Chicago facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Chicago
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Etymology: Miami-Illinois: šikaakwa ('wild onion' or 'wild garlic') | |||||
| Nicknames:
The Windy City and others
|
|||||
| Mottoes:
Latin: Urbs in Horto (City in a Garden); I Will
|
|||||
| Country | |||||
| State | |||||
| Counties | Cook (small part of Chicago O'Hare Airport in DuPage) | ||||
| Settled | c. 1780 | ||||
| Incorporated (town) | August 12, 1833 | ||||
| Incorporated (city) | March 4, 1837 | ||||
| Founded by | Jean Baptiste Point du Sable | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Mayor–council | ||||
| • Body | Chicago City Council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 234.53 sq mi (607.44 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 227.73 sq mi (589.82 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 6.80 sq mi (17.62 km2) | ||||
| Elevation
(mean)
|
597.18 ft (182.02 m) | ||||
| Highest elevation
– near Blue Island |
672 ft (205 m) | ||||
| Lowest elevation
– at Lake Michigan |
578 ft (176 m) | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • City | 2,746,388 | ||||
| • Estimate
(2024)
|
2,721,308 | ||||
| • Rank | |||||
| • Density | 12,059.84/sq mi (4,656.33/km2) | ||||
| • Urban | 8,671,746 (US: 3rd) | ||||
| • Urban density | 3,709.2/sq mi (1,432.1/km2) | ||||
| • Metro | 9,408,576 (US: 3rd) | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Chicagoan | ||||
| GDP | |||||
| • Metro | $894.862 billion (2023) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−06:00 (CST) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−05:00 (CDT) | ||||
| ZIP Code prefixes |
606xx, 607xx, 608xx
|
||||
| Area codes | 312, 773, 872 | ||||
| FIPS code | 17-14000 | ||||
| GNIS feature ID | 0428803 | ||||
Chicago is the largest city in the state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With over 2.7 million people, it is the third-most populous city in the United States. Only New York City and Los Angeles have more residents. Chicago is also the main city of the larger Chicago metropolitan area, often called "Chicagoland," which is home to 9.6 million people.
Chicago is located on the shore of Lake Michigan. It became a city in 1837 near a special path that connected the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River. This location helped it grow very quickly in the mid-1800s. In 1871, a huge event called the Great Chicago Fire destroyed many parts of the city. More than 100,000 people lost their homes. But Chicago rebuilt and kept growing. The city is famous for its ideas in urban planning and amazing buildings, like the first skyscraper.
Today, Chicago is a major center for many things. These include money, culture, business, education, and transportation. O'Hare International Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world. The Chicago area also has one of the highest economic outputs of any city region globally. Chicago's economy is very diverse, meaning no single industry is too big.
Chicago is a popular place for tourists. People visit its many museums and enjoy the beaches along Lake Michigan. Chicago's culture has given a lot to the world. This includes art, books, movies, theater, comedy, food, dance, and music. Famous music styles like jazz, blues, and house music started here. The city is home to the Chicago Symphony Orchestra and the Art Institute of Chicago. Many important universities are also in the Chicago area, such as the University of Chicago and Northwestern University. Chicago also has professional teams in all major sports leagues.
Contents
- What's in a Name? Chicago's Story
- Chicago's Past: A Journey Through Time
- Chicago's Landscape: Where is it?
- People of Chicago: A Diverse Mix
- Chicago's Economy: A Hub of Activity
- Life and Culture in Chicago
- Sports in Chicago: Go Teams!
- Parks and Green Spaces: City in a Garden
- Learning in Chicago: Schools and Universities
- Chicago in the Media
- Getting Around Chicago: Transportation
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? Chicago's Story
The name Chicago comes from an old Native American word, shikaakwa. This word means "wild onion" or "wild garlic." These plants grew a lot in the area long ago. The first time the name "Checagou" was written down was around 1679. It was used by a French explorer named Robert de LaSalle.
Chicago has many fun nicknames. Some of the most famous are the Windy City, Chi-Town, and Second City.
