Human facts for kids
Quick facts for kids HumanTemporal range: 0.35 mya to present Middle Pleistocene – Recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| An adult human man (left) and woman (right) from the Akha tribe in Northern Thailand. | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Subfamily: | Homininae |
| Tribe: | Hominini |
| Genus: | Homo |
| Species: |
H. sapiens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Homo sapiens Linnaeus, 1758
|
|
| Subspecies | |
|
†Homo sapiens idaltu White 2003 |
|
 |
|
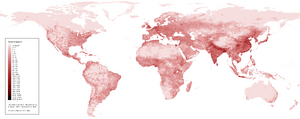
| Homo sapiens population density | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
A human is a member of the species Homo sapiens. This name means 'wise man' in Latin. Humans are a type of hominid. Our closest living relatives are chimpanzees, gorillas, bonobos, and orangutans.
Humans are mammals and also social animals. They usually live in groups. They help and protect each other. They also care for their children. Humans are bipedal, which means they walk on two legs.
Humans have a very complex brain. It is much larger than the brains of other living apes. Humans use language, create ideas, and feel emotions. Because their arms are not needed for walking, humans can use tools. Humans use tools much more than any other species.
Humans live on every continent. As of 2020, there were over 7,600 million people living on Earth. Having too many people in one place can sometimes be a problem.
Contents
Understanding Human Features
Humans have a long time of development after they are born. Their lives depend less on instinct and more on learning. Human brains are not fully developed at birth compared to other mammals. This leads to a very long childhood, which makes family life important. If their brains were more developed at birth, they would be larger. This would make birth more difficult. During birth, a baby's head must pass through the 'birth canal' in the mother's pelvis.
Many animals use signs and sounds to talk to each other. But humans have a complex system called language. It lets them share ideas using words. Humans can create abstract ideas and tell them to others. Human language can talk about things that are not present. It can also discuss events that are not happening right now. These things might be far away, and events may have happened in another place or time.
No known animals have a way of communication as detailed as human language. By using words to talk, humans create complex communities. These communities have laws, traditions, and customs. Humans like to understand the world around them. They try to explain things through myth, science, and philosophy. Wanting to understand has helped humans make important discoveries.
Humans are the only species alive today known to build fires. They also cook their food and wear clothes. Humans use more technology than any other animal ever has. Humans enjoy things that are beautiful. They like to make art, literature, and music. Humans use education and teaching to pass on skills, ideas, and customs to the next generations.
Where Did Humans Come From?
Humans are part of the animal kingdom. They are mammals, meaning females give birth to live young. They also feed their babies with breast milk. Humans belong to the order of primates. Apes like gorillas and orangutans are also primates. The closest living relatives of humans are the two chimpanzee species: the common chimpanzee and the bonobo. Scientists have looked at the genes of humans and chimpanzees. They compared their DNA. Studies showed that 95% to 99% of human and chimpanzee DNA is the same.
Biologists explain the similarity between humans and other hominoids. They say it is because they came from a common ancestor. In 2001, a hominid skull was found in Chad. The skull is about 7 million years old. It has been named Sahelanthropus tchadensis. This skull might show that humans started to evolve (develop differently) from other primates 2 million years earlier than thought.
Humans are part of a subfamily called the Homininae (or hominins). This group is inside the hominids or great apes.
Long ago, other types of hominins lived on Earth. They were like modern humans but not exactly the same. Homo sapiens are the only type of hominins alive today. The earliest known fossils of the genus Homo are called Homo habilis (handy man). The first fossils of Homo habilis were found in Tanzania. Homo habilis is thought to have lived about 2.2 to 1.7 million years ago. Another human species thought to be an ancestor of modern humans is Homo erectus. Many other extinct species of Homo are known today. Many of them were likely our 'cousins'. They developed differently from our ancestors. A theory called the Sahara pump theory explains how different plants and animals moved from Africa to the Middle East. Early humans may have moved from Africa to other parts of the world in the same way.
How Humans Spread Across the World
The first truly modern humans appeared between 300,000 and 200,000 years ago. This happened in East Africa. In paleontology, 200,000 years is a "short" time. So, scientists talk about a "recent single origin" for humans. These early humans later moved out from Africa. By about 90,000 years ago, they had moved into Eurasia. This was an area where Neanderthals, Homo neanderthalensis, had lived for a long time (at least 350,000 years).
By about 42,000 to 44,000 years ago, Homo sapiens had reached western Europe. This included Britain. In Europe and western Asia, Homo sapiens replaced the Neanderthals by about 35,000 years ago. We don't know all the details of how this happened.
