Decolonization of the Americas facts for kids
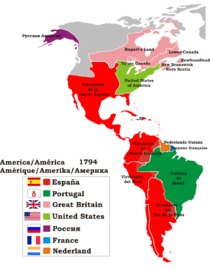
The decolonization of the Americas is the story of how most countries in the Americas became independent from European rule. This process happened over many centuries. The American Revolution was the first big step, where the United States won its freedom from Britain. This victory, helped by France and Spain, showed that a colony could defeat a powerful European country.
After that, the French Revolution in Europe also inspired people. These events greatly impacted the colonies of Spain, Portugal, and France in the Americas. A wave of revolutions followed, leading to many new independent countries in Latin America.
The Haitian Revolution (1791–1804) was a major uprising that led to the independence of Haiti, a French slave colony. Later, when Napoleon took over Spain, Spanish colonists in the Americas started to question their loyalty. This led to the Spanish American wars of independence (1808–1833). These wars were mostly fought between different groups of colonists, with some fighting against Spanish forces.
Around the same time, the Portuguese royal family moved to Brazil to escape Napoleon. When the king returned to Portugal, his son, Pedro, stayed in Brazil. In 1822, he declared Brazil independent and became its first emperor.
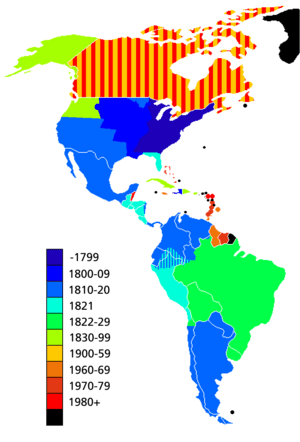
Spain lost its last three Caribbean colonies by the late 1800s. The Dominican Republic became independent in 1821, but later rejoined Spain for a short time before gaining independence again in 1865. Cuba fought for its freedom in several wars, finally gaining independence in 1902 after the Spanish–American War, which also led to the United States gaining Puerto Rico and Guam.
In the second half of the 20th century, many colonies gained independence peacefully, as European powers chose to withdraw. However, some British and Dutch islands in the Caribbean, and some French territories like French Guiana, Guadeloupe, and Martinique, are still connected to their European parent countries.
Contents
Why Revolutions Started
Weakening European Control
In the 1700s, Spain tried to regain its strength, but constant wars in Europe from 1793 put a lot of pressure on its resources. This meant that local people in the colonies had to help pay for defense and join local armies. This was different from the idea of a strong, central government. Spain even made promises, like freedom from forced labor in Chiloé, for local people who helped defend new forts. This increased local involvement eventually weakened Spain's control and helped the independence movements grow.
Impact of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of big wars in Europe from 1799 to 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte led France against alliances of countries like Britain, Spain, and Russia.
In 1808, Napoleon captured Spain's King Fernando VII and his father, Carlos IV. He then put his own brother, Joseph Bonaparte, on the Spanish throne. This caused a huge problem in Spain and its colonies. Many colonists, especially the local elites called Creoles, felt that their link to Spain was broken. They started forming local governments called juntas, believing that power returned to the community when the king was absent.
Most people were loyal to King Fernando VII at first. But when he returned to power in 1814, he tried to rule with absolute power again and punished those who had supported the new ideas. This made many colonists want to break away from Spain completely.
Spanish Army in the Colonies
The Spanish army in the Americas was made up of local Americans and Europeans who supported King Ferdinand. Most of these soldiers were Americans. There were two main types of units: regular Spanish army units sent from Europe or formed by local Europeans, and local militias. Only a small percentage of these militias were European or white Americans. After 1820, Spain stopped sending soldiers to the Americas. By the Battle of Ayacucho in 1824, very few European soldiers remained in the royalist armies.
Other Important Factors
The Enlightenment was a time when new ideas about freedom and reform spread. These ideas, like free trade, encouraged people to think about changing society and the economy in the Americas.
Independence movements in South America were also influenced by slave revolts. In 1791, a huge slave revolt in Haiti started a general uprising against the French plantation system. This inspired other revolts, like one in Venezuela in 1795.
Toussaint L'Ouverture, a former slave in Haiti, became a key leader in the Haitian Revolution. He joined the rebellion to end slavery, but later pushed for equal human rights for everyone in Haiti. He feared that France might bring back slavery. In the end, slavery was abolished in French colonies in 1794, and Haiti declared independence from France in 1804.
