize
Recently, Latin music, including reggaeton and banda, has become very popular in Belize. This is alongside traditional styles like punta and brukdown. This trend shows the influence of nearby Latin American countries and the cultural connections in the region. The growing popularity of Latin music in Belize highlights the country's lively and diverse music scene.
Punta music is clearly Caribbean. Some say it could become internationally popular, like reggae or calypso.
Brukdown is a modern Belizean music style related to calypso. It grew from the music and dance of loggers. Reggae, dance hall, and soca from Trinidad and Jamaica are also popular with young people in Belize. So are rap, hip-hop, heavy metal, and rock music from the United States.
Sports and Games
The main sports in Belize are football, basketball, volleyball, and cycling. Smaller groups follow boat racing, athletics, softball, cricket, and rugby. Fishing is also popular in coastal areas.
The Cross Country Cycling Classic is one of Belize's most important sports events. This one-day race is for amateur cyclists but is also known worldwide. The idea for this race came from a small village where people cycled long distances for cricket games.
Another big yearly sports event is the La Ruta Maya Belize River Challenge. This is a 4-day canoe marathon held every March. The race goes from San Ignacio to Belize City, covering 180 miles (290 kilometers).
On Easter day, people in Dangriga have a yearly fishing tournament. Prizes are given based on the size, type, and number of fish caught.
The Belize national basketball team is the only national team that has won major international victories. They won the 1998 CARICOM Men's Basketball Championship.
Simone Biles, who won four gold medals in the 2016 Rio Summer Olympics, is a citizen of both the United States and Belize. She considers Belize her second home.
National Symbols

The national flower of Belize is the black orchid (Prosthechea cochleata). The national tree is the mahogany tree (Swietenia macrophylla). This tree inspired the national motto, Sub Umbra Floreo, which means "Under the shade I flourish." The national ground animal is the Baird's tapir, and the national bird is the keel-billed toucan.
Interesting Facts About Belize
- It is the only Central American country where English is the official language.
- Belize is the least populated country in Central America. It also has the lowest population density.
- In 2023, Belize became the second Central American country to get a special award. This award was for getting rid of malaria. It was given by the WHO.
- Over 60% of Belize's land is covered by lush forest.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Belice para niños
In Spanish: Belice para niños
- List of Belize-related topics
- Outline of Belize
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |