Massachusetts facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Massachusetts
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Commonwealth of Massachusetts | |||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Bay State (official)
The Pilgrim State; The Puritan State The Old Colony State The Baked Bean State |
|||
| Motto(s):
Ense petit placidam sub libertate quietem (Latin)
By the sword we seek peace, but peace only under liberty |
|||
| Anthem: "All Hail to Massachusetts" | |||
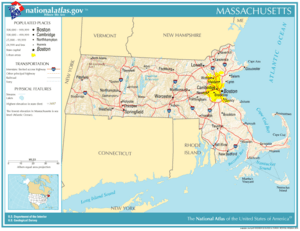
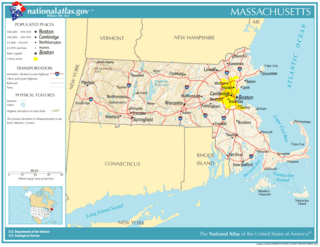
Location of Massachusetts within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Province of Massachusetts Bay | ||
| Admitted to the Union | February 6, 1788 (6th) | ||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Boston | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Middlesex | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Greater Boston | ||
| Legislature | General Court | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court | ||
| U.S. senators | Elizabeth Warren (D) Ed Markey (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 9 Democrats (list) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 10,565 sq mi (27,363 km2) | ||
| • Land | 7,800 sq mi (20,202 km2) | ||
| • Water | 2,715 sq mi (7,032 km2) 26.1% | ||
| Area rank | 44th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 190 mi (296 km) | ||
| • Width | 115 mi (184 km) | ||
| Elevation | 508 ft (150 m) | ||
| Highest elevation | 3,489 ft (1,063.4 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Atlantic Ocean)
|
0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 16th | ||
| • Density | 914.89/sq mi (353.24/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 3rd | ||
| • Median household income | $99,900 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 1st | ||
| Demonym(s) | Bay Stater (official)
Masshole Massachusite (traditional) Massachusettsan (recommended by the U.S. GPO) |
||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English | ||
| • Spoken language |
|
||
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
MA
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-MA | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | Mass. | ||
| Latitude | 41°14′ N to 42°53′ N | ||
| Longitude | 69°56′ W to 73°30′ W | ||
| Dance | Square dance |
|---|---|
| Bird | Black-capped chickadee, wild turkey |
| Fish | Cod |
| Flower | Mayflower |
| Tree | American elm |
| Insect | Ladybug |
| Sport | Basketball |
Massachusetts is a state located in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is officially known as the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. To its east, it touches the Atlantic Ocean. It shares borders with Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York to the west. Massachusetts is one of the smallest states in the U.S. by land area.
With a population of over 7 million people in 2024, Massachusetts is the most populated state in New England. It is also one of the most densely populated states in the entire United States.
Massachusetts played a big role in early English settlement in America. The Plymouth Colony was started here in 1620 by the Pilgrims who arrived on the Mayflower. Later, the Massachusetts Bay Colony was founded in 1630, named after the native Massachusett people. This colony established important cities like Boston and Salem. In the late 1700s, Boston became known as the "Cradle of Liberty" because of the strong feelings there that led to the American Revolution. Massachusetts was also a leader in the Industrial Revolution, changing from farming and fishing to manufacturing.
Today, Massachusetts is known for its strong economy, especially in biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and higher education. It is home to famous universities like Harvard University and MIT, which are among the best in the world. The state's public schools are also highly ranked. Massachusetts is considered one of the most educated and wealthiest states in the U.S.
Contents
- Understanding Massachusetts: Its Name and History
- Exploring the Geography of Massachusetts
- Environmental Efforts in Massachusetts
- How Massachusetts is Governed
- People and Population in Massachusetts
- Learning and Knowledge: Education in Massachusetts
- The Economy of Massachusetts
- Getting Around: Transportation in Massachusetts
- Major Cities and Towns
- Arts, Culture, and Fun in Massachusetts
- Media and News in Massachusetts
- Sports in Massachusetts
- See also
Understanding Massachusetts: Its Name and History
What's in a Name? The Origin of Massachusetts
The name "Massachusetts" comes from the Massachusett people. They were an indigenous population who lived in the area.
The official name of the state is the "Commonwealth of Massachusetts". A commonwealth is a traditional term for a state where the people have a say in their government.
Early Days: Before European Settlers Arrived
Before Europeans came, tribes like the Wampanoag, Narragansett, and Massachusett lived here. They spoke Algonquian languages. These tribes mostly hunted, gathered food, and fished. They also grew some crops like squash and corn. Their homes were called wigwams or longhouses. Leaders were called sachems.
In the early 1600s, after Europeans arrived, many native people became sick. Diseases like smallpox spread, and sadly, many people passed away.
Colonial Times: The First English Settlements
The first English settlers were the Pilgrims. They came on the ship Mayflower in 1620. They landed at Plymouth. The Pilgrims became friends with the native Wampanoag people. This was the second successful English colony in North America.
The Pilgrims celebrated their first harvest with a three-day event. This is known as the "First Thanksgiving". Other Puritans soon followed. They started the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1630. This colony included areas like Boston and Salem.
In 1691, the Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth colonies joined together. They formed the Province of Massachusetts Bay. Around this time, the Salem Witch Trials happened. This was a sad period when many people were wrongly accused of witchcraft.
The Road to Revolution: Massachusetts' Role
Massachusetts was a key place for the movement to become independent from Great Britain. Colonists here often had difficult relationships with the British king.
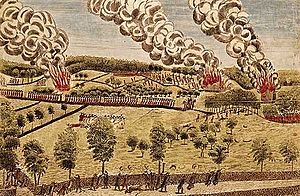
The Battles of Lexington and Concord started the American Revolutionary War. These battles took place in Massachusetts towns. George Washington took command of the Continental Army here. His first victory was the Siege of Boston in 1775–76. This forced the British to leave Boston.
Forming a Nation: After the Revolution
John Adams from Boston was very important in the fight for independence. He also helped create the new United States. His son, John Quincy Adams, also from Massachusetts, later became the sixth U.S. President.
From 1786 to 1787, a revolt called Shays' Rebellion happened. It was led by American Revolutionary War veteran Daniel Shays. This uprising showed the need for a stronger national government. It helped lead to the creation of the Constitution of the United States. On February 6, 1788, Massachusetts became the sixth state to approve the U.S. Constitution.
The 1800s: Industry and Change
In 1820, Maine became a separate state from Massachusetts. This happened because of the Missouri Compromise.

