Hawaii facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Hawaii
Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| State of Hawaii Mokuʻāina o Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian)
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Aloha State (official), Paradise of the Pacific, The Islands of Aloha, The 808 State
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Ua Mau ke Ea o ka ʻĀina i ka Pono
("The Life of the Land Is Perpetuated in Righteousness") |
|||
| Anthem: Hawaiʻi Ponoʻī (Hawaiʻi's Own True Sons) |
|||
Location of Hawaii within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Territory of Hawaii | ||
| Admitted to the Union | August 21, 1959 (50th) | ||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Honolulu | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Honolulu | ||
| Legislature | State Legislature | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Hawaii | ||
| U.S. senators |
|
||
| U.S. House delegation | 1: Ed Case (D) 2: Jill Tokuda (D) (list) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 10,931 sq mi (28,311 km2) | ||
| • Land | 6,423 sq mi (16,638 km2) | ||
| • Water | 4,507 sq mi (11,672 km2) 41.2% | ||
| Area rank | 43rd | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 1,522 mi (2,450 km) | ||
| • Width | n/a mi (n/a km) | ||
| Elevation | 3,030 ft (920 m) | ||
| Highest elevation
(Mauna Kea )
|
13,796 ft (4,205.0 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Pacific Ocean)
|
0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 40th | ||
| • Density | 221/sq mi (82.6/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 13th | ||
| • Median household income | $95,300 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 6th | ||
| Demonym(s) | Hawaii resident, Hawaiian | ||
| Language | |||
| • Official languages | |||
| Time zone | UTC−10:00 (Hawaii) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
HI
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-HI | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | H.I. | ||
| Latitude | 18° 55′ N to 28° 27′ N | ||
| Longitude | 154° 48′ W to 178° 22′ W | ||
| Dance | Hula |
|---|---|
| Bird | Nene |
| Fish | Humuhumunukunukuāpuaʻa |
| Flower | Pua aloalo |
| Tree | Kukui tree |
| Insect | Pulelehua |
| Sport | Heʻe nalu (surfing) |
Hawaii (pronounced huh-WY-ee) is an island state in the United States. It is located in the Pacific Ocean, about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. Hawaii is special because it is the only U.S. state not on the North American continent. It is also the only state made up entirely of islands, and the only one in the tropics.
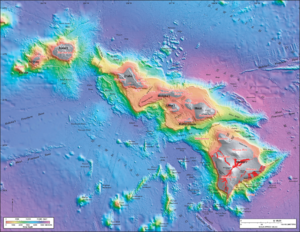
Hawaii has 137 volcanic islands. These islands make up almost the entire Hawaiian archipelago. The state stretches for 1,500 miles (2,450 km). Hawaii's coastline is the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about 750 miles (1,200 km). The eight main islands are Niʻihau, Kauaʻi, Oʻahu, Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, Maui, and Hawaiʻi. The state is named after the island of Hawaiʻi. This island is often called the "Big Island" to avoid confusion with the state. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands are part of a huge protected area. This area is called the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument. It is the largest protected area in the U.S.
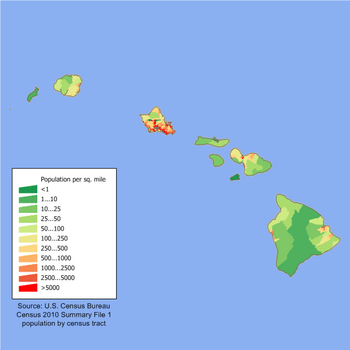
Hawaii is the eighth-smallest U.S. state by land area. It is also the 11th-least populated state. However, with 1.4 million people, it ranks 13th in population density. Most residents live on Oʻahu, where the capital city, Honolulu, is located. Hawaii is one of the most diverse states in the country. This is because of its location in the Pacific and a long history of people moving there. It has the largest Asian American population and the most people of mixed races in the U.S. Hawaii is a unique mix of North American, East Asian, and indigenous Hawaiian cultures.
Polynesians first settled Hawaii between 1000 and 1200 CE. The islands were home to many independent chiefdoms. In 1778, British explorer James Cook was the first non-Polynesian to reach the islands. Early British influence can be seen in the state flag, which has a Union Jack. Hawaii became a united kingdom in 1810. It stayed independent until American and European businessmen overthrew the monarchy in 1893. This led to Hawaii becoming part of the U.S. in 1898. As a U.S. territory, Hawaii was attacked by Japan at Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. This event brought Hawaii global importance and led to America joining World War II. Hawaii became the 50th U.S. state on August 21, 1959. In 1993, the U.S. government formally apologized for its role in the overthrow of Hawaii's government.
Hawaii's economy was once focused on large farms called plantations. Today, it is still a major farm exporter because of its rich soil and tropical climate. Since the mid-20th century, the economy has grown to include other areas. Tourism and military defense are now the two largest parts of the economy. Hawaii attracts visitors, surfers, and scientists. They come for its beautiful nature, warm climate, beaches, active volcanoes, and clear skies. Hawaii is home to the United States Pacific Fleet, the world's largest naval command. It also has 75,000 Defense Department employees. Living in Hawaii can be expensive because it is so isolated. However, Hawaii is the third-wealthiest state. Its residents also have the longest life expectancy in the U.S., at 80.7 years.
Contents
- What's in a Name? The Etymology of Hawaii
- Exploring Hawaii's Geography and Environment
- A Look at Hawaii's History
- How Hawaii's Government Works
- People and Population in Hawaii
- Hawaii's Economy and How People Live
- Hawaii's Culture and Traditions
- Tourism: A Big Part of Hawaii's Economy
- Education in Hawaii
- Transportation in Hawaii
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? The Etymology of Hawaii
The state of Hawaii gets its name from its largest island, Hawaiʻi. A common Hawaiian story says the island was named after Hawaiʻiloa, a legendary figure. He is believed to have discovered the islands when people first settled there.
The Hawaiian word Hawaiʻi is similar to an old Polynesian word, *Sawaiki. This word meant "homeland." Similar words are found in other Polynesian languages. For example, in Māori, it's Hawaiki, and in Samoan, it's Savaiʻi.
Exploring Hawaii's Geography and Environment
Hawaii is made up of eight main islands. Seven of them are inhabited, but only six are open to visitors. Niʻihau is privately owned and access is limited. It is also home to native Hawaiians. Access to the uninhabited island of Kahoʻolawe is also restricted. This island was a military base during the world wars. It might still have unexploded bombs, making it dangerous.
How Far is Hawaii from the Mainland?
The Hawaiian archipelago is about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the mainland United States. Hawaii is the southernmost U.S. state. It is the second westernmost after Alaska. Like Alaska, Hawaii does not share a border with any other U.S. state. It is the only U.S. state not in North America. It is also the only one completely surrounded by water and made entirely of islands.
Besides the eight main islands, Hawaii has many smaller islands and islets. Kaʻula is a small island near Niʻihau. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands are a group of nine small, older islands. They stretch northwest from Kauaʻi. These islands are what's left of much larger ancient volcanoes. There are also about 130 small rocks and islets across the archipelago. These are made of volcanic or ocean rock.
Hawaii's tallest mountain, Mauna Kea, is 13,796 feet (4,205 meters) above sea level. It is even taller than Mount Everest if measured from its base. Mauna Kea's base is on the floor of the Pacific Ocean. From there, it rises about 33,500 feet (10,200 meters).
How Hawaii's Volcanoes Shaped the Islands
The Hawaiian islands were formed by volcanoes. This volcanic activity started at an undersea magma source called the Hawaiʻi hotspot. The process is still creating new islands. The Earth's tectonic plate under the Pacific Ocean moves northwest. But the hotspot stays in place. This slowly creates new volcanoes. Because of the hotspot's location, all active land volcanoes are on the southern part of Hawaiʻi Island. The newest volcano, Kamaʻehuakanaloa, is off the coast of Hawaiʻi Island.
The last volcanic eruption outside Hawaiʻi Island happened at Haleakalā on Maui. This was before the late 1700s. In 1790, Kīlauea exploded. This was the deadliest eruption known in modern U.S. history. Volcanic activity and erosion have created amazing landforms. Hawaii Island has the second-highest point among all the world's islands.
Volcano slopes can be unstable. This has caused damaging earthquakes and tsunamis. Major ones happened in 1868 and 1975. Large debris avalanches on the underwater parts of the volcanoes have created steep cliffs.
Kīlauea erupted in May 2018. It opened 22 cracks, or fissure vents, on its eastern side. This eruption destroyed at least 36 buildings. The lava flows and sulfur dioxide fumes forced over 2,000 people to leave their homes.
Hawaii's Unique Plants and Animals

The Hawaiian islands are very far from other land. Scientists believe life arrived there by wind, waves, and birds. Hawaii has more endangered species than any other U.S. state. It has also lost a higher percentage of its unique species. For example, the plant Brighamia now needs people to pollinate it by hand. Its natural pollinator is believed to be gone. There are only about 120 Brighamia plants left in the wild. Biologists climb down 3,000-foot (914-meter) cliffs to help these plants make seeds.
Understanding Hawaii's Ecosystems
The main islands of Hawaii have been above the ocean for less than 10 million years. This is a short time for plants and animals to arrive and evolve. The islands are known for their diverse environments. This is due to high mountains and trade winds. Native Hawaiians developed clever ways to farm using the natural environment. Their cultural practices taught them to care for nature. This led to rich biodiversity and strong connections between people and their environment.
On a single island, the climate near the coasts can be very dry tropical. It gets less than 20 inches (500 mm) of rain each year. On the slopes, it can be a tropical rainforest. These areas get more than 200 inches (5,000 mm) of rain per year. The climate then changes to a temperate climate and even alpine conditions. Alpine areas have a cold, dry climate. The amount of rain affects how soil develops. This then impacts where streams and wetlands are found.
Protected Areas in Hawaii

Several areas in Hawaii are protected by the National Park Service. Hawaii has two national parks. Haleakalā National Park on Maui has the dormant volcano Haleakalā. Hawaii Volcanoes National Park on Hawaiʻi Island has the active volcano Kīlauea.
There are also three national historical parks. Kalaupapa National Historical Park on Molokaʻi was once a leper colony. Kaloko-Honokohau National Historical Park is in Kailua-Kona on Hawaiʻi Island. Puʻuhonua o Hōnaunau National Historical Park is an ancient place of refuge on Hawaiʻi Island's west coast. Other protected areas include the Ala Kahakai National Historic Trail and the USS Arizona Memorial at Pearl Harbor on Oʻahu.
President George W. Bush created the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in 2006. This monument covers about 140,000 square miles (360,000 km²) of reefs and ocean. It is larger than all U.S. national parks combined.
Hawaii's Climate and Weather Patterns
Hawaii has a tropical climate. Temperatures and humidity are not usually extreme. This is because of constant trade winds from the east. In summer, daytime highs reach about 88°F (31°C). Nighttime lows are around 75°F (24°C). In winter, daytime temperatures are usually around 83°F (28°C). At low elevations, they rarely drop below 65°F (18°C) at night.