Chicago's Past: A Journey Through Time
How Chicago Began
In the mid-1700s, the Potawatomi tribe lived in the Chicago area. They took over from other tribes like the Miami and Sauk. The first known person to settle permanently in Chicago was Jean Baptiste Point du Sable. He was a trader of African descent. He started his settlement in the 1780s and is known as the "Founder of Chicago."
In 1795, after a war, some land in Chicago was given to the U.S. for a military base. In 1803, the U.S. Army built Fort Dearborn there. This fort was later destroyed during the War of 1812 but was rebuilt. After the war, more land was given to the U.S. The Potawatomi tribe was later forced to move west of the Mississippi River.
Chicago in the 1800s
The Town of Chicago was officially started on August 12, 1833, with about 200 people. In just seven years, it grew to over 6,000 people. On March 4, 1837, Chicago became a city. For many decades, it was one of the fastest-growing cities in the world.
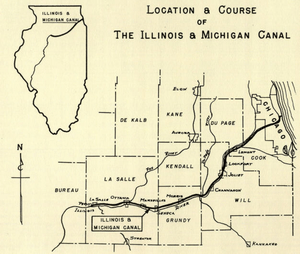
Because of its location, Chicago became a key place for transportation. It connected the eastern and western United States. The first railway, the Galena and Chicago Union Railroad, opened in 1848. The Illinois and Michigan Canal also opened that year. This canal allowed boats to travel between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River.
Chicago's growing economy attracted many new people. They came from rural areas and other countries. Manufacturing, retail, and finance became very important. The Chicago Board of Trade started in 1848. It was the first place to trade special contracts called futures.
In the 1850s, Chicago became important in national politics. Abraham Lincoln was nominated for U.S. president in Chicago in 1860. This event helped lead to the American Civil War.
To handle its fast growth, Chicago improved its systems. In 1856, the city built the first modern sewer system in the U.S. They even used jackscrews to lift many buildings higher! This helped improve health, but sewage still flowed into the Chicago River and Lake Michigan. To fix this, in 1900, engineers did an amazing thing: they reversed the flow of the Chicago River. Now, the water flows away from Lake Michigan.

In 1871, the Great Chicago Fire destroyed a large part of the city. But Chicago quickly rebuilt. From the ashes, new buildings of steel and stone rose up. In 1885, Chicago built the world's first skyscraper using a steel frame. This set a new example for building around the world.
The city grew bigger by adding many nearby towns. This happened between 1851 and 1920. People wanted to join the city because it offered better services. Many immigrants from Europe and migrants from the U.S. also moved to Chicago. By 1900, most of the people in Chicago were either foreign-born or had foreign parents.
The fast growth also led to labor conflicts. Important events like the Haymarket affair in 1886 and the Pullman Strike in 1894 happened here. People like Jane Addams and Ellen Gates Starr started Hull House in 1889. This place helped poor immigrants and became a model for social work.
Chicago also became a leader in public health. New laws improved medical care and fought diseases like cholera. The city built many large, beautiful parks with public restrooms. John H. Rauch was a key person in this. He helped create Lincoln Park and a new Chicago Board of Health.
By 1910, Chicago was the nation's railroad center. Over 20 railroads operated out of six downtown stations. In 1883, Chicago's railway managers created the standardized system of North American time zones. This system then spread across the continent.
In 1893, Chicago hosted the World's Columbian Exposition, a huge world's fair. It attracted 27.5 million visitors. The University of Chicago also moved to its current location around this time.
Chicago in the 1900s and Today
Early 1900s: Growth and Change
During World War I and the 1920s, industries in Chicago grew a lot. Many African Americans from the Southern U.S. moved to Chicago for jobs. This was part of the Great Migration. It had a big impact on Chicago's art, literature, and music. This time was called the Chicago Black Renaissance.
From 1919 to 1933, the U.S. had Prohibition. This made alcohol illegal. During this time, gangsters like Al Capone became famous in Chicago. They fought with law enforcement and each other. The famous St. Valentine's Day Massacre happened in 1929.
In the early 1920s, Chicago had tenant rent strikes. This led to new laws to protect renters. Chicago was also the first American city to have a group for homosexual rights in 1924.
The Great Depression in the 1930s caused a lot of hardship in Chicago. Many industrial jobs were lost. The city's economy suffered greatly. In 1933, Chicago Mayor Anton Cermak was hurt in a shooting that was meant for President-elect Franklin D. Roosevelt. Also in 1933 and 1934, Chicago hosted another World's Fair. This fair celebrated new technology.
Mid-1900s: War and New Leaders

During World War II, Chicago produced a huge amount of steel. It made more steel than the United Kingdom every year from 1939 to 1945. On December 2, 1942, a scientist named Enrico Fermi created the world's first controlled nuclear reaction at the University of Chicago. This was part of the secret Manhattan Project.
Richard J. Daley became mayor in 1955. He was a very powerful mayor. During his time, many big construction projects happened. These included the Willis Tower (once the world's tallest building), the University of Illinois at Chicago, and O'Hare International Airport. In the 1960s, many white residents moved from the city to the suburbs. This was called white flight.
In 1966, Martin Luther King Jr. led the Chicago Freedom Movement to fight for civil rights. Two years later, in 1968, the city hosted the 1968 Democratic National Convention. There were many protests and clashes with police during this event.
Late 1900s to Today
In 1979, Jane Byrne became Chicago's first female mayor. She helped the city's school system out of money problems. In 1983, Harold Washington became Chicago's first black mayor. He focused on helping poor neighborhoods.
Richard M. Daley, son of Richard J. Daley, became mayor in 1989. He served for a long time, improving parks and promoting green development. In 1992, a construction accident caused a major flood in downtown Chicago. Tunnels under the city filled with water, causing a lot of damage.
In 2011, Rahm Emanuel became mayor. He was followed by Lori Lightfoot in 2019. She was the city's first African American woman mayor and its first openly LGBTQ mayor. In 2023, Brandon Johnson became the 57th mayor of Chicago.
Chicago's Landscape: Where is it?
The Lay of the Land

Chicago is in northeastern Illinois, right on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan. It's the main city in the Chicago Metropolitan Area. The city sits on a continental divide, a place where water flows in different directions. This spot connects the Mississippi River and the Great Lakes. Besides Lake Michigan, two rivers, the Chicago River and the Calumet River, flow through the city.
Chicago's history and economy are closely tied to Lake Michigan. The lake also helps keep Chicago's weather milder. Waterfront areas are a bit warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
When Chicago started in 1837, most buildings were near the Chicago River. The city's land is mostly flat. The average height above sea level is about 579 feet. The lowest points are along the lake shore, and the highest is a ridge called Blue Island in the far south.
Lake Shore Drive runs along much of Chicago's waterfront. Parks like Lincoln Park, Grant Park, and Jackson Park are found here. There are 24 public beaches along 26 miles of the waterfront. Some land was even created by filling in parts of the lake. This made space for places like Navy Pier and the Museum Campus. Most of the city's tall buildings are near the water.
The term "Chicagoland" is an informal name for the entire Chicago metropolitan area. It includes the city and all its suburbs.
City Sections and Neighborhoods
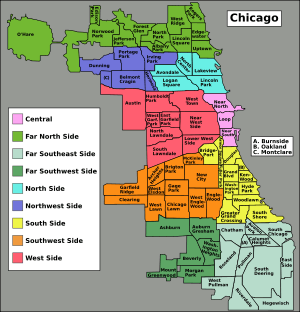
Chicago has three main sections: the North, South, and West Sides. The central business area is called the Loop. These three sides are shown by white stripes on the Flag of Chicago. The North Side is very populated with many tall buildings along the lake. The South Side is the largest part of the city. It holds most of the Port of Chicago facilities.
In the 1920s, experts divided Chicago into 77 community areas. These can be broken down further into over 200 smaller neighborhoods.
City Layout and Buildings
Chicago's streets are laid out in a grid pattern. This made it easy to develop new areas. Some diagonal streets, which were once Native American trails, also cross the city.
In 2021, Chicago was ranked the fourth-most walkable large city in the United States. Many residential streets have wide grassy areas or trees between the street and sidewalk. This keeps people walking further from traffic. Western Avenue is the longest continuous urban street in the world.
The Great Chicago Fire led to a huge building boom. In 1885, the first steel-framed high-rise building was built in Chicago. This started the skyscraper era around the world. Today, Chicago has one of the tallest and densest skylines.
Some of the tallest towers in the U.S. are in Chicago. The Willis Tower (formerly Sears Tower) is the second tallest in the Western Hemisphere. The Trump International Hotel and Tower is the third tallest in the country. Many famous architects have designed buildings in Chicago.
Chicago gave its name to the Chicago School of architecture. It was also home to the Prairie School style. You can find many types of homes and apartment buildings throughout the city. A popular tourist activity is to take a boat tour along the Chicago River to see the architecture.
Art and Monuments
Chicago is known for its outdoor public art. Many famous modern artists have works here. These include Chagall's Four Seasons, the Chicago Picasso, and Cloud Gate (also known as "The Bean"). Cloud Gate has become a symbol of the city. Some artworks also remember important events in Chicago's history. Two fountains, Crown Fountain and Buckingham Fountain, are also famous works of art.
Chicago's Weather
Chicago has a humid continental climate with four clear seasons. Summers are hot and humid, with many heat waves. Temperatures often reach 90°F (32°C). Winters are cold and snowy. January and February are the coldest months. Blizzards can happen.
Spring and autumn are mild and short. Most of Chicago's rain comes from thunderstorms. The area can have strong thunderstorms in spring and summer. These can bring large hail, strong winds, and sometimes tornadoes.
The city is usually warmer than the countryside around it, especially at night and in winter. This is called an urban heat island. Lake Michigan also helps keep the lakefront areas cooler in summer and less cold in winter.
People of Chicago: A Diverse Mix
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 4,470 | — | |
| 1850 | 29,963 | 570.3% | |
| 1860 | 112,172 | 274.4% | |
| 1870 | 298,977 | 166.5% | |
| 1880 | 503,185 | 68.3% | |
| 1890 | 1,099,850 | 118.6% | |
| 1900 | 1,698,575 | 54.4% | |
| 1910 | 2,185,283 | 28.7% | |
| 1920 | 2,701,705 | 23.6% | |
| 1930 | 3,376,438 | 25.0% | |
| 1940 | 3,396,808 | 0.6% | |
| 1950 | 3,620,962 | 6.6% | |
| 1960 | 3,550,404 | −1.9% | |
| 1970 | 3,366,957 | −5.2% | |
| 1980 | 3,005,072 | −10.7% | |
| 1990 | 2,783,726 | −7.4% | |
| 2000 | 2,896,016 | 4.0% | |
| 2010 | 2,695,598 | −6.9% | |
| 2020 | 2,746,388 | 1.9% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 2,664,452 | −1.2% | |
| United States Census Bureau 2010–2020 |
|||
For its first 100 years, Chicago was one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. In 1833, fewer than 200 people lived there. By 1890, the population was over 1 million. By the end of the 19th century, Chicago was the 5th most populous city in the world. Its population reached its highest point in 1950, with 3.6 million people.
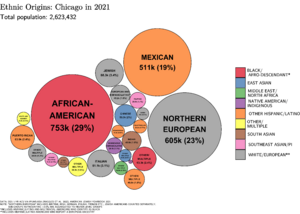
From the late 1800s, many immigrants came to Chicago. They came from Ireland, Southern, Central, and Eastern Europe. These groups formed the city's working class. Many African Americans also moved from the American South to Chicago. Chicago also has a large Bosnian population.
Most of Chicago's foreign-born residents come from Mexico, Poland, or India. Chicago's population decreased in the second half of the 20th century. But it has started to rise again in recent years.
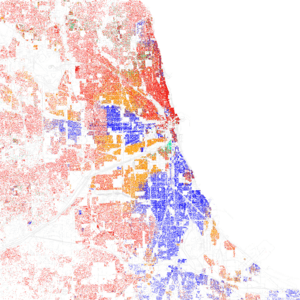
As of 2019, Chicago's largest groups are non-Hispanic White (32.8%), Blacks (30.1%), and Hispanic (29.0%).
| Racial composition | 2020 | 2010 | 1990 | 1970 | 1940 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 31.4% | 31.7% | 37.9% | 59.0% | 91.2% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 29.8% | 28.9% | 19.6% | 7.4% | 0.5% |
| Black or African American (non-Hispanic) | 28.7% | 32.3% | 39.1% | 32.7% | 8.2% |
| Asian (non-Hispanic) | 6.9% | 5.4% | 3.7% | 0.9% | 0.1% |
| Two or more races (non-Hispanic) | 2.6% | 1.3% | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Race or Ethnicity |
Race Alone | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 35.9% |
|
45.6% |
|
| Black or African American | 29.2% |
|
30.8% |
|
| Hispanic or Latino | — | 29.8% |
|
|
| Asian | 7.0% |
|
8.0% |
|
| Native American | 1.3% |
|
2.6% |
|
| Mixed | 10.8% |
|
— | |
| Other | 15.8% |
|
— | |
Chicago has one of the largest LGBT populations in the U.S. In 2012, Chicago became a "sanctuary city." This means it has policies to protect undocumented immigrants.
In 2022, the average household income in Chicago was $70,386. About 17.2% of the population lived below the poverty line.
Religion in Chicago
Religion in Chicago (2014) Protestantism (35%) Roman Catholicism (34%) Eastern Orthodoxy (1%) Jehovah's Witness (1%) No religion (22%) Judaism (3%) Islam (2%) Buddhism (1%) Hinduism (1%)
Most people in Chicago practice Christianity (71%). Roman Catholicism and Protestantism are the largest Christian groups. Chicago also has many people who follow other religions. These include Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism. Many people also say they have no religion.
Chicago is home to the main offices of several religious groups. It also has many important churches and cathedrals. The first two Parliament of the World's Religions meetings were held in Chicago. Many international religious leaders have visited the city.
Chicago's Economy: A Hub of Activity
Chicago has the third-largest economy of any city area in the United States. It is known for having a very balanced economy, meaning it's not too dependent on one type of business. Chicago is also a major center for science and engineering jobs. Many important business leaders helped build Chicago's economy.
Chicago is a big global financial center. It has the second-largest downtown business area in the U.S. The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago is located here. The city also has major financial markets, like the Chicago Stock Exchange and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.
The Chicago area has a huge number of workers, about 4.63 million. Many large companies have their headquarters in Chicago. For six years in a row (2013-2018), Chicago was ranked the top city area for companies to move to.
Manufacturing, printing, and food processing are also big parts of Chicago's economy. Many medical product companies are based here. Famous food companies like McDonald's and Kraft Heinz also have their main offices in Chicago. The city has been a retail hub for a long time.
Chicago is a major place for conventions. McCormick Place is the city's main convention center. It is the largest in the U.S. and third-largest in the world.
Life and Culture in Chicago

Chicago's location on the water and its lively nightlife attract many people. Over a third of the city's population lives in neighborhoods along the lakefront. The city has many fancy restaurants and also many areas with ethnic foods. These include Mexican, Puerto Rican, Greek, Italian, Chinese, Polish, and Korean neighborhoods.
Downtown Chicago is the center of the city's financial, cultural, and business life. This area is often called "The Loop" because of the elevated train tracks that circle it. The central area also includes the Near North Side and Near South Side. These areas have famous skyscrapers, many restaurants, shopping, and museums.

Lincoln Park has the Lincoln Park Zoo and a beautiful conservatory. The River North Gallery District has the most modern art galleries outside of New York City. Lake View is home to Boystown, a big center for LGBT nightlife and culture. The Chicago Pride Parade is held here every June.
The South Side neighborhood of Hyde Park is where former U.S. President Barack Obama lived. It also has the University of Chicago and the Museum of Science and Industry. The South Side hosts the annual Bud Billiken Parade and Picnic, a large African American parade.
The West Side has the Garfield Park Conservatory, which has many tropical plants. It also has Latino cultural spots like the Institute of Puerto Rican Arts and Culture. The University of Illinois at Chicago is on the Near West Side.
Chicago has a unique accent, often heard in movies and TV shows. It's a special way of speaking English found in cities around the Great Lakes.
Fun and Arts in Chicago

Chicago has many famous theater companies. These include the Goodman Theatre and the Steppenwolf Theatre Company. You can also see Broadway-style shows at five different theaters. Chicago is where modern improvisational theater began. Groups like The Second City are very well known.
The Chicago Symphony Orchestra (CSO) is one of the best orchestras in the world. They perform at Symphony Center. In the summer, many outdoor concerts are held in Grant Park and Millennium Park. The Lyric Opera of Chicago performs at the Civic Opera House.
Chicago is also known for its dance groups, like the Joffrey Ballet. The city has a rich history of live music. This includes Chicago blues, Chicago soul, jazz, and gospel. Chicago is the birthplace of house music and industrial music. It also has a strong hip hop scene.

Chicago has a unique fine art tradition. Many artists from Chicago are known for their figurative surrealism. Henry Darger is a famous outsider artist from Chicago.
Visiting Chicago: Tourist Fun
In 2014, Chicago attracted over 50 million visitors. These visitors spent more than $13.7 billion in the city. People love to shop along the Magnificent Mile and State Street. They also enjoy Chicago's amazing buildings and thousands of restaurants.
Chicago is the third-largest city for conventions in the U.S. Most conventions are held at McCormick Place. Navy Pier is a long pier with shops, restaurants, museums, and auditoriums. The Willis Tower is also a very popular place for tourists to visit.
Museums to Explore
Chicago has many fantastic museums. Some of the most famous are the Adler Planetarium & Astronomy Museum, the Field Museum of Natural History, and the Shedd Aquarium. These are all part of the Museum Campus. The Art Institute of Chicago is also a world-famous art museum.
Other museums include the Chicago History Museum, the DuSable Museum of African American History, the Museum of Contemporary Art, and the Museum of Science and Industry. The University of Chicago also has a museum with ancient artifacts.
Chicago's Famous Food

Chicago is known for its special foods that show its diverse roots. One of the most famous is deep-dish pizza. This thick, cheesy pizza is said to have started at Pizzeria Uno. The Chicago-style thin crust is also very popular.
The Chicago-style hot dog is another must-try. It's an all-beef hot dog loaded with toppings like pickle relish, yellow mustard, sport peppers, tomato, and a dill pickle spear. It's all on a poppy seed bun. People who love Chicago hot dogs usually don't put ketchup on them!
The Italian beef sandwich is a unique Chicago sandwich. It has thinly sliced beef cooked in its own juices. It's served on an Italian roll with sweet peppers or spicy giardiniera. Another popular choice is the Maxwell Street Polish, a grilled sausage on a hot dog bun.
Chicken Vesuvio is a tasty chicken dish with roasted potatoes. The jibarito is a sandwich that uses fried plantains instead of bread. The tradition of serving the Greek dish saganaki (flaming cheese) also started in Chicago. Chicago is also known for its Chicago-style barbecue, especially rib tips and hot links.
Many annual festivals, like Taste of Chicago, feature these famous dishes. Chicago is home to Alinea, one of the world's most highly-rated restaurants.
Chicago in Books
Chicago literature often focuses on the city itself. It tells stories about its people and places. Early writers had to find new ways to describe Chicago's fast growth.
Several periods in Chicago's history have influenced American literature. These include the time after the Great Chicago Fire, the Chicago Literary Renaissance in the 1910s, and the Great Depression era.
The famous Poetry magazine was founded in Chicago in 1912. It helped discover many important poets. The magazine was key in starting new poetry movements. In the 1980s, a modern form of poetry performance, the poetry slam, began in Chicago.
Sports in Chicago: Go Teams!