During the 1800s, Massachusetts became a leader in the Industrial Revolution. Factories in cities like Lowell and Boston made textiles and shoes. Factories in Springfield produced tools and paper.
Massachusetts was the first state to create an African American regiment with White officers. This was the 54th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment. In 1852, Massachusetts also became the first state to require children to go to school.
Alexander Graham Bell is known for inventing the first practical telephone. In 1876, at Boston University, he made the first phone call to his assistant.
The 1900s: Economic Shifts and Famous Families

In the early 1900s, many factories moved away. This caused the state's industrial economy to slow down. The Great Depression in the 1920s also hurt industries like textiles and shoemaking.
During World War II, Massachusetts produced a lot of military equipment. After the war, the economy in Eastern Massachusetts changed. It moved from heavy industry to service-based jobs.
The Kennedy family was very important in Massachusetts politics. John F. Kennedy was a U.S. Senator and President. His brothers, Robert F. Kennedy and Ted Kennedy, were also senators. Eunice Kennedy Shriver helped start the Special Olympics. In 1966, Massachusetts was the first state to elect an African American, Edward Brooke, to the U.S. Senate by popular vote.
Exploring the Geography of Massachusetts
Massachusetts is the 7th smallest state in the United States. It is part of the New England region. About a quarter of its total area is water. Boston is the largest city. It sits at the very inside of Massachusetts Bay.
Even though it's small, Massachusetts has many different types of land. The eastern part has a large coastal plain along the Atlantic Ocean. This is where most of the state's people live, including Greater Boston. The unique Cape Cod peninsula is also here. To the west, you'll find the hilly, rural area of Central Massachusetts. Beyond that is the Connecticut River Valley. The highest part of the state is in Western Massachusetts, called the Berkshires.
The U.S. National Park Service manages several natural and historical places in Massachusetts.
Nature and Wildlife: Massachusetts Ecology

Most of inland Massachusetts has temperate deciduous forests. Long ago, much of the land was cleared for farming. But now, forests cover about 62% of the state again.
Many animals are doing well in Massachusetts, even in cities. Peregrine falcons nest on tall buildings. Coyotes are also increasing in number. You can find white-tailed deer, raccoons, wild turkeys, and eastern gray squirrels everywhere. In the western, more rural areas, larger animals like moose and black bears have returned. This is because the forests have grown back.
Massachusetts is on the Atlantic Flyway. This is a big path for migratory waterfowl. Lakes in central Massachusetts have many fish and waterfowl. Some rare birds, like the common loon, live here. Small islands and beaches are important breeding spots for birds like roseate terns and the piping plover. Protected areas, like the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge, help these birds and other marine life. This includes many grey seals.
Freshwater fish include bass, carp, and trout. In the ocean, you can find Atlantic cod, haddock, and American lobster. Other marine animals include Harbor seals and different types of whales, like the endangered North Atlantic right whale.
Weather Patterns: Massachusetts Climate
Most of Massachusetts has a humid continental climate. This means it has cold winters and warm summers. Areas along the far southeast coast have a milder, more temperate climate. Frosts are common in winter, even near the coast. This is because winds usually blow from inland. Massachusetts can also be affected by hurricanes and tropical storms from the Atlantic Ocean.
Environmental Efforts in Massachusetts
Facing Climate Change in Massachusetts
Climate change affects both cities and rural areas in Massachusetts. This includes forests, fishing, farming, and coastal areas. The Northeast is expected to warm faster than the global average. By 2035, it could be more than 3.6°F (2°C) warmer than it used to be. Massachusetts has already warmed by over two degrees Fahrenheit.
Changing temperatures also mean different rainfall patterns. There are more heavy rain events now. This increased rain happens mostly in winter and spring. Warmer temperatures and more rain can lead to earlier snow melts. This means drier soil in the summer.
Climate change could cause billions of dollars in damage in Boston alone from storms. Warmer temperatures also affect bird migration and when plants bloom. Deer populations might increase, which could reduce plants that smaller animals use for hiding. Also, warmer weather means more Lyme disease cases. This is because ticks can spread the disease when temperatures are above 45 degrees.
To fight climate change, Massachusetts wants to reduce its carbon pollution. The state plans to reach net-zero emissions by 2050. This means reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 85 percent overall.
Green Initiatives: Powering the Future
Massachusetts offers many programs to encourage renewable energy and energy-efficient homes. The Mass Save program gives money back to homeowners and renters. This helps them upgrade to efficient heating, cooling, and appliances.
The Mass Save program started in 2008. Its goal is to use less fossil fuels and encourage new, efficient technologies. Several power and gas companies work together on this program.
The state also provides tax credits for installing solar panels. Residents can get money back for buying electric vehicles or plug-in hybrid cars. This is part of the Massachusetts Offers Rebates for Electric Vehicles (MOR-EV) program.
For families with lower incomes, Mass Save helps with home upgrades. These upgrades make homes more energy efficient. This includes new heating systems, insulation, and appliances.
In late 2020, Governor Charlie Baker's team released a plan. It aims for net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The plan includes big investments in offshore wind and solar energy. It also wants all new cars sold in the state to be electric or hydrogen powered by 2035.
How Massachusetts is Governed
The government of Massachusetts has three main parts. These are the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. Each branch has its own responsibilities.
Executive Branch: The Governor's Role
The governor of Massachusetts leads the executive branch. The governor signs or rejects new laws. They also appoint judges and other officials. The governor prepares the state's yearly budget. They also command the Massachusetts National Guard. Governors in Massachusetts are called "His/Her Excellency."
The governor works with the Massachusetts Governor's Council. This council includes the lieutenant governor and eight elected members. The council helps approve appointments and other important decisions.
There are also four other elected officials in the executive branch. These include the secretary of the commonwealth, attorney general, state treasurer, and state auditor.
Legislative Branch: Making Laws
The Massachusetts General Court is the state's legislature. It has two parts: the Massachusetts House of Representatives and the Massachusetts Senate. The House has 160 members, and the Senate has 40 members.
The members of both parts are elected for two-year terms. They choose their own leaders. The House leader is called the Speaker. The Senate leader is called the President. Both parts of the legislature have different committees that work on laws.
Judicial Branch: Upholding Justice
The Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court is the highest court. It has a chief justice and six other judges. The governor appoints all judges in the state. The Governor's Council must approve these appointments.
Federal court cases in Massachusetts are heard in the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Appeals from these cases go to the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit.
People and Population in Massachusetts
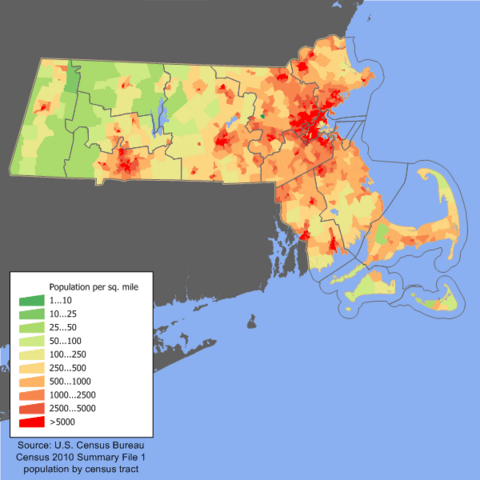
In 2020, Massachusetts had over 7 million people. This was a 7.4% increase since 2010. Massachusetts is the third-most densely populated state in the U.S. This means many people live in a small area.
Most people in Massachusetts live in the Boston area. This is called Greater Boston. It includes Boston and nearby towns. Other big population centers are Worcester and Springfield.
The population of Massachusetts has grown steadily. This is because of the good quality of life and many colleges. People also move here from other countries. Many immigrants come from Central or South America and Asia.
Diverse Backgrounds: Race and Ancestry

