South Island facts for kids
|
Te Waipounamu (Māori)
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Geography | |
| Location | Oceania |
| Coordinates | 43°59′S 170°27′E / 43.983°S 170.450°E |
| Archipelago | New Zealand |
| Area | 150,437 km2 (58,084 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 12th |
| Length | 840 km (522 mi) |
| Coastline | 5,842 km (3,630.1 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 3,724 m (12,218 ft) |
| Highest point | Aoraki / Mount Cook |
| Administration | |
|
New Zealand
|
|
| ISO 3166-2:NZ | NZ-S |
| Regions | 7 |
| Territorial authorities | 23 |
| Largest settlement | Christchurch (pop. 384,800) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Kiwi, South Islander |
| Population | 1,225,000 (June 2023) |
| Pop. density | 8.1 /km2 (21 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | European (82.8%), Māori (11.3%), Asian (10.3%), Pacific peoples (3.4%) |
The South Island (Māori: Te Waipounamu) is the largest of New Zealand's three main islands. Its Māori name, Te Waipounamu, means 'the waters of Greenstone'. The other main islands are the North Island and Stewart Island.
The South Island is surrounded by water. To the north is Cook Strait, and to the west is the Tasman Sea. The Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean are to the south. The Pacific Ocean borders the east.
This island covers about 150,437 square kilometers. This makes it the 12th largest island in the world. It makes up 56% of New Zealand's land area. The lower parts of the island have an oceanic climate.
The Southern Alps mountain range runs through the island. Aoraki / Mount Cook, New Zealand's highest peak, is here. It stands at 3,724 meters tall. The Kaikōura Ranges are in the northeast.
The Canterbury Plains are on the east side of the island. The West Coast has rugged shorelines like Fiordland. It also has many native forests and national parks. The famous Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers are also found here.
The main cities are Christchurch and Dunedin. The island's economy depends on farming, fishing, and tourism. Manufacturing and services are also important.
About 1.18 million people live in the South Island. This is about 24% of New Zealand's total population. In the 1860s, after gold was found, the South Island had more European people and wealth. But in the 1900s, more people moved to the North Island.
Contents
- Understanding the South Island's Name
- Māori Legends of the South Island
- A Look at South Island History
- Population and People of the South Island
- Economy and Energy in the South Island
- Fun and Travel: Tourism in the South Island
- Getting Around: Transport in the South Island
- Exploring South Island Geography
- South Island's Unique Natural History
- Education and Healthcare
- Culture and Community
- Images for kids
- See also
Understanding the South Island's Name

The island has been known as the South Island for many years. Its Māori name, Te Waipounamu, is also officially recognized. However, most people still use "South Island".
Te Waipounamu means "the Water(s) of Greenstone". It might have come from Te Wāhi Pounamu, meaning "the Place of Greenstone".
When Captain James Cook visited in 1769, he wrote down the name as "Toai poonamoo".
In the 1800s, some maps called it Middle Island or New Munster. The name South Island was sometimes used for today's Stewart Island / Rakiura. In 1907, it was decided that only "South Island" should be used.
In 2009, the New Zealand Geographic Board found that the South Island had no official name. After asking the public, the board officially named it South Island or Te Waipounamu in 2013.
People often say "the South Island" using "the". For example, "Christchurch is in the South Island." Maps and headings usually just say "South Island".
Because it's much bigger than the North Island but has fewer people, some residents jokingly call it the "mainland" of New Zealand.
Māori Legends of the South Island
The South Island is also known as Te Waka a Māui. This means "Māui's Canoe". In some Māori stories, the South Island was Māui's boat. The North Island was the giant fish he caught.
Different Māori iwi (tribes) sometimes use other names. Some call the South Island Te Waka o Aoraki. This refers to another Māori legend. In this story, Aoraki and his three brothers visited their mother, Papatūānuku (the earth mother). Their canoe crashed, turning into the island. The four brothers became the mountain ranges.
A Look at South Island History
Early History and Māori Settlement
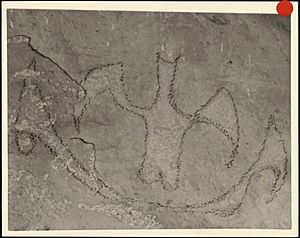
Charcoal drawings can be found in rock shelters in the central South Island. These drawings are between 500 and 800 years old. They show animals, people, and amazing creatures. Some birds pictured, like the moa, are now extinct. Early Māori drew them, but later Māori did not know their origins.
The early people of the South Island were the Waitaha. The Kāti Mamoe tribe later joined them through marriage and battles. In the 17th century, the Kāi Tahu tribe moved south. They also joined with the Kāti Mamoe.
Around this time, some Māori moved to the Chatham Islands. They developed a unique culture called Moriori. They focused on peace, which became a problem when Māori warriors arrived in the 1830s.
In the early 1700s, the Kāi Tahu tribe from the North Island moved to the northern South Island. They fought other tribes and moved south. By the 1730s, Kāi Tahu had settled in Canterbury. They then spread further south and to the West Coast.
In the 1820s and 1830s, there were battles between Ngāti Toa and Kāi Tahu tribes. Te Rauparaha, a Ngāti Toa leader, attacked Kāi Tahu at Kaikoura. He also captured a Kāi Tahu chief at Akaroa. Fighting continued, but Kāi Tahu eventually gained control. Peace was made between the tribes around 1839.
European Discovery and Settlement

The first Europeans to reach the South Island were from Dutch explorer Abel Tasman's crew in 1642. They anchored in Golden Bay. Tasman named it Moordenaar's Bay (Murderers Bay) after a clash with Māori. He called the islands Staten Landt. Later, Dutch mapmakers changed it to Nova Zeelandia.
James Cook later changed the name to New Zealand in 1769. The first European settlement in the South Island was at Bluff in 1823.
In 1827, French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville explored Tasman Bay. Many places there are named after him or his crew.
When Britain took over New Zealand in 1840, the South Island became part of New South Wales. This happened because France tried to colonize Akaroa. Also, the New Zealand Company wanted to start a separate colony.
In 1843, Māori and British settlers clashed at Wairau. This event, known as the Wairau Affray, was the first serious fight after the Treaty of Waitangi. Four Māori and 22 Europeans died.
The Otago Settlement began in 1848. It was supported by the Free Church of Scotland. The first immigrant ships arrived from Scotland.
While the North Island had the New Zealand Wars in the 1860s and 1870s, the South Island was mostly peaceful. In 1861, gold was found at Gabriel's