United States of America
The United States of America declared its independence from Great Britain on July 4, 1776. This made it the first independent nation in the Americas recognized by other countries. Britain officially accepted American independence in 1783 after losing the American Revolutionary War. The U.S. victory inspired other independence movements across the Americas.
The United States initially only controlled land east of the Mississippi River. Over time, it expanded its territory across North America, acquiring land from the British, French, Spanish, and Russians. While this ended European control in those areas, it also led to the expansion of American settlements into lands belonging to Native American nations, especially after gold was discovered in places like the Dakotas and California.
Haiti and French Colonies
The American and French Revolutions deeply affected the Spanish, Portuguese, and French colonies in the Americas. Haiti, a French slave colony, was the first to follow the United States to independence. This happened during the Haitian Revolution, which lasted from 1791 to 1804. After failing to rebuild a French empire in North America, Napoleon Bonaparte sold Louisiana to the United States. This marked the end of France's big plans for a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere.
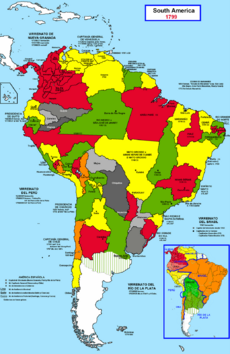
Spanish America
Most Spanish colonies in the Americas gained their independence in the early 1800s, except for Cuba and Puerto Rico.
When Napoleon put his brother, Joseph Bonaparte, on the Spanish throne and captured King Fernando VII, it caused a crisis. Local leaders, called Criollos (people of Spanish descent born in Latin America), started forming assemblies after 1810. They wanted to take back control and govern their lands in the name of the captured King Fernando VII.
This experience of self-government, along with new ideas from the Enlightenment and the French Revolution and American Revolution, led to a fight for independence. Leaders known as the Libertadores led these struggles. The territories became free, often with help from foreign fighters. The United States and Europe stayed neutral, but they wanted to trade with these new countries without Spain's control.
In South America, Simón Bolívar and José de San Martín were key leaders in the final part of the independence struggle. Bolívar tried to keep the Spanish-speaking parts of the continent united, but they quickly became independent countries.
A similar process happened in what is now Mexico and Central America from 1810 to 1821, known as the Mexican War of Independence. Independence was achieved in 1821 when different groups united under Agustín de Iturbide. They stayed united for a short time as the First Mexican Empire. Later, the region fought against the United States, losing lands like California and Texas in the Mexican–American War (1846–1848).
In 1898, the United States won the Spanish–American War and took control of Cuba and Puerto Rico, ending Spain's rule in the Americas.
Argentina's Freedom
After Spain's defeat in the Peninsular War and King Fernando VII giving up his throne, the Spanish government in the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata became very weak. This area included present-day Argentina, most of Bolivia, and parts of Chile, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
Without a rightful king, the local elites, who were tired of Spanish trade rules and taxes, took action. In the May Revolution of 1810, they removed the Spanish viceroy and formed their own local government.
After years of battles and expeditions led by José de San Martín across the Andes to end Spanish rule in America, Argentina formally declared full independence on July 9, 1816. The Argentine Constitution was signed in 1853, creating the Argentine Republic.
Bolivia's Independence
Following the changes caused by the May Revolution in Argentina and independence movements in Chile and Venezuela, Bolivia also started its own fight for freedom. After two failed revolutions, a struggle of over sixteen years led to the creation of a republic. The fight for independence officially ended with the Battle of Ayacucho on December 9, 1824.
Chile's Fight for Freedom
The independence movement in Chile was led by General José de San Martín, with help from Chilean exiles like Bernardo O'Higgins. The local independence movement was made up of Chilean-born Creoles who wanted political and economic freedom from Spain. Not everyone in Chile supported independence, and people were divided between those who wanted independence and those loyal to Spain. What started as a political movement by the elite ended up as a full civil war.
Ecuador's Independence
The first uprising against Spanish rule in Ecuador happened in 1809. In 1810, Creoles in Ecuador set up a local government. However, Ecuador didn't fully gain independence until 1822, when it joined Gran Colombia. It later became a separate country in 1830. At the Battle of Pichincha, near Quito, Ecuador, on May 24, 1822, General Antonio José de Sucre's forces defeated the Spanish army, securing Ecuador's freedom.
Guatemala and Central America
When Mexico gained its independence in 1821, the Captaincy General of Guatemala, which ruled Central America, also became politically independent without a violent struggle. Guatemala declared its independence on September 15, 1821. However, Guatemala chose to join the First Mexican Empire for a short time. When Mexico became a republic, Central America declared its full independence on July 1, 1823.
Mexico's Long Struggle
Independence in Mexico was a long fight from 1808 until the Spanish government fell in 1821. In 1808, when Napoleon invaded Spain, local American-born Spaniards saw a chance to take control. Some elites, including a priest named Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, called for independence. Hidalgo's rebellion was very violent and he was captured and executed in 1811. His student, José María Morelos, continued the fight but was also killed in 1815.
The rebellion continued under other leaders. From 1815 to 1820, there was a stalemate. Then, events in Spain changed things again. A liberal constitution was restored, which worried conservatives in Mexico. A royal military officer, Agustín de Iturbide, allied with a rebel leader, Vicente Guerrero. Iturbide proposed a plan for independence, equality, and a monarchy. The Spanish rule in Mexico collapsed when a new viceroy signed a treaty recognizing Mexico's independence. Iturbide became emperor for a short time but was overthrown in 1823, and Mexico became a republic.
Paraguay's Independence
Paraguay gained its independence quickly on the night of May 14 and morning of May 15, 1811. This was thanks to a plan organized by pro-independence leaders like Fulgencio Yegros and José Gaspar Rodríguez de Francia.
Peru's Last Stand
Spain initially had strong support in Peru, making it the last stronghold of the Spanish Monarchy in South America. However, local rebellions did break out in 1812 and 1814, but they were put down.
Peru finally became free after major campaigns led by José de San Martín (1820–1823) and Simón Bolívar (1824). San Martín, who had already freed Chile, landed in Peru in 1820 and declared Peru's independence in Lima on July 28, 1821. Four years later, the Spanish Monarchy was finally defeated at the Battle of Ayacucho in late 1824.
After independence, Peru faced challenges in organizing the country due to conflicts among different groups and the ambitions of local leaders.
Uruguay's Path to Freedom
Following the events of the May Revolution in Argentina, José Gervasio Artigas led a successful revolt against Spanish forces in Uruguay in 1811. In 1821, Portugal invaded Uruguay, trying to make it part of Brazil.
Argentina fought back against Brazil in a war that lasted over two years. Neither side won a clear victory, and the war was very expensive. To end the conflict, the 1828 Treaty of Montevideo was signed in 1828, with Britain's help. This treaty declared Uruguay an independent state.
Venezuela's Struggle

General Francisco de Miranda had early successes against the Spanish in Venezuela. He convinced Simón Bolívar to join the fight. However, Bolívar made a mistake that led to the Spanish regaining control. Miranda was forced to surrender in 1812.
Bolívar then fled but returned with a new army. The war became very violent. Bolívar's forces invaded Venezuela in 1813, fighting with extreme determination. They defeated the Spanish army in several battles, taking Caracas in August 1813.
However, loyalist forces fought back with equal intensity. An army led by José Tomás Boves, made up of fierce horsemen called Llaneros, pushed Bolívar out of Venezuela again in 1814.
Bolívar returned in 1816, leading a difficult fight against Spain. In 1819, he successfully invaded New Granada (modern-day Colombia), and returned to Venezuela in April 1821 with a large army. At the Battle of Carabobo on June 24, his forces decisively defeated the Spanish and colonial armies, winning Venezuela's independence.
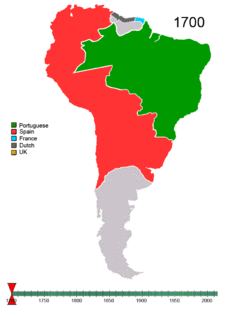
Brazil's Peaceful Independence
Unlike the Spanish colonies, the Portuguese did not divide their territory in the Americas. Brazil was a single, unified colony. Because of this, Brazil did not split into several countries when it became independent in 1822, unlike its Spanish-speaking neighbors. Also, Brazil chose to become a monarchy instead of a republic, which helped keep the nation united.