At roughly the same time, Homo sapiens arrived in Australia. Their arrival in the Americas was much later, about 15,000 years ago. All these early groups of modern humans were hunter-gatherers. This means they hunted animals and gathered plants for food.
The Rise of Civilization

Early human history is often divided into three main ages. These time periods are named after the material used for tools.
- The Stone Age
- The Bronze Age
- The Iron Age
The "Stone Age" is usually split into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods.
Up to about 10,000 years ago, most humans were hunter-gatherers. They did not live in one place. Instead, they moved around as the seasons changed. The start of planting crops for food, called farming, led to the Neolithic revolution. Some people chose to live in settlements. This also led to the invention of metal tools and the training of animals. About 6,000 years ago, the first proper civilizations began. These were in places like Egypt, India, and Syria. People formed governments and armies for protection. They competed for areas to live and resources. Sometimes they fought with each other. About 4,000 years ago, some states took over or conquered other states. They made empires. Examples include ancient Greece and the Roman Empire.
Some modern-day religions also began at this time, such as Judaism and Hinduism. From the Middle Ages and beyond, humanity saw many new technologies and inventions. The printing press, the car, the train, and electricity are all examples. Because of these developments, modern humans live in a world where everyone is connected. This happens, for example, by telephone or by the internet. People now control and change the environment around them in many ways.
Where Humans Live and How Many There Are

In early times, humans usually settled near water and other natural resources. In modern times, if people need things, they can transport them from somewhere else. So, living close to resources is not as important as it once was. Since 1800, the number of humans, or population, has increased by six billion. Most humans (61%) live in Asia. The rest live in the Americas (14%), Africa (14%), Europe (11%), and Oceania (0.5%).
Most people live in towns and cities. This number is expected to get higher. In 2005, the United Nations said that by the end of that year, over half the world would be living in cities. This is a big change in how humans settle. A century earlier, in 1900, only 14% of people lived in cities. In 2000, 47% of the world's population lived in cities. In developed countries, like the United States, 80% of the population lives in cities.
Humans have a large effect on the world. Humans are at the top of the food chain. They are generally not eaten by any animals. Humans have been called super predators because of this. Because of industry and other reasons, humans are said to be a big cause of global climate change.
Human Biology
Physical Appearance of Humans
Human body types can be very different. The average height of an adult human is between 5 and 6 feet. The average weight is between 76 and 83 kg for males. For females, it is between 54 and 64 kg.
Humans have longer hair that grows on the underarms, genitals, and the top of the head in adults of both genders. It also grows on the legs and face of all adult males. Many adult males also have hair on their chest and back. In human children of both genders, long hair grows only on the top of the head. Humans might seem to have less hair than most primates, but they actually have more hair follicles. These are the tiny holes where hair grows from. Human hair can be brown, red, blond, or most commonly, black. Modern humans can also change their hair to many different colors using dye. When humans get older, hair can turn grey or even white.
Human skin colors vary greatly. They can be a very pale pink all the way to dark brown. There is a reason why people in tropical areas have dark skins. The dark pigment (melanin) in the skin protects them against ultraviolet rays from sunlight. Damage from UV rays can cause skin cancer in some people. Therefore, natural selection favors darker skin color in sunny places. Sun tanning is a temporary process and is not inherited. In colder climates, light-colored skin is an advantage because it radiates less heat.
Humans are not as strong as other primates of the same size. An average female orangutan is at least three times as strong as an average human man.
The average human male needs 7 to 8 hours of sleep a day. People who sleep less than this are generally not as healthy. A child needs more sleep, 9 to 10 hours on average.
The Human Life Cycle
The human life cycle is quite similar to most other mammals. The young grow inside the female mother for nine months. After this time, the baby is born.
Unlike most other animals, human childbirth can be somewhat difficult. Because human brains are so big, babies' heads are wide. The mothers' pelvis bones are also not very wide because people walk on two legs. This combination means that sometimes either the mother or baby may face serious health risks during childbirth. The number of mothers facing these risks in childbirth is less in the 21st century. This is because of better medication and treatment. In many poorer countries, the number of mothers facing risks is higher. Sometimes it is up to 10 times as many as in richer countries.
The average human baby weighs 3–4 kg at birth. It is 50–60 cm tall. This is often less in poorer countries. Many babies in poor countries often die early because of this.
Humans have four main stages in their lives: childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and old age.
Life expectancy is how long you are expected to live. This depends on many things, including where you live. The highest life expectancy is for people from Monaco, at 89.52 years. The lowest is for people from Chad, where life expectancy is only 49.81 years.