Chicago has two Major League Baseball (MLB) teams. The Chicago Cubs play at Wrigley Field on the North Side. The Chicago White Sox play at Rate Field on the South Side. The Cubs are one of the oldest MLB teams and have played in Chicago since 1871. They won the World Series in 2016, ending a very long championship drought. The White Sox have won three World Series titles.
The Chicago Bears are one of the oldest teams in the National Football League (NFL). They have won nine NFL Championships, including the 1985 Super Bowl XX. The Bears play their home games at Soldier Field.

The Chicago Bulls of the National Basketball Association (NBA) are one of the most famous basketball teams in the world. In the 1990s, led by Michael Jordan, the Bulls won six NBA championships.
The Chicago Blackhawks of the National Hockey League (NHL)] started in 1926. They are one of the "Original Six" teams. The Blackhawks have won six Stanley Cups. Both the Bulls and the Blackhawks play at the United Center.
| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Attendance | Founded | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicago Bears | NFL | Football | Soldier Field | 61,142 | 1919 | 9 Championships (1 Super Bowl) |
| Chicago Cubs | MLB | Baseball | Wrigley Field | 41,649 | 1870 | 3 World Series |
| Chicago White Sox | MLB | Baseball | Rate Field | 40,615 | 1900 | 3 World Series |
| Chicago Blackhawks | NHL | Ice hockey | United Center | 21,653 | 1926 | 6 Stanley Cups |
| Chicago Bulls | NBA | Basketball | 20,776 | 1966 | 6 NBA Championships | |
| Chicago Fire | MLS | Soccer | Soldier Field | 17,383 | 1997 | 1 MLS Cup, 1 Supporters Shield |
| Chicago Sky | WNBA | Basketball | Wintrust Arena | 10,387 | 2006 | 1 WNBA Championships |
| Chicago Red Stars | NWSL | Soccer | SeatGeek Stadium | 5,863 | 2013 | 1 WPSL Elite championship |
Chicago Fire FC is the city's professional soccer team. They play in Major League Soccer (MLS). The Chicago Red Stars are a women's professional soccer team. The Chicago Sky is a professional women's basketball team.

The Chicago Marathon is held every year and is one of the six major marathons in the world. Many colleges in the Chicago area also have Division I sports teams.
Parks and Green Spaces: City in a Garden
Chicago's motto is Urbs in Horto, which means "City in a Garden" in Latin. The Chicago Park District manages over 570 parks. These parks cover more than 8,000 acres of land. They include 31 sand beaches, many museums, and nature areas. Lincoln Park is the city's largest park. It gets over 20 million visitors each year.
Chicago has a historic boulevard system. This is a network of wide, tree-lined streets that connect many of the city's parks. This system was started in 1869. Many neighborhoods grew along these boulevards.
The Chicago Park District also runs the nation's largest system of municipal harbors for boats. In recent years, new parks have been added. These include Ping Tom Memorial Park and Millennium Park. Millennium Park is in the corner of one of Chicago's oldest parks, Grant Park.
The Cook County Forest Preserves add even more green space. These natural areas are just outside the city. They include the Chicago Botanic Garden and the Brookfield Zoo. Washington Park is another large park in the city.
Learning in Chicago: Schools and Universities
Schools and Libraries

Chicago Public Schools (CPS) runs over 600 public elementary and high schools. This includes special selective-admission schools for advanced students. CPS is the third-largest school district in the U.S.
Chicago also has many private schools. These include religious schools and secular schools. The Chicago Public Library system has a central library and 77 neighborhood branches. The central Harold Washington Library is one of the largest public library buildings in the world.
Colleges and Universities

Since the 1850s, Chicago has been a world center for higher education. Many universities here are ranked among the top in the United States. These include the University of Chicago, Northwestern University, Illinois Institute of Technology, Loyola University Chicago, and DePaul University.
Other notable schools include Columbia College Chicago and the University of Illinois Chicago. Chicago also has many community colleges, like the seven City Colleges of Chicago. The city is also home to many graduate schools and seminaries.