Massachusetts has a diverse population. The largest group is people of Irish ancestry. They make up almost 25% of the population. Many also have Italian backgrounds. English Americans are another large group.
Many people also have French and French Canadian roots. Lowell has the second-largest Cambodian community in the U.S. There are also many Chinese Americans in Boston. The city has a growing Chinatown.

Massachusetts also has several Native American communities. The Wampanoag people have reservations on Martha's Vineyard and Cape Cod. The Nipmuc tribe has reservations in central Massachusetts.
Languages Spoken in Massachusetts
Most people in Massachusetts speak English at home. However, many other languages are also spoken. Spanish is the most common non-English language. Portuguese, Chinese, and French are also widely spoken.

Beliefs and Faith: Religion in Massachusetts
Massachusetts was founded by Puritans in 1620. Today, most people in Massachusetts are Christians. About 34% are Roman Catholics. This is due to many immigrants from Catholic countries like Ireland and Italy. About 21% are Protestants.
There is also a significant Jewish population. Other religions like Buddhists, Hindus, and Muslims can also be found. About 32% of the population identifies as having no religion.
Learning and Knowledge: Education in Massachusetts
In 2018, Massachusetts's education system was ranked the best in the United States. It was the first state in North America to require towns to have a teacher or a school. This happened in 1647.
Massachusetts is home to some of the oldest schools in America. This includes the oldest public elementary school (The Mather School, founded 1639) and the oldest high school (Boston Latin School, founded 1635). It also has the oldest college (Harvard University, founded 1636).
Massachusetts spends a lot of money on its public schools. Its students perform very well in academics, ranking among the best in the world.
The state has 121 colleges and universities. Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) are both in Cambridge. They are consistently ranked among the world's best universities. Other highly ranked universities include Tufts University, Boston College, and Boston University.
The public University of Massachusetts (UMass) has five campuses. Its main campus is in Amherst. Massachusetts has the highest percentage of adults over 25 with a bachelor's degree or a graduate degree.
The Economy of Massachusetts
In 2020, Massachusetts's economy was worth $584 billion. The average income per person in 2012 was $53,221, making it the third-highest in the nation. As of January 2023, the state's general minimum wage is $15.00 per hour.
Many large companies are based in Massachusetts. These include Liberty Mutual, TJX Companies, and Raytheon. Massachusetts is often ranked as one of the most innovative states in America. It also has a high number of millionaires.
Boston-Logan International Airport is the busiest airport in New England. It serves millions of passengers each year.
Key parts of the Massachusetts economy include higher education, biotechnology, information technology, finance, healthcare, and tourism. The Route 128 corridor near Boston is a major center for venture capital and high technology. Tourism is also very important. Popular places to visit include Boston, Cape Cod, Salem, Plymouth, and the Berkshires. Massachusetts is the sixth-most popular state for foreign tourists.
Manufacturing still plays a role in the state's economy. It produces medical devices, paper goods, chemicals, and electronics.
Over 33,000 non-profit organizations in Massachusetts employ a large part of the state's workforce. In 2017, Massachusetts was ranked the best state in the U.S. based on many factors. These included healthcare, education, and the economy.
Farming and Agriculture
As of 2012, Massachusetts had 7,755 farms. These farms covered over 523,000 acres. Products like flowers, plants, and sod make up a big part of the state's farm output. Cranberries, sweet corn, and apples are also important crops. Massachusetts is the second-largest cranberry-producing state.
Taxes in Massachusetts
The amount of state and local taxes paid in Massachusetts is about average compared to other states. The state has a flat-rate personal income tax of 5.00%. There is also a 6.25% sales tax on most goods. However, groceries, clothing under $175, and periodicals are usually exempt.
Energy Use
Massachusetts's electricity generation market is competitive. This means customers can choose their electricity supplier. In 2018, Massachusetts used less energy per person than most states. About 31% of its energy came from natural gas. Massachusetts has been ranked as one of the most energy-efficient states.
Getting Around: Transportation in Massachusetts
The Massachusetts Department of Transportation handles statewide transportation planning. Transportation is the biggest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the state.
Public Transit in Cities
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA), also known as "The T", runs public transportation in the Metro Boston area. This includes subway, bus, and ferry systems.
Other regional transit authorities provide bus services in the rest of the state. There are also four heritage railways for tourists.
Trains and Buses for Long Distances
Amtrak operates several inter-city rail lines in Massachusetts. Boston's South Station is a major hub. From here, you can take trains to cities like New York City and Washington DC. Another station, North Station, has trains going north to Portland.
Amtrak also connects other cities in Massachusetts. For example, the Hartford Line connects Springfield to New Haven.
For longer trips, private bus companies like Peter Pan Bus Lines and Greyhound Lines offer frequent service.
The MBTA Commuter Rail serves the larger Greater Boston area. It connects Boston to towns like Worcester and Lowell. In the summer, the CapeFLYER train runs between Boston and Cape Cod.
Ferry Services
Many ports north of Cape Cod have ferry services. These ferries connect downtown Boston with towns like Hingham and Salem. There are also seasonal ferries between Boston and Provincetown.
On the southern coast, ferries connect Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket to mainland ports. These include Woods Hole and Hyannis. The Steamship Authority manages most of these services.
Freight Trains
Freight railroads also operate in Massachusetts. CSX is the largest company. Massachusetts has over 1,100 miles of freight tracks.
Air Travel