How the Human Mind Works
Psychology is the study of how the human mind works. The human brain is the main controller of what a person does. Everything from moving and breathing to thinking is done by the brain. The human neocortex is huge compared with other mammals. It gives us our thinking ability. It also gives us the ability to speak and understand language.
Neurology is the study of how the brain works. Psychology is the study of how and why people think and feel. Many parts of life are also affected by the hormone system. This includes growth and sexual development. The hormonal system (especially the pituitary gland) is partly controlled by the brain.
Human behavior is hard to understand. So, sometimes psychologists study animals because they may be simpler and easier to learn from. Psychology connects with many other sciences. These include medicine, biology, computer science, and linguistics.
Human Culture
Language: How We Communicate
Language at its most basic is talking, reading, and writing. The study of language is called linguistics. Humans have the most complicated languages on Earth. Almost all animals communicate, but human language is unique. Its use of syntax (sentence structure) and its huge learned vocabulary are its main features. There are over 7,300 languages spoken around the world. The world's most spoken first language is Mandarin Chinese. The most spoken language overall is English. This includes people who speak English as a second language.
Art, Music, and Stories
Art has existed almost as long as humans. People have been doing some types of art for thousands of years. The picture on the right shows this. Art shows how someone feels. It can be a painting, a sculpture, or a photograph.
Music has also been around for thousands of years. Music can be made with only your voice. But most of the time, people use instruments. Music can be made using simple instruments like drums. It can also use complex ones like electric guitars, keyboards, and violins. Music can be loud, fast, quiet, slow, or many different styles. Music shows how the people who are playing it feel.
Literature is anything made or written using language. This includes books, poetry, legends, myths, and fairy tales. Literature is important. Without it, many things we use today, such as Wikipedia, would not exist.
Groups and Identity
Humans often put themselves into groups by race or ethnicity. Modern biologists know that human gene sequences are very similar. This is compared to many other animals. This is because of the "recent single origin" of modern humans. That is one reason why there is only one human race.
Ethnic groups are often connected by language, culture, family history, and national or regional ties. Race and ethnicity can lead to different social treatment, sometimes called racism.
Beliefs and Spirituality
Religion is a belief or faith in a higher being, spirit, or any system of ideas that a group of people believe in. To have faith in a belief means to believe it without proof that it is true. Faith can bring people together because they all believe in the same thing. Some things religions talk about are what happens after death, why humans exist, how humans came to exist (creation), and what is good or bad to do (morality). Some people are very religious. Many people believe in one all-powerful god. Some people believe in more than one god. Some people are atheists, who do not believe in a god. And some people are agnostics, who are not sure if there is a god.
Science and Technology: Shaping Our World

Technology refers to the tools and methods humans use to make tasks easier. Science is about understanding how the universe and everything in it works. Technology used to be quite simple. It was passed on by people telling others, until writing was invented. This allowed technology to develop much quicker. Now people understand more and more about the world and the universe. The use of the telescope by Galileo, Einstein's theory of relativity, lasers, and computing are all scientific discoveries. Technology is very important to science, to medicine, and to everyday life.
War: Conflict Among Humans
A war is a deadly fight between large groups of people. These are usually countries or states. A war involves using deadly weapons as both sides try to harm the other. It is thought that between 167 and 188 million humans died because of war in the 20th century. The people who fight for a state in wars are called soldiers. People who fight in wars but not for a state are usually called "fighters."
Modern wars are very different from wars a thousand or even a hundred years ago. Modern war involves sabotage, terrorism, propaganda, and guerrilla warfare. In modern-day wars, civilians (people who are not soldiers) are often targets. An example of this is the nuclear bomb dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki at the end of World War II. The bombs killed as many as 140,000 people in Hiroshima and 80,000 in Nagasaki by the end of 1945. About half died on the days the bombs were dropped. Since then, thousands more have died from injuries or illness because of exposure to radiation from the bombs. In both cities, most of the dead were civilians. In Germany, Austria, and Great Britain, regular bombs were used. About 60,595 British and 550,000 German civilians were killed by planes bombing cities.
Images for kids
-
Reconstruction of Lucy, the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found.
-
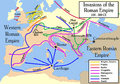
Routes taken by barbarian invaders of the Roman Empire during the Migration Period.
-
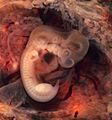
A 10 mm human embryo at 5 weeks.
-
Illustration of grief from Charles Darwin's 1872 book The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals.
-
Shango, the Orisha of fire, lightning, and thunder, in the Yoruba religion, shown on horseback.
-
The Dunhuang map, a star map showing the North Polar region. China circa 700.
-
The Silk Road (red) and spice trade routes (blue).
See also
 In Spanish: Ser humano para niños
In Spanish: Ser humano para niños