Snow, which is unusual for the tropics, falls on Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa on Hawaii Island. This happens at 13,796 feet (4,205 meters) in some winter months. Snow rarely falls on Haleakalā. Mount Waiʻaleʻale on Kauaʻi gets the second-highest average annual rainfall on Earth. It receives about 460 inches (11,700 mm) per year. Most of Hawaii has only two seasons. The dry season is from May to October, and the wet season is from October to April.
Overall, Hawaii is getting drier and hotter due to climate change. The warmest temperature ever recorded in the state was 100°F (38°C). This happened in Pahala in 1931. Hawaii's record low temperature is 12°F (-11°C). This was observed in May 1979 on the summit of Mauna Kea. Hawaii is the only state that has never recorded temperatures below 0°F (-18°C).
Climates vary greatly on each island. They can be divided into windward and leeward areas. Windward sides face the clouds and get more rain.
A Look at Hawaii's History
Hawaii is one of only four U.S. states that were independent nations before becoming a state. The others were the Vermont Republic, the Republic of Texas, and the California Republic. Hawaii, along with Texas, was formally recognized by other countries as its own nation.
The Kingdom of Hawaiʻi was an independent country from 1810 until 1893. In 1893, American and European businessmen living in Hawaii overthrew the monarchy. Hawaii then became an independent republic from 1894 until August 12, 1898. On that date, it officially became a territory of the United States. Hawaii was admitted as a U.S. state on August 21, 1959.
First People: Ancient Hawaii (800–1778)
Archaeological evidence suggests that people first lived in the Hawaiian Islands around 300 CE. These were likely Polynesian settlers from the Marquesas Islands. A second group of people migrated from Raiatea and Bora Bora in the 11th century. These later immigrants may have brought new chiefs, a strict social system called kapu, and the practice of building temples called heiau.
The islands' history shows a slow but steady growth in population. The size of the chiefdoms also grew to cover entire islands. Local chiefs, called aliʻi, ruled their settlements. They also fought wars to expand their power and protect their communities. Ancient Hawaii had a caste-based society.
European Arrival and Its Impact

It is possible that Spanish explorers reached the Hawaiian Islands in the 1500s. This was 200 years before Captain James Cook's first recorded visit in 1778. Spanish records show a map with islands at Hawaii's latitude. Some scholars believe these records might describe Hawaii.
The first confirmed European contact with Hawaii was in 1778. British explorer James Cook arrived then. Cook named the islands the Sandwich Islands to honor his sponsor. Cook published the islands' location and called the native name Owyhee. This spelling is still used in Owyhee County, Idaho.
Cook visited the Hawaiian Islands twice. During his second visit in 1779, a disagreement happened. Cook's party retreated to their ship, and Cook was killed.
After Cook's visit, many European explorers, traders, and whalers came to Hawaii. They found the islands to be a good place to stop for supplies. Early British influence can be seen in the design of the flag of Hawaiʻi. It has the Union Jack in the top-left corner. These visitors brought diseases to the islands. Native Hawaiians had no protection against diseases like influenza, smallpox, and measles. By 1820, disease, hunger, and wars killed more than half of the Native Hawaiian population. In the 1850s, measles alone killed one-fifth of Hawaii's people.
The first Chinese immigrants to Hawaii arrived in 1778 with Captain Cook. More came in 1789 with an American trader. It is believed that leprosy was brought by Chinese workers by 1830. This disease also caused great harm to the Hawaiians.
The Kingdom of Hawaiʻi (1810–1893)
The Rule of the Kamehameha Family

During the late 1700s, chiefs often fought for power. After many battles, all inhabited islands were united under one ruler in 1795. This ruler became known as King Kamehameha the Great. He started the House of Kamehameha, a family line that ruled the kingdom until 1872.
When Kamehameha II became king in 1819, American Protestant missionaries arrived. They converted many Hawaiians to Christianity. They used their influence to end many traditional practices. During the rule of King Kamehameha III, Hawaii became a Christian monarchy. This happened with the signing of the 1840 Constitution. Other missionaries and their families became involved in business and politics. This led to disagreements between the monarchy and American residents.
The death of Kamehameha V in 1872 led to an election for the next king. Lunalilo was chosen, but he died the next year without naming an heir. In 1874, the election was between Kalākaua and Emma. After riots, the United States and Britain sent troops to restore order. King Kalākaua was chosen as monarch by the Legislative Assembly.
The 1887 Constitution and the Monarchy's End
In 1887, King Kalākaua was forced to sign the 1887 Constitution. This document was written by white businessmen and lawyers. It took away much of the king's power. It also made it harder for most Hawaiians and immigrant workers to vote. This favored the wealthier, white elite. Because the 1887 Constitution was signed under threat, it is known as the Bayonet Constitution. King Kalākaua, with reduced power, ruled until his death in 1891. His sister, Queen Liliʻuokalani, became the last monarch of Hawaiʻi.
In 1893, Queen Liliʻuokalani announced plans for a new constitution. On January 14, 1893, a group of mostly Euro-American business leaders formed the Committee of Safety. They planned to overthrow the kingdom and seek annexation by the United States. The U.S. Government Minister, John L. Stevens, called for U.S. Marines. These troops made it difficult for the monarchy to protect itself.
The Republic of Hawaii (1894–1898)


In January 1893, Queen Liliʻuokalani's government was overthrown. A temporary government, made of members of the American Committee of Safety, took over. American lawyer Sanford B. Dole became President of the Republic in 1894. The Queen tried to get her throne back. President Grover Cleveland's administration investigated and found the overthrow had been illegal. The U.S. government first asked for Queen Liliʻuokalani to be put back in power, but the temporary government refused.