Boston Logan International Airport is the biggest airport in New England. It serves millions of passengers each year. Other airports include Hanscom Field and Worcester Regional Airport. Massachusetts has 39 public-use airfields. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) oversees air travel here.
Roads and Highways
Massachusetts has over 36,800 miles of highways. Interstate 90 (I-90) is the longest interstate in the state. It runs from west to east. Other major interstates include I-91 (north-south) and I-93 (through Boston). I-95 connects Providence, Rhode Island, with Greater Boston.
I-495 forms a large loop around the outer part of Greater Boston. Many interstates were built in the mid-1900s. Some projects, like the Big Dig in Boston, were very large and costly.
Major Cities and Towns
|
Largest cities or towns in Massachusetts
Source: |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Boston | 692,600 |
| 2 | Worcester | 185,428 |
| 3 | Springfield | 153,606 |
| 4 | Cambridge | 118,927 |
| 5 | Lowell | 110,997 |
| 6 | Brockton | 95,708 |
| 7 | New Bedford | 95,363 |
| 8 | Quincy | 94,470 |
| 9 | Lynn | 94,299 |
| 10 | Fall River | 89,541 |
Boston is the state capital and largest city. The Greater Boston area has over 4.8 million people. Other big cities with over 100,000 people include Worcester, Springfield, Lowell, and Cambridge. Plymouth is the largest town by land area.
Arts, Culture, and Fun in Massachusetts

Massachusetts has a rich history in American arts and culture. It has produced many famous writers, artists, and musicians. The state also has important museums and historical sites.
Massachusetts was a center for the Transcendentalist movement. This philosophy focused on intuition and connecting with nature. Ralph Waldo Emerson and Henry David Thoreau were key figures. Thoreau wrote Walden; or, Life in the Woods about his time living simply at Walden Pond.
Other famous authors from Massachusetts include Louisa May Alcott, Emily Dickinson, and Theodor Seuss Geisel. Famous painters like Winslow Homer and Norman Rockwell also came from here. Many of Rockwell's works are at the Norman Rockwell Museum.
Massachusetts is also important for performing arts. The Boston Symphony Orchestra and Boston Pops Orchestra are based here. Tanglewood in western Massachusetts is a famous music venue. It hosts music festivals and is the summer home for the Boston Symphony Orchestra.
The state has produced many popular music bands. These include Aerosmith, Boston, and the Pixies. Film festivals like the Boston Film Festival are also held here.

Massachusetts has many museums and historical sites. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston and the Clark Art Institute are major art museums. Historical sites include the Springfield Armory National Historic Site and Boston's Freedom Trail. These sites preserve places important to the American Revolution. Plymouth Rock marks where the Pilgrims landed.
Plimoth Plantation and Old Sturbridge Village are "living museums." They show what life was like in the 17th and 19th centuries.

Popular events include Boston's St. Patrick's Day parade and "Harborfest." Harborfest is a week-long Fourth of July celebration. The Boston Marathon is also a very famous annual event.
For outdoor fun, Massachusetts has long hiking trails like the Appalachian Trail. Other activities include sailing, fishing, whale watching, skiing, and hunting.
Media and News in Massachusetts
Massachusetts has two main television markets. The Boston/Manchester area is one of the largest in the U.S. WGBH-TV in Boston is a major public television station. It produces national shows like Nova and Frontline.
The largest daily newspapers are The Boston Globe, Boston Herald, and Springfield Republican. There are also many local newspapers. Many radio stations serve Massachusetts. Some colleges and universities also have their own TV and radio stations.
Sports in Massachusetts

Massachusetts is home to five major professional sports teams:
- The Boston Celtics (NBA basketball)
- The Boston Red Sox (MLB baseball)
- The Boston Bruins (NHL hockey)
- The New England Patriots (NFL football)
- The New England Revolution (MLS soccer)
Basketball and volleyball were both invented in Massachusetts cities. Basketball was invented in Springfield. Volleyball was invented in Holyoke. The Basketball Hall of Fame is in Springfield. The Volleyball Hall of Fame is in Holyoke.
Many universities in Massachusetts have strong sports teams. These include Boston College and the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Massachusetts also hosts major rowing events like the Head of the Charles Regatta. Many big golf events have taken place here too.
The state has produced several successful Olympians. These include athletes in track and field, figure skating, swimming, gymnastics, and ice hockey.
See also
 In Spanish: Massachusetts para niños
In Spanish: Massachusetts para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |