Caesium facts for kids
Caesium (say it: SEE-zee-əm) is a special chemical element you can find on the periodic table. Its number is 55, and its symbol is Cs.
 |
|||||||||||||||
| Caesium | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈsiːziəm/ |
||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery gold | ||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Cs) | 132.90545196(6) | ||||||||||||||
| Caesium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 55 | ||||||||||||||
| Group | group 1: hydrogen and alkali metals | ||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Block | s | ||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 6s1 | ||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 301.7 K (28.5 °C, 83.3 °F) | ||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 944 K (671 °C, 1240 °F) | ||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 1.93 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 1.843 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 1938 K, 9.4 MPa | ||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.09 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 63.9 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 32.210 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
|||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −1, +1 (a strongly basic oxide) | ||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 0.79 | ||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 265 pm | ||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 244±11 pm | ||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 343 pm | ||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of caesium | |||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||
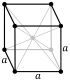
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc) | ||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 97 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 35.9 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 205 n Ω⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | ||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 1.7 GPa | ||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 1.6 GPa | ||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 0.14 MPa | ||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-46-2 | ||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Caesium is an alkali metal. It has a very low melting point, which means it turns into a liquid easily. It melts at just 28.5 °C (83.3 °F). This is only a little warmer than room temperature!
Caesium is extremely reactive. Because it reacts so easily with other things, it can be dangerous. It can even catch fire by itself in the air. If it touches water, it explodes! This reaction is much stronger than with other alkali metals. To keep it safe, caesium is stored in mineral oil.
Caesium is a rare element. There isn't much of it on Earth, so it costs a lot. Your body does not need caesium. In large amounts, it can be a little harmful. This is because it is similar to potassium, which your body does need.
History of Caesium
Caesium was first found in 1861. Two scientists, Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen, discovered it. They were looking at mineral water from a place called Bad Dürkheim.
After they took out other elements like calcium and lithium, they saw two bright blue lines. These lines appeared when they used a special tool called a spectroscope. The blue lines told them there was a new, unknown substance in the water. They named this new element caesium. The name comes from the Latin word for "sky blue."
Caesium's Forms and Uses
Caesium has many different forms called isotopes. Scientists know of at least 39 isotopes of caesium. But only one of them, called 133Cs, is stable. This means it doesn't change over time.
133Cs is the natural form of caesium. It is not radioactive. This stable isotope is very important for atomic clocks. These clocks use the exact vibrations of 133Cs atoms to measure time. This is how we define the length of one second!
Another isotope is 137Cs. This one is not found naturally. It is made after a process called nuclear fission. 137Cs is very radioactive. It is used in industries as a source of gamma rays.
Caesium also forms compounds with many other elements. For example, caesium formate is a compound used in oil drilling. It's used because it is very heavy or "dense."
Images for kids
-
High-purity caesium-133 stored in argon.
-
Monatomic caesium halide wires grown inside double-wall carbon nanotubes (TEM image).
-
Gustav Kirchhoff (left) and Robert Bunsen (centre) discovered caesium with their newly invented spectroscope.
See also
 In Spanish: Cesio para niños
In Spanish: Cesio para niños