In 1993, the U.S. Congress passed a resolution. It apologized for the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom. It also recognized that the United States had taken Hawaii unlawfully.
Becoming a U.S. Territory (1898–1959)

After William McKinley became U.S. president in 1896, people pushed to make Hawaii part of the U.S. The previous president, Grover Cleveland, was a friend of Queen Liliʻuokalani. McKinley was open to the idea. He met with people who wanted Hawaii to join the U.S. After talks, a treaty to annex Hawaii was agreed upon in 1897. However, the U.S. Senate never approved the treaty.
Despite many native Hawaiians being against it, Hawaii became a U.S. territory. This happened through the Newlands Resolution. The resolution was passed by the House of Representatives in June 1898 and by the Senate in July 1898.
In 1900, Hawaii was given self-governance. The ʻIolani Palace became the territorial capitol building. Hawaii remained a territory for sixty years, even after several attempts to become a state. Plantation owners found it useful to be a territory. This allowed them to bring in cheap labor from other countries. Such labor practices were not allowed in many states.
People from Puerto Rico started coming to Hawaii in 1899. This was after hurricanes damaged Puerto Rico's sugar industry. Hawaiian sugar plantation owners needed experienced workers. Two waves of Korean immigrants also came to Hawaii. The first was between 1903 and 1924. The second started in 1965.
Oʻahu was attacked by Imperial Japan at Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. This surprise attack brought the United States into World War II.
Becoming a State (1959–Present)
In March 1959, Congress passed the Hawaii Admission Act. U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed it into law. This act made Hawaii a state. It did not include Palmyra Atoll, which had been part of the Kingdom and Territory of Hawaii.
On June 27, 1959, Hawaii residents voted on the statehood bill. 94.3% voted in favor of becoming a state. The United Nations later removed Hawaii from its list of non-self-governing territories.
After becoming a state, Hawaii quickly modernized. There was a lot of construction. The tourism economy also grew rapidly. Later, state programs worked to promote Hawaiian culture. The 1978 Hawaii State Constitutional Convention created groups like the Office of Hawaiian Affairs. These groups help promote the indigenous language and culture.
How Hawaii's Government Works
The Hawaiian royal family moved from Hawaiʻi Island to Maui, and then to Oʻahu. This explains where the main population centers are today. Kamehameha III chose Honolulu as his capital. This was because of its natural harbor. Honolulu is now the state capital. It is located on the southeast coast of Oʻahu.
Hawaii has five counties: City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii County, Maui County, Kauai County, and Kalawao County.
Hawaii has the fewest local governments among U.S. states. Unlike most states, Hawaii does not have separate city governments. All local governments are managed at the county level. The only incorporated area is Honolulu County. This is a combined city and county government that covers all of Oʻahu. County leaders are called mayors. There are no local school districts. All public education is managed by the state's Hawaii Department of Education.
The State Government of Hawaii

Hawaii's state government is similar to the U.S. federal government. It has three branches of government: executive, legislative, and judicial. The executive branch is led by the Governor of Hawaii. The governor is helped by the Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii. Both are elected together. The governor is the only state official elected by all voters. Others are appointed by the governor. The official home of the governor is Washington Place.
The legislative branch has two parts: the Hawaii State Legislature. It includes the 51-member Hawaii House of Representatives and the 25-member Hawaii Senate. The Legislature meets at the State Capitol. Hawaii's judicial branch is the Hawaii State Judiciary. The state's highest court is the Supreme Court of Hawaii. Its chambers are in Aliiolani Hale.
Hawaii's Role in the Federal Government
Hawaii is represented in the United States Congress by two senators and two representatives.
People and Population in Hawaii
Hawaii's Population Over Time
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 84,165 | — | |
| 1860 | 69,800 | −17.1% | |
| 1890 | 89,990 | — | |
| 1900 | 154,001 | 71.1% | |
| 1910 | 191,909 | 24.6% | |
| 1920 | 255,912 | 33.4% | |
| 1930 | 368,336 | 43.9% | |
| 1940 | 423,330 | 14.9% | |
| 1950 | 499,794 | 18.1% | |
| 1960 | 632,772 | 26.6% | |
| 1970 | 768,561 | 21.5% | |
| 1980 | 964,691 | 25.5% | |
| 1990 | 1,108,229 | 14.9% | |
| 2000 | 1,211,537 | 9.3% | |
| 2010 | 1,360,301 | 12.3% | |
| 2020 | 1,455,271 | 7.0% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 1,435,138 | 5.5% | |
| 1778 (est.) = 300000, 1819 (est.) = 145000, 1835–1836 = 107954, 1872 = 56897, 1884 = 80578, 1896 = 109020 | |||
When Europeans and Americans first arrived, Hawaii's population, which was only Indigenous Hawaiians, dropped sharply. Many died from foreign diseases. The population fell from 300,000 in the 1770s to 24,000 in 1920. The population finally started to grow again after many Asian settlers arrived. They came as workers in the late 1800s.
As of 2010, about 156,000 people said they were only Native Hawaiian. Another 371,000 people said they had Native Hawaiian ancestry mixed with other races.
As of 2018, Hawaii's population was about 1,420,491. This was an increase of 60,190 people since 2010. Most of this growth came from more births than deaths. Some also came from people moving to Hawaii from other countries.
The center of Hawaii's population is on the island of O'ahu. Many Native Hawaiians have moved to Las Vegas. It is sometimes called the "ninth island" of Hawaii.
Oʻahu is the most populated island. It has the highest population density. Almost one million people live on its 597 square miles (1,546 km²). This is about 1,650 people per square mile. Hawaii's 1.4 million residents are spread across 6,000 square miles (15,500 km²) of land. This results in an average population density of 188.6 people per square mile.
People born in Hawaii in 2000 are expected to live 79.8 years on average. This is longer than the average lifespan in any other U.S. state. As of 2011, the U.S. military had 42,371 personnel on the islands.
In 2018, the top countries of origin for immigrants in Hawaii were the Philippines, China, Japan, Korea, and the Marshall Islands.
Hawaii's Diverse Ancestry
According to the 2020 U.S. Census, Hawaii's population was 1,455,271. The state's population identified as:
- 37.2% Asian
- 25.3% Multiracial
- 22.9% White
- 10.0% Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders
- 9.5% Hispanic and Latinos (of any race)
- 1.6% Black or African American
- 1.8% from some other race
- 0.3% Native American and Alaskan Native
Hawaii has the highest percentage of Asian Americans and multiracial Americans. It has the lowest percentage of White Americans of any state. It is the only state where Asian Americans are the largest ethnic group. In 2012, 14.5% of babies under age 1 were non-Hispanic white.
Hawaii's Asian population includes:
- 198,000 (14.6%) Filipino Americans
- 185,000 (13.6%) Japanese Americans
- About 55,000 (4.0%) Chinese Americans
- 24,000 (1.8%) Korean Americans
There are more than 80,000 Indigenous Hawaiians. This is 5.9% of the population. Including those with partial ancestry, Samoan Americans are 2.8% of Hawaii's population. Tongan Americans are 0.6%.
Over 120,000 (8.8%) Hispanic and Latino Americans live in Hawaii. Mexican Americans are over 35,000 (2.6%). Puerto Ricans are over 44,000 (3.2%). Multiracial Americans make up almost 25% of Hawaii's population. This is over 320,000 people. Eurasian Americans are a notable mixed-race group, numbering about 66,000 (4.9%). The non-Hispanic White population is around 310,000. This is just over 20% of the population. The multiracial population is slightly larger than the non-Hispanic white population.
The five largest European ancestries in Hawaii are German (7.4%), Irish (5.2%), English (4.6%), Portuguese (4.3%), and Italian (2.7%). About 82.2% of the state's residents were born in the United States. Roughly 75% of foreign-born residents come from Asia. Hawaii is a majority-minority state. This means that no single racial or ethnic group makes up more than 50% of the population.
The third group of foreigners to arrive in Hawaii were from China. Chinese workers on Western trading ships settled in Hawaii starting in 1789. In 1820, the first American missionaries arrived to teach Christianity and Western ways. As of 2015, a large part of Hawaii's population has Asian ancestry. This includes Filipino, Japanese, and Chinese people. Many are descendants of immigrants who came to work on sugarcane plantations in the mid-to-late 1800s. The first 153 Japanese immigrants arrived in Hawaii on June 19, 1868.
Almost 13,000 Portuguese migrants had arrived by 1899. They also worked on the sugarcane plantations. By 1901, more than 5,000 Puerto Ricans were living in Hawaii.
Languages Spoken in Hawaii

English and Hawaiian are Hawaii's official languages. This is stated in the state's 1978 constitution. However, the use of Hawaiian is limited in public acts. Hawaiʻi Creole English, often called "Pidgin," is the native language for many residents. It is a second language for many others.
As of the 2000 Census, 73.4% of Hawaii residents aged 5 and older speak only English at home. According to a 2008 survey, 74.6% of Hawaii's residents older than 5 speak only English at home. In their homes, 21.0% of residents speak an Asian language. 2.6% speak Spanish, and 1.6% speak other European languages.
After English, other widely spoken languages in the state are Tagalog, Japanese, and Ilocano. Many European immigrants and their descendants also speak their native languages. The most common are German, Portuguese, Italian, and French. 5.4% of residents speak Tagalog. 5.0% speak Japanese, and 4.0% speak Ilocano. 1.2% speak Chinese, 1.7% speak Hawaiian, 1.7% speak Spanish, 1.6% speak Korean, and 1.0% speak Samoan.
The Hawaiian Language
The Hawaiian language has about 2,000 native speakers. This is about 0.15% of the total population. According to the United States Census, there were more than 24,000 total speakers of the language in Hawaii between 2006 and 2008. Hawaiian is a Polynesian language. It belongs to the Austronesian language family. It is closely related to other Polynesian languages, like Marquesan, Tahitian, and Māori.
Before Captain James Cook arrived, the Hawaiian language had no written form. American Protestant missionaries developed a written form between 1820 and 1826. They used letters from the Latin alphabet for Hawaiian sounds. Interest in Hawaiian grew a lot in the late 20th century. With help from the Office of Hawaiian Affairs, special schools were created. In these schools, all subjects are taught in Hawaiian. The University of Hawaii also developed a Hawaiian language program for advanced studies.
Hawaiian tells the difference between long and short vowel sounds. In modern writing, a macron (kahakō) shows a long vowel. The Hawaiian language also uses the glottal stop (ʻOkina) as a consonant. It is written like an apostrophe.
Hawaiian Pidgin: A Unique Way of Speaking
Some residents of Hawaii speak Hawaiʻi Creole English (HCE). It is locally called pidgin or pidgin English. The words in HCE mainly come from English. But it also uses words from Hawaiian, Chinese, Japanese, Portuguese, Ilocano, and Tagalog. In the 1800s, more immigrants came to Hawaii. This led to the development of this mixed English language. By the early 1900s, children of pidgin speakers learned it as their first language.
HCE speakers use some Hawaiian words. Many place names are kept from Hawaiian. Some names for plants and animals are also Hawaiian. For example, tuna fish is often called ahi. HCE speakers have also changed the meanings of some English words. For example, "aunty" and "uncle" can refer to any adult friend. Or they can be used to show respect to an elder.
The grammar of HCE is different from standard American English. For example, instead of "it is hot today, isn't it?", an HCE speaker might say "stay hot, eh?". The term da kine is used as a filler word. It can replace almost any word or phrase. During the surfing boom in Hawaii, HCE was influenced by surfer slang. Some HCE phrases, like brah and da kine, have spread to other surfing communities.
Hawaiʻi Sign Language
Hawaiʻi Sign Language is a sign language for the Deaf. It is based on the Hawaiian language. It has been used in the islands since the early 1800s. However, its use is decreasing. American Sign Language is becoming more common in schools and other places.
Religion in Hawaii
Hawaii is one of the most religiously diverse states in the U.S. One in ten residents practices a non-Christian faith. Christianity is still the main religion. It is mostly represented by various Protestant groups and Roman Catholics. The second largest religion is Buddhism. It is mainly found in the Japanese community. Hawaii has a larger percentage of Buddhists than any other state. People who are not religious make up about half the population. This makes Hawaii one of the most secular states.
The Cathedral Church of Saint Andrew in Honolulu was once the main church of the Kingdom of Hawaii. The Cathedral Basilica of Our Lady of Peace and the Co-Cathedral of Saint Theresa of the Child Jesus are the main churches for the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu.
The largest Christian groups by membership in 2010 were:
- Roman Catholic Church: 249,619 members
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints: 68,128 members in 2009
- United Church of Christ: 115 churches and 20,000 members
- Southern Baptist Convention: 108 churches and 18,000 members
All non-denominational churches had 128 churches and 32,000 members.
Hawaii's Economy and How People Live
Hawaii's economy has changed over time. It was once focused on sandalwood, then whaling, then sugarcane and pineapple. Now, the military, tourism, and education are very important. By the 1840s, sugar plantations were a big part of Hawaii's economy. This was because of high demand for sugar in the U.S. and fast transport by steamships. Large sugar companies, known as "the Big Five," controlled the sugar industry.
When Hawaii was being considered for annexation in 1898, pineapple farming grew. Pineapple became the main export for Hawaii's plantation economy. Since becoming a state in 1959, tourism has been the largest industry. It made up 24.3% of the state's total economic output in 1997. The state's total economic output in 2003 was $47 billion. The average income for Hawaii residents in 2014 was $54,516. Hawaii exports include food and clothing. These industries are smaller because of the long shipping distance to markets. The state's food exports include coffee, macadamia nuts, pineapple, livestock, sugarcane, and honey.
Honey bees might be the state's most valuable export by weight. In 2012, seeds brought in $264 million and supported 1,400 workers. As of December 2015, the state's unemployment rate was 3.2%. In 2009, the U.S. military spent $12.2 billion in Hawaii. This was 18% of the state's spending that year. 75,000 U.S. Department of Defense personnel live in Hawaii.
Taxes in Hawaii
The Hawaii Department of Taxation collects taxes. Most government money comes from personal income taxes and a general excise tax (GET) on businesses. There is no statewide sales tax. Property taxes are among the lowest in the country. Many tourists visit Hawaii, and they pay taxes through the GET and a hotel room tax. However, Hawaii residents generally pay some of the highest state taxes per person in the U.S.
Some people believe Hawaii's tax burden is too high. They say it leads to higher prices and makes it hard for businesses. Former State Senator Sam Slom said Hawaii's high tax rate is because the state government handles education, health care, and social services. In most other states, these are handled by county or city governments.
The Cost of Living in Hawaii
The cost of living in Hawaii, especially Honolulu, is high compared to most major U.S. cities. However, it is 6.7% lower than New York City and 3.6% lower than San Francisco. These numbers might not include all costs. For example, flights are more expensive, and there are extra shipping fees. Many online stores do not offer free shipping to Hawaii.
Hawaiian Electric Industries provides electricity to 95% of the state. Most of this electricity comes from power plants that use fossil fuels. In October 2014, average electricity prices were almost three times the national average. They were 80% higher than in Connecticut, the state with the second-highest prices.
The average home value in Hawaii in 2000 was $272,700. The national average was $119,600. Hawaii's home values were the highest of all states. In 2010, the average sale price of a single-family home in Honolulu was $607,600. This was the highest of any U.S. city.
Hawaii's very high cost of living is due to several factors. Like other places with good weather all year, such as California, Hawaii residents might pay a "sunshine tax". Also, because Hawaii is an island, shipping goods there costs more. This problem affects many island states and territories.
The Jones Act can also increase shipping costs. This law generally requires that goods transported between places within the U.S., including Hawaii, use only U.S.-owned, built, and crewed ships. These ships are often more expensive to build and operate. This can drive up shipping costs. Hawaii relies on receiving most goods from the U.S. west coast on these ships. This may contribute to the higher cost of some goods and the overall cost of living.
Hawaii's Culture and Traditions
The original culture of Hawaii is Polynesian. Hawaii is the northernmost part of the large Polynesian Triangle in the Pacific Ocean. While traditional Hawaiian culture is still present in modern Hawaii, there are also re-enactments of old ceremonies and traditions. Some of these cultural influences, like the lūʻau and hula, are well-known in the wider United States.
Delicious Hawaiian Cuisine

The cuisine of Hawaii is a mix of many foods. These foods were brought by immigrants to the Hawaiian Islands. This includes the first Polynesians and Native Hawaiian cuisine. It also includes influences from American, Chinese, Filipino, Japanese, Korean, and Portuguese foods. Plants and animals are brought from all over the world for farming in Hawaii.
