Egypt facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Arab Republic of Egypt
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Cairo 30°2′N 31°13′E / 30.033°N 31.217°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| National language | Egyptian Arabic |
| Religion | See Religion in Egypt |
| Demonym(s) | Egyptian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic under an authoritarian regime |
| Abdel Fattah el-Sisi | |
| Mostafa Madbouly | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
|
• Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt
|
c. 3150 BC |
|
• Fall of Memphis
|
343 BC |
| 639–642 | |
| 1171/4–1517 | |
|
• Muhammad Ali dynasty inaugurated
|
9 July 1805 |
| 28 February 1922 | |
|
• Revolution Day
|
23 July 1952 |
|
• Republic declared
|
18 June 1953 |
|
• Current constitution
|
18 January 2014 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,010,408 km2 (390,121 sq mi) (30th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.632 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
|
|
• 2017 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
106.20/km2 (275.1/sq mi) (106th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2019) | ▲ 31.9 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 105th |
| Currency | Egyptian pound (LE/E£/£E) (EGP) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EGY) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +20 |
| ISO 3166 code | EG |
| Internet TLD |
|
Egypt (Arabic: مصر Miṣr), officially known as the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country that connects North Africa and Western Asia. It includes the Sinai Peninsula in Asia and a large part of northeastern Africa.
Egypt is a powerful country in North Africa, the Middle East, and the Islamic world. It is also an important country worldwide. Egypt helped start the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the Arab League, the African Union, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. It is also a member of BRICS.
Contents
- History of Egypt
- What's in a Name?
- How Egypt is Governed
- Laws of the Land
- Where is Egypt?
- Geography of Egypt
- Egypt's Climate
- Amazing Wildlife
- Administrative Divisions
- Largest Cities
- Egypt's Economy
- Egypt's Population
- Religion in Egypt
- Languages Spoken
- Egyptian Culture
- National Symbols
- National Flag
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Egypt
Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country. Its story goes back thousands of years along the Nile Delta. It is seen as a "cradle of civilization" because it was one of the first places where people started writing, farming, building cities, having organized religions, and central governments. Egypt's long and rich culture is a big part of who Egyptians are today. This is because Egypt is located in a unique spot, connecting the Mediterranean Sea, the Middle East, and North Africa. Egypt was also an early and important center for Christianity. Later, in the seventh century, it became mostly Islamic.
Modern Egypt became an independent country in 1922. Before that, it was a monarchy (ruled by a king or queen) under the British Empire. After the 1952 revolution, Egypt became a republic. In 1958, it joined with Syria to form the United Arab Republic, but this union ended in 1961.
In the second half of the 1900s, Egypt faced some challenges. It had several conflicts with Israel and experienced political changes. In 1978, Egypt signed a peace agreement, recognizing Israel. After the 2011 Egyptian revolution in 2011, which led to the removal of President Hosni Mubarak, the country went through a period of political change.
What's in a Name?
The ancient Egyptians called their country
|
|
(𓆎 𓅓 𓏏𓊖) km.t. This name means "black land." It probably referred to the rich, dark soil left behind by the Nile River's floods. This was different from the deshret, or "red land," which was the desert. Another ancient name for Egypt was ⟨tꜣ-mry⟩ meaning "land of the riverbank."
How Egypt is Governed
Egypt is a semi-presidential republic. This means it has both a president and a prime minister.
The House of Representatives is where laws are made. Its members are chosen by the people and serve for five years.
Egypt has a very old tradition of having a parliament. The first people's assembly was set up in 1866.
Laws of the Land
Egypt's legal system is based on Islamic law and civil law, which is similar to the Napoleonic Code. There is also a Supreme Court that reviews laws.
Where is Egypt?
Egypt is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north. To the northeast, it shares borders with the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel. The Red Sea is to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia.
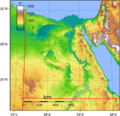
Geography of Egypt
Egypt is located mostly between 22° and 32°N latitude and 25° and 35°E longitude. It covers about 1,010,450 square kilometers, making it the 30th largest country in the world. Most of Egypt's climate is very dry. This means that almost all of the population lives along the narrow Nile Valley and its delta. About 99% of Egyptians live on only about 5.5% of the total land area.
Egypt shares borders with Libya to the west, Sudan to the south, and the Gaza Strip and Israel to the east. It is a transcontinental nation, meaning it is in both Africa and Asia. It has a land bridge called the Isthmus of Suez. This land bridge is crossed by the Suez Canal, a waterway that connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Indian Ocean through the Red Sea.