Chicago in the Media
The Chicago area is a major media hub. It is the third-largest media market in the United States. All the big U.S. television networks have stations in Chicago.
Chicago has also been home to many famous talk shows. These include The Oprah Winfrey Show and The Jerry Springer Show.
Television Stations
Most of Chicago's TV stations are owned by big networks. They are:
- WBBM-TV (2), owned by CBS.
- WMAQ-TV (5), owned by NBC.
- WLS-TV (7), owned by ABC.
- WGN-TV (9), a CW station.
- WTTW (11), a PBS station.
- WCIU-TV (26), an independent station.
- WFLD (32), owned by Fox.
- WWTO-TV (35), owned by TBN.
- WCPX-TV (38), owned by Ion Television.
- WSNS-TV (44), owned by Telemundo.
- WPWR-TV (50), owned by MyNetworkTV.
- WYIN (56), a PBS station.
- WTVK (59), an independent station.
- WXFT-DT (60), owned by Unimas.
- WJYS (62), an independent station.
- WGBO-DT (66), owned by Univision.
Newspapers
Chicago has two main daily newspapers: the Chicago Tribune and the Chicago Sun-Times. There are also many other newspapers and magazines for different interests. These include the Chicago Reader and the Chicago Defender.
Radio
Chicago has many powerful AM radio stations. It is also home to several national radio shows. Chicago Public Radio produces popular programs like This American Life and Wait Wait...Don't Tell Me!.
Getting Around Chicago: Transportation
Chicago is a major transportation hub in the United States. It's a very important place for moving goods around the world.
Many households in Chicago do not own a car. In 2016, about 27.5% of Chicago households did not have a car.
Parking
If you live in Chicago and own a car, you need to buy a Chicago City Vehicle Sticker. In some areas, only local residents can buy special parking stickers.
Since 2009, Chicago has leased its public street parking system to a private company. This deal was for 75 years.
Highways
Seven major interstate highways run through Chicago and its suburbs. These roads are often named after important politicians or former U.S. Presidents. The Kennedy and Dan Ryan Expressways are the busiest roads in Illinois.
Public Transit Systems

The Regional Transportation Authority (RTA) helps manage Chicago's public transportation. This includes the CTA, Metra, and Pace.
- The Chicago Transit Authority (CTA) runs buses and the "L" train system. The "L" is an elevated and subway train system. It has lines named by colors. The "L" trains also go to both Midway and O'Hare Airports. The Red and Blue lines run 24 hours a day. This makes Chicago one of the few cities in the world with 24-hour train service.
- Metra is a commuter rail service. It has 11 lines that serve Chicago and its suburbs.
- Pace provides bus service in over 200 suburbs around Chicago.
Many people in Chicago use public transit for their daily commute.
Passenger Trains
Amtrak trains start from Union Station in Chicago. Chicago is one of the largest hubs for passenger train service in the U.S. Trains from Chicago go to many cities across the country.
Bikes and Scooters
In 2013, Chicago launched Divvy, a bicycle-sharing system. You can rent bikes from many stations around the city. In 2019, Chicago also started a pilot program for electric scooters.
Freight Trains
Chicago is the largest hub for the railroad industry. All five major freight railroads meet in Chicago. There can be a lot of train traffic. A program called CREATE is working to improve how quickly freight trains move through the Chicago area.
Airports
Chicago is served by two main airports: O'Hare International Airport and Midway International Airport. O'Hare is one of the busiest airports in the world. Both airports are owned and run by the City of Chicago. United Airlines has its world headquarters in Chicago.
Port Authority
The Port of Chicago has several large port facilities. These are managed by the Illinois International Port District. The main part of the port is Calumet Harbor. It has warehouses and storage for goods.
Images for kids
-
Home Insurance Building (1885)
-
Court of Honor at the World's Columbian Exposition in 1893
-
Men outside a soup kitchen during the Great Depression (1931)
-
.
Protesters in Grant Park outside the 1968 Democratic National Convention
See also
 In Spanish: Chicago para niños
In Spanish: Chicago para niños