Poi, a starchy food made from pounded taro, is a traditional island food. Many local restaurants serve the popular plate lunch. This meal has two scoops of rice, macaroni salad, and various toppings. These toppings can include hamburger patties, a fried egg, and gravy (a loco moco). Other options are Japanese-style tonkatsu or traditional lūʻau favorites like kālua pork and laulau. Spam musubi is an example of how different cultures' foods mixed on the islands. In the 1990s, chefs created Hawaii regional cuisine. This is a modern mix of different flavors.
Customs and Etiquette in Hawaii
When visiting a home in Hawaii, it is polite to bring a small gift for your host. For example, a dessert is a good idea. Parties are often potlucks, where everyone brings a dish. Most local people take off their shoes before entering a home. It is a tradition for Hawaiian families to hold a luau to celebrate a child's first birthday. At Hawaiian weddings, especially Filipino weddings, the bride and groom often do a money dance. Local media and residents suggest calling non-Hawaiians "locals of Hawaii" or "people of Hawaii."
Hawaiian Mythology: Ancient Stories and Beliefs
Hawaiian mythology includes the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient Hawaiian people. It is a unique version of a larger Polynesian mythology. This unique character developed over several centuries before the 1800s. It is connected to the Hawaiian religion. This religion was officially stopped in the 1800s. However, some people have kept it alive to this day. Important figures and terms include Aumakua, the spirit of an ancestor or family god. Kāne is the highest of the four major Hawaiian deities.
Polynesian mythology refers to the oral traditions of the people of Polynesia. Polynesia is a group of islands in the Central and South Pacific Ocean. These islands are part of the Polynesian triangle. Polynesians speak languages that came from an older language called Proto-Polynesian. This language was likely spoken around Tonga and Samoa around 1000 BC.
Before the 1400s, Polynesian people traveled east to the Cook Islands. From there, they went to other island groups like Tahiti and the Marquesas. Their descendants later discovered islands like Tahiti, Rapa Nui, and later the Hawaiian Islands and New Zealand.
The Polynesian languages are part of the Austronesian language family. Many are similar enough in words and grammar to be understood by speakers of other Polynesian languages. There are also many cultural similarities among the different groups. This is especially true in how societies are organized, how children are raised, and in farming and building skills. Their mythologies also show local versions of shared stories. Polynesian cultures each have unique but related oral traditions. Legends or myths are traditionally believed to tell ancient history. They also tell about the adventures of gods ("atua") and honored ancestors.
Hawaii's State Parks: Places to Explore
There are many Hawaiian state parks.
- The Island of Hawaiʻi has state parks, recreation areas, and historical parks.
- Kauaʻi has the Ahukini State Recreation Pier, six state parks, and the Russian Fort Elizabeth State Historical Park.
- Maui has two state monuments, several state parks, and the Polipoli Spring State Recreation Area. Moloka'i has the Pala'au State Park.
- Oʻahu has several state parks, many state recreation areas, and monuments. These include the Ulu Pō Heiau State Monument.
Literature from Hawaii
The literature of Hawaii is very diverse. It includes authors like Kiana Davenport, Lois-Ann Yamanaka, and Kaui Hart Hemmings. Hawaiian magazines include Hana Hou!, Hawaii Business, and Honolulu.
The Sounds of Hawaiian Music

The music of Hawaii includes traditional and popular styles. These range from native Hawaiian folk music to modern rock and hip hop.
Styles like slack-key guitar are known worldwide. Hawaiian-influenced music is often heard in Hollywood movies. Hawaii also made a big contribution to country music by introducing the steel guitar.
Traditional Hawaiian folk music is a major part of the state's musical heritage. The Hawaiian people have lived on the islands for centuries. They have kept much of their traditional musical knowledge. Their music is often religious. It includes chanting and dance music.
Hawaiian music has had a huge impact on the music of other Polynesian islands. According to Peter Manuel, Hawaiian music has helped unite the development of modern Pacific music. Native Hawaiian musician Israel Kamakawiwoʻole was famous for his medley of "Somewhere Over the Rainbow/What a Wonderful World". He was called "The Voice of Hawaii" by NPR in 2010.
Sports in Hawaii
Because Hawaii is far from the U.S. mainland, team sports there are mostly for youth, college, and amateur teams. Some professional sports teams have played in the state. These include The Hawaiians (football), the Hawaii Islanders (baseball), and Team Hawaii (soccer).
Important college sports events in Hawaii include the Maui Invitational Tournament (basketball), Diamond Head Classic (basketball), and Hawaii Bowl (football). The only top-level college team in Hawaii is the Hawaii Rainbow Warriors and Rainbow Wahine. They compete in various conferences. There are also three teams in NCAA Division II.
Surfing has been a key part of Polynesian culture for centuries. Since the late 1800s, Hawaii has become a major place for surfers worldwide. Famous competitions include the Triple Crown of Surfing and The Eddie. Hawaii has also produced top swimmers. These include five-time Olympic medalist Duke Kahanamoku and Buster Crabbe.
Hawaii has hosted many major sports events. These include the Sony Open in Hawaii (golf), the Tournament of Champions (golf), and the Lotte Championship (golf). It also hosts the Honolulu Marathon, the Ironman World Championship triathlon, and the Ultraman triathlon. The National Football League's Pro Bowl was held in Hawaii from 1980 to 2016.