Apart from the Nile Valley, most of Egypt's land is desert. There are a few oases scattered around. Winds create many sand dunes that can be over 30 meters high. Egypt includes parts of the Sahara desert and the Libyan Desert.
The Sinai Peninsula is home to Egypt's highest mountain, Mount Catherine, which is 2,642 meters tall. The Red Sea Riviera, on the east side of the peninsula, is famous for its beautiful coral reefs and sea life.
Egypt's Climate
Most of Egypt's rain falls during the winter. South of Cairo, there is very little rain, only about 2 to 5 millimeters per year. Sometimes it doesn't rain for many years. Along a small strip of the northern coast, rainfall can be as high as 410 millimeters, mostly from October to March. Snow falls on the mountains in Sinai and in some northern coastal cities. It rarely snows in Alexandria. A very small amount of snow fell on Cairo in December 2013, which was the first time in many decades. Frost can also happen in central Sinai and central Egypt.
Egypt has a very hot, sunny, and dry climate. Average high temperatures are warm in the north but very hot in the rest of the country during summer. Cooler winds from the Mediterranean Sea blow over the northern coast. This helps keep temperatures more moderate there, especially in summer. The Khamaseen is a hot, dry wind that comes from the vast deserts in the south. It blows in the spring or early summer. It brings scorching sand and dust. It can make daytime temperatures go over 40°C and sometimes even over 50°C inland. The air can become very dry.
Before the Aswan Dam was built, the Nile River flooded every year. This flooding made Egypt's soil rich and fertile, helping farmers have good harvests year after year.
Rising sea levels due to global warming could be a problem for Egypt's crowded coastal areas. This could affect the country's economy, farming, and industries. Some experts believe that if sea levels rise a lot, millions of Egyptians might have to move from their homes by the end of the 21st century.
Amazing Wildlife
Egypt cares about its wildlife and has a plan to protect its many different species.
Scientists have recorded many types of living things in Egypt. For example, there are:
- Algae (1,483 types)
- Animals (about 15,000 types, with over 10,000 being insects)
- Fungi (over 627 types)
- Bacteria (319 types)
- Plants (2,426 types)
- Protozoans (371 types)
For some groups, like lichen-forming fungi and tiny worms called nematodes, the exact number of species is still unknown. For larger, well-studied groups like amphibians, birds, fish, mammals, and reptiles, the numbers are more certain. However, for many other groups, the number of recorded species is likely to grow as more discoveries are made in Egypt. For example, over 2,200 types of fungi have been found, and the real number is probably much higher. Also, 284 native and naturalized types of grasses have been found in Egypt.
Administrative Divisions
Egypt is divided into 27 areas called governorates. These governorates are then split into smaller regions. These regions contain towns and villages. Each governorate has a main city, which sometimes has the same name as the governorate itself.
Largest Cities
Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt. Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important place for industry and tourism on the Mediterranean coast.
Top Cities by Population
|
Largest cities or towns in Egypt
2017 census |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Cairo | 9,153,135 |
| 2 | Alexandria | 5,039,975 |
| 3 | Giza | 4,146,340 |
| 4 | Shubra El Kheima | 1,165,914 |
| 5 | Port Said | 751,073 |
| 6 | Suez | 660,592 |
| 7 | Mansoura | 548,259 |
| 8 | El Mahalla El Kubra | 522,799 |
| 9 | Tanta | 508,754 |
| 10 | Faiyum | 475,139 |
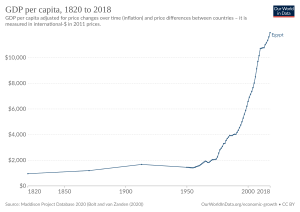
Egypt's Economy
Egypt is a developing country with a varied economy. It is the third-largest economy in Africa.
Egypt's economy mainly relies on farming, media, oil exports, natural gas, and tourism. Also, more than three million Egyptians work in other countries. The completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1970 and the creation of Lake Nasser changed how the Nile River affects Egypt's farming and environment. A fast-growing population and limited arable land (land that can be farmed) continue to put pressure on Egypt's resources and economy.
Tourism in Egypt

Tourism is one of the most important parts of Egypt's economy. In 2008, over 12.8 million tourists visited Egypt, bringing in almost $11 billion. The tourism industry employs about 12% of Egypt's workers.
The Giza Necropolis, with its famous pyramids, is one of Egypt's best-known tourist spots. It is the only one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World that is still standing today.
Egypt's beaches along the Mediterranean and Red Sea are also popular. They stretch for over 3,000 kilometers. Places like the Gulf of Aqaba beaches, Safaga, Sharm el-Sheikh, Hurghada, Luxor, Dahab, Ras Sidr, and Marsa Alam are favorite destinations for tourists.
Energy Sources
Egypt has a well-developed energy market that uses coal, oil, natural gas, and hydro power (energy from water). There are large coal deposits in the northeast Sinai, and about 600,000 tons are mined each year. Oil and gas are found in the western desert, the Gulf of Suez, and the Nile Delta. Egypt has huge reserves of gas, estimated at 2,180 cubic kilometers.
Egypt produces its own energy. However, it has been importing oil since 2008 and is quickly becoming a country that imports natural gas.
Egypt is currently building its first nuclear power plant in El Dabaa. This project is being built with $25 billion in funding from Russia.
Getting Around: Transport
Transportation in Egypt is mostly centered around Cairo and follows where people live along the Nile River. The main railway line, which is 40,800 kilometers long, runs from Alexandria to Aswan. It is run by Egyptian National Railways. The road network has grown quickly to over 21,000 miles. It covers the Nile Valley and Delta, the Mediterranean and Red Sea coasts, the Sinai, and the Western oases.
The Cairo Metro has three lines that are currently working, with a fourth line planned for the future.
EgyptAir is the country's main airline and was started in 1932. It is now owned by the Egyptian government. The airline is based at Cairo International Airport and flies to over 75 places in the Middle East, Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. EgyptAir currently has 80 airplanes.
The Suez Canal
The Suez Canal is a man-made waterway in Egypt. It connects the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. It opened in November 1869 after 10 years of building. This canal allows ships to travel between Europe and Asia without having to go all the way around Africa. The northern end is Port Said, and the southern end is Port Tawfiq, near the city of Suez. Ismailia is on its west bank, about 3 miles from the halfway point.
The canal is 193.30 kilometers long, 24 meters deep, and 205 meters wide as of 2010. It has a single lane for ships, with wider areas for ships to pass each other in the Ballah By-Pass and the Great Bitter Lake. There are no locks in the canal, so seawater flows freely through it.
In August 2014, a plan was made to open a New Suez Canal. Work on this new canal was finished in July 2015. The new channel was officially opened with a ceremony on August 6, 2015.
Egypt's Population
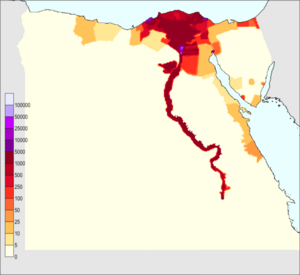
With about 100 million people, Egypt is the 14th most populated country in the world. It is also the third most populated country in Africa, after Nigeria and Ethiopia. Egypt has the largest population in the Arab world, and many people live in cities.
Most Egyptians live near the banks of the Nile River. This area is about 40,000 square kilometers and is the only place where land can be farmed. The large areas of the Sahara desert, which make up most of Egypt's land, have very few people living there. About 43% of Egyptians live in cities, mostly in the crowded areas of greater Cairo, Alexandria, and other big cities in the Nile Delta.
Religion in Egypt
Islam is the official religion of Egypt.
Languages Spoken
The official language of Egypt is Literary Arabic. The languages people speak every day include:
- Egyptian Arabic (68%)
- Sa'idi Arabic (29%)
- Eastern Egyptian Bedawi Arabic (1.6%)
- Sudanese Arabic (0.6%)
- Domari (0.3%)
- Nobiin (0.3%)
- Beja (0.1%)
- Siwi and others.
Also, Greek, Armenian, and Italian are spoken by some immigrants. More recently, African languages like Amharic and Tigrigna are also spoken by immigrants.
The main foreign languages taught in schools are English, French, German, and Italian, in order of how popular they are.
Historically, Egyptian was spoken. The latest form of this language is Coptic Egyptian. People mostly stopped speaking Coptic by the 17th century, but it might have been spoken in some isolated areas in Upper Egypt until the 1800s. It is still used as the religious language of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria. It is a separate branch within the family of Afro-Asiatic languages.
Egyptian Culture
Egypt is known for setting cultural trends in the Arabic-speaking world. Modern Arabic and Middle Eastern culture is greatly influenced by Egyptian books, music, movies, and TV shows. Egypt became a leader in the region during the 1950s and 1960s, which further boosted the importance of Egyptian culture in the Arabic-speaking world.
Egyptian identity has changed over a long time due to different influences. It now includes Islam, Christianity, and Judaism. A new language, Arabic, and its spoken form, Egyptian Arabic, which has many ancient Egyptian words, are also part of this identity.
In the early 1800s, a scholar named Rifa'a al-Tahtawi sparked new interest in Egyptian history. He also introduced ideas from the Age of Enlightenment to Egyptian society.
Egyptian Arts

The Egyptians were one of the first major civilizations to create clear rules for art and architecture. Egyptian blue, a color also known as calcium copper silicate, was used by Egyptians for thousands of years. It is thought to be the first man-made color. The paintings on walls made for the Pharaohs followed strict rules about how they looked and what they meant. Egyptian civilization is famous for its huge pyramids, temples, and large tombs.
Well-known examples include the Pyramid of Djoser, designed by the ancient architect Imhotep, the Sphinx, and the temple of Abu Simbel. Modern Egyptian art is very diverse. It includes the traditional architecture of Hassan Fathy and Ramses Wissa Wassef, the sculptures of Mahmoud Mokhtar, and the unique Coptic art of Isaac Fanous. The Cairo Opera House is the main place for performing arts in Egypt's capital.
Literature from Egypt
Egyptian literature goes back to ancient Egypt and is some of the earliest known writing. In fact, Egyptians were the first culture to develop literature as we know it today, including the book. It is a very important part of Egyptian life. Egyptian novelists and poets were among the first to try out modern styles of Arabic literature. The styles they created have been copied throughout the Arab world. The first modern Egyptian novel, Zaynab by Muhammad Husayn Haykal, was published in 1913. Egyptian novelist Naguib Mahfouz was the first Arabic-language writer to win the Nobel Prize in Literature. Egyptian women writers include Nawal El Saadawi, known for her feminist work, and Alifa Rifaat, who also writes about women and traditions.
Poetry written in everyday language is perhaps the most popular type of writing among Egyptians. Famous poets include Ahmed Fouad Negm and Salah Jahin.
Media and Movies
Egyptian media is very important throughout the Arab world. This is because many people watch it, and it has more freedom from government control. The freedom of the media is protected in the constitution, but some laws still limit this right.
Egyptian Cinema


Egyptian movies became very popular in the region when sound was added to films. In 1936, Studio Misr, funded by Talaat Harb, became the leading Egyptian movie studio. It held this role for thirty years. For over 100 years, more than 4,000 films have been made in Egypt. This is three-quarters of all movies made in the Arab world. Egypt is seen as the top country in cinema in the Arab world. Actors from all over the Arab world want to appear in Egyptian movies to become famous. The Cairo International Film Festival is ranked as one of the top 11 film festivals worldwide.
The number of movie theaters grew with talking films, reaching 395 in 1958. This number started to drop after TV began in 1960. By 1995, there were only 141 cinemas. However, new laws encouraged building private cinemas, especially in shopping centers. So, the number grew again to 200 in 2001 and 400 in 2009.
Music of Egypt
Egyptian music is a rich mix of local, Mediterranean, African, and Western styles. It has been a key part of Egyptian culture since ancient times. The ancient Egyptians believed that one of their gods, Hathor, invented music. Osiris then used music to help civilize the world. Egyptians have used musical instruments since then.
Modern Egyptian music started with artists like Abdu al-Hamuli and Mahmoud Osman. They influenced later famous musicians such as Sayed Darwish, Umm Kulthum, Mohammed Abdel Wahab, and Abdel Halim Hafez. Popular modern Egyptian pop singers include Amr Diab and Mohamed Mounir.
Egyptian Dances
Today, Egypt is often thought of as the home of belly dance. Egyptian belly dance has two main styles: raqs baladi and raqs sharqi. There are also many traditional and character dances that an Egyptian-style belly dancer might perform. Modern street dance, called shaabi, also shares some moves with raqs baladi.
Museums to Explore

Egypt has one of the oldest civilizations in the world. It has been in contact with many other civilizations and countries. It has also gone through many different time periods, from prehistoric times to the modern age, including the Pharonic, Roman, Greek, and Islamic eras. There are at least 60 museums in Egypt.

The three main museums in Egypt are The Egyptian Museum, which has over 120,000 items, the Egyptian National Military Museum, and the 6th of October Panorama.