When Napoleon Bonaparte forced the Portuguese royal family out of Lisbon, they moved to Brazil. For eight years, Rio de Janeiro was the capital of the Portuguese empire. In 1815, the king declared Rio and Lisbon equal centers of the empire. King Dom João VI was forced back to Lisbon in 1821, but he left his son, Pedro, in charge of Rio. A year later, Dom Pedro declared Brazil's independence and became Emperor Pedro I. Brazil's independence was mostly peaceful, but some small battles were fought against Portuguese loyalists until 1824. Portugal officially recognized Brazil's independence in 1825.
Canada's Gradual Independence
Canada became independent from British rule slowly, over many decades, mostly through political changes rather than violent revolutions. Attempts to revolt against the British, like the Rebellions of 1837–1838, were short-lived and quickly stopped.
Canada was declared a self-governing area within the British Empire in 1867. At first, the Canadian Confederation included only a few eastern provinces. Other British colonies in what is now Canada, like British Columbia and Newfoundland, joined later. By 1931, the United Kingdom had given up control over Canada's foreign policy. The few remaining political ties between Canada and the UK were formally ended in 1982 with the Canada Act.
20th Century Independence
Many other countries gained independence in the 20th century:
From Spain:
- Cuba (1902)
From the United Kingdom:
- Jamaica: 1962
- Trinidad and Tobago: 1962
- Guyana: 1966
- Barbados: 1966
- Bahamas: 1973
- Grenada: 1974
- Dominica: 1978
- Saint Lucia: 1979
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines: 1979
- Antigua and Barbuda: 1981
- Belize (formerly British Honduras): 1981
- Saint Kitts and Nevis: 1983
From the Netherlands:
- Suriname: 1975
Current Non-Sovereign Territories
Some parts of the Americas are still governed by European countries or the United States today:
- Anguilla (United Kingdom)
- Aruba (Netherlands)
- Bermuda (United Kingdom)
- Bonaire (Netherlands)
- British Virgin Islands (United Kingdom)
- Cayman Islands (United Kingdom)
- Curacao (Netherlands)
- Falkland Islands (United Kingdom)
- French Guiana (France)
- Greenland (Kingdom of Denmark)
- Guadeloupe (France)
- Martinique (France)
- Montserrat (United Kingdom)
- Puerto Rico (United States)
- Saba (Netherlands)
- Saint Barthelemy (France)
- Saint Martin (France)
- Saint-Pierre and Miquelon (France)
- Sint Eustatius (Netherlands)
- Sint Maarten (Netherlands)
- South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands (United Kingdom)
- Turks and Caicos Islands (United Kingdom)
- United States Virgin Islands (United States)
Some of these territories have chosen to remain connected to their parent countries and have a lot of self-government. For example, Aruba became a self-governing part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1986 and stopped its move towards full independence. French Guiana, Guadeloupe, and Martinique are considered full parts of France, not just colonies. However, some regions, like Puerto Rico and Martinique, still have movements that want to change their political status, including becoming fully independent.
Timeline of Independence
World Reaction to Independence
United States and Great Britain's Roles
After many countries in the Americas became independent, Great Britain and the United States became rivals for influence in these new nations. To protect the new countries' freedom and prevent other European powers from interfering, U.S. President James Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams created the Monroe Doctrine. This policy stated that the United States would not allow any European interference in the Western Hemisphere. Since the U.S. was a new nation, it needed Britain's help to enforce this doctrine.
Britain's trade with Latin America grew a lot during this time, as it was no longer restricted by Spain's old trade rules. Britain's influence was strong enough to stop Spain from trying to regain control of its lost colonies.
Attempts at Unity in the Americas
Simón Bolívar, a key leader in South American independence, suggested that American republics should work together. In 1826, he proposed creating a league of American republics with a common army, a defense agreement, and a shared parliament. Representatives from Gran Colombia (which included modern-day Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela), Peru, the United Provinces of Central America, and Mexico attended this meeting. However, the vast distances, geographical barriers, and different national interests made it impossible to unite.
Much later, in 1890, the Commercial Bureau of the American Republics was formed. This organization eventually became today's Organization of American States, which promotes cooperation among countries in the Americas.
Images for kids
-
The Battle of Boyacá sealed Colombia's independence
See also
 In Spanish: Descolonización de América para niños
In Spanish: Descolonización de América para niños
- Colonialism
- Decolonization
- Wars of national liberation
- Spanish Empire
- Libertadores
- History of Central America
- History of South America
- History of Cuba
- History of the Dominican Republic
- History of Puerto Rico
- Age of Revolution