Hawaii has produced many notable Mixed Martial Arts fighters. These include former UFC champions B.J. Penn and Max Holloway. Hawaiians have also been successful in sumo wrestling. Takamiyama Daigorō was the first foreigner to win a sumo title in Japan. His student Akebono Tarō became a top-level sumo wrestler in the 1990s. Akebono was the first foreign-born Sumo wrestler to reach the highest rank, Yokozuna.
Tourism: A Big Part of Hawaii's Economy

Tourism is a very important part of Hawaii's economy. It makes up about one-quarter of the economy. In 2019, over 10 million visitors came to Hawaii. This was a 5% increase from the year before. They spent almost $18 billion. In 2019, tourism provided over 216,000 jobs across the state. It also contributed more than $2 billion in tax money. Because the weather is mild all year, tourists visit Hawaii throughout the year. In 2019, over 1 million tourists came from the U.S. East. Almost 2 million came from Japan, and nearly 500,000 from Canada.
Hawaii hosts many cultural events. The annual Merrie Monarch Festival is an international Hula competition. The Hawaii International Film Festival is the main film festival for movies from the Pacific Rim. Honolulu also hosts the state's long-running LGBT film festival, the Rainbow Film Festival.
Education in Hawaii
Public Schools in Hawaii

Hawaii has the only statewide public school system in the U.S. Decisions are made by the fourteen-member state Hawaii Board of Education. This board sets policies and hires the superintendent of schools. The superintendent oversees the Hawaii Department of Education. The Department of Education is divided into seven districts. Four are on Oʻahu, and one for each of the other three counties.
Public school test scores in Hawaii are below national averages on tests required by the No Child Left Behind Act. The Hawaii Board of Education requires all eligible students to take these tests. It also reports all student test scores. In August 2005, 185 out of 282 schools failed to meet federal minimum standards in math and reading. The ACT college placement tests show that in 2005, seniors scored slightly above the national average. However, in the SAT exams, Hawaii's college-bound seniors scored below the national average in most subjects.
The first public charter school controlled by Native Hawaiians was the Kanu O Ka Aina New Century Charter School.
Private Schools in Hawaii
Hawaii has the highest rates of private school attendance in the nation. During the 2011–2012 school year, Hawaii public and charter schools had 181,213 students. Private schools had 37,695 students. Private schools taught over 17% of students in Hawaii that year. This is almost three times the national average of about 6%. This is partly because private schools in Hawaii are relatively less expensive than those on the mainland. They also have good reputations.
Hawaii has four of the largest independent schools: ʻIolani School, Kamehameha Schools, Mid-Pacific Institute, and Punahou School. Pacific Buddhist Academy, the second Buddhist high school in the U.S., was founded in 2003.
Independent schools can choose their students. Most public schools are open to all students in their area. The Kamehameha Schools are unique in the U.S. because they openly admit students based on their ancestry. They are also one of the wealthiest schools in the world. In 2005, Kamehameha enrolled 5,398 students. This was 8.4% of the Native Hawaiian children in the state.
Colleges and Universities in Hawaii
The largest higher education institution in Hawaii is the University of Hawaiʻi System. It includes a research university at Mānoa. It also has two other campuses at Hilo and University of Hawaiʻi – West Oʻahu. There are also seven community colleges. Private universities include Brigham Young University–Hawaii, Chaminade University of Honolulu, Hawaii Pacific University, and Wayland Baptist University. Saint Stephen Diocesan Center is a seminary for the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu. Kona is home to the University of the Nations.
Transportation in Hawaii
A system of state highways circles each main island. Only Oʻahu has federal highways. It is also the only place outside the main 48 states to have Interstate highways. Narrow, winding roads and traffic in busy areas can slow things down. Each major island has a public bus system.
Honolulu International Airport (IATA: HNL) is Hawaii's main commercial aviation hub. It shares runways with the nearby Hickam Field (IATA: HIK). This airport offers flights to North America, Asia, Australia, and Oceania. Hawaiian Airlines and Mokulele Airlines use jets to fly between the large airports in Honolulu, Līhuʻe, Kahului, Kona, and Hilo. These airlines also carry cargo between the islands. On May 30, 2017, the airport was officially renamed the Daniel K. Inouye International Airport.
Before air travel began in the 1920s, private boats were the only way to travel between islands. Seaflite operated hydrofoils between the main islands in the mid-1970s.
The Hawaii Superferry ran between Oʻahu and Maui from December 2007 to March 2009. More routes were planned for other islands. Protests and legal issues about environmental impact statements stopped the service. Currently, there is a passenger ferry service in Maui County between Lānaʻi and Maui. This ferry does not carry vehicles. A passenger ferry to Molokaʻi stopped in 2016. Now, Norwegian Cruise Lines and Princess Cruises offer passenger cruise ship services between the larger islands.
Rail Systems in Hawaii
At one time, Hawaii had a network of railroads on each of the larger islands. These railroads carried farm products and passengers. Most were 3-foot (0.91 m) narrow gauge systems. The standard gauge in the U.S. is 4 feet 8.5 inches (1.435 m). The largest railroad was the Oahu Railway and Land Company (OR&L). It ran lines from Honolulu across the western and northern parts of Oahu.
The OR&L was important for moving troops and goods during World War II. Traffic on this line was busy enough to need signals for trains. It also needed wigwag signals at some crossings to protect drivers. The main line was officially closed in 1947. However, part of it was bought by the U.S. Navy and operated until 1970. 13 miles (21 km) of track remain. People who want to preserve the railway sometimes run trains on a part of this line.
Skyline is an elevated passenger rail line on Oahu. It was built to help with highway traffic. It opened for service in 2023.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hawái para niños
In Spanish: Hawái para niños