The Grand Egyptian Museum (GEM), also known as the Giza Museum, is a new museum being built. It will hold the largest collection of ancient Egyptian artifacts in the world. It has been called the world's largest archaeological museum. The museum is located about 2 kilometers from the Giza Necropolis.
Festivals and Celebrations
Egypt celebrates many festivals and religious carnivals, also called mulid. These are usually linked to a specific Coptic or Sufi saint. However, Egyptians often celebrate them no matter their religion.
The ancient spring festival of Sham en Nisim (Ϭⲱⲙ‘ⲛⲛⲓⲥⲓⲙ shom en nisim) has been celebrated by Egyptians for thousands of years. It usually takes place between the Egyptian months of Paremoude (April) and Pashons (May), after Easter Sunday.
Delicious Cuisine

Egyptian food uses a lot of legume and vegetable dishes. While food in Alexandria and along the coast often includes fish and seafood, most Egyptian dishes are based on foods that grow from the ground. Meat has been very expensive for most Egyptians throughout history. Because of this, many vegetarian dishes have been created.
Some people consider kushari (a mix of rice, lentils, and macaroni) to be the national dish. Also, ful medames (mashed fava beans) is one of the most popular dishes. Fava beans are also used to make falafel (also known as "ta'miya"). Falafel may have started in Egypt and then spread to other parts of the Middle East. Garlic fried with coriander is added to molokhiya, a popular green soup made from finely chopped jute leaves. Sometimes chicken or rabbit is added to it.
Popular Sports

Football (soccer) is the most popular national sport in Egypt. The Cairo Derby is one of the most intense football rivalries in Africa. The BBC even called it one of the 7 toughest derbies in the world. Al Ahly is the most successful club of the 20th century in Africa, followed closely by their rivals Zamalek SC. They are known as the "African Club of the Century." With twenty titles, Al Ahly is currently the world's most successful club in terms of international trophies.
The Egypt national football team, known as the Pharaohs, has won the Africa Cup of Nations seven times. This includes winning three times in a row in 2006, 2008, and 2010. They are considered the most successful African national team and have reached the top 10 in FIFA world rankings. Egypt has qualified for the FIFA World Cup three times. Two goals from star player Mohamed Salah in their last qualifying game helped Egypt get to the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The Egyptian Youth National team won the Bronze Medal in the 2001 FIFA youth world cup in Argentina. Egypt finished 4th in the football tournament at the 1928 and 1964 Olympics.
Squash and tennis are other popular sports in Egypt. The Egyptian squash team has been very strong in international championships since the 1930s. Amr Shabana, Ali Farag, and Ramy Ashour are Egypt's best players, and all of them have been ranked as the world's number one squash player. Egypt has won the Squash World Championships five times, with the most recent title in 2019.
In 1999, Egypt hosted the IHF World Men's Handball Championship, and hosted it again in 2021. In 2001, the national handball team achieved its best result by reaching fourth place. Egypt has won the African Men's Handball Championship five times, making it the best team in Africa. It also won the Mediterranean Games in 2013, the Beach Handball World Championships in 2004, and the Summer Youth Olympics in 2010. Among all African nations, the Egypt national basketball team has the best performance record at the FIBA Basketball World Cup and at the Summer Olympics. The team has also won a record 16 medals at the FIBA Africa Championship.
Egypt has participated in the Summer Olympic Games since 1912. It has also hosted several other international sports events. These include the first Mediterranean Games in 1951, the 1991 All-Africa Games, the 2009 FIFA U-20 World Cup, and the 1953, 1965, and 2007 editions of the Pan Arab Games.
National Symbols

- The Eastern Imperial Eagle is the national animal of Egypt.
- The Egyptian lotus is the national flower of Egypt.
- The Doum palm (Hyphaene thebaica) is the national tree.
National Flag
The national flag of Egypt (علم مصر) is a tricolour flag. It has three equal horizontal stripes of red, white, and black. These colors come from the Egyptian revolutionary flag used during the 1952 Egyptian Revolution. The flag has Egypt's national symbol, the Egyptian eagle of Saladin, in the middle of the white stripe.
The red stripe stands for the blood of Egyptians shed in the fight against colonization. The white stripe symbolizes the purity of the Egyptians' hearts. The black stripe below the white represents how darkness is overcome.
The same horizontal three-color design is used by Iraq, Syria, Sudan, and Yemen. The only difference is whether they have national symbols in the white stripe.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Egipto para niños
In Spanish: Egipto para niños
- Outline of ancient Egypt
- Outline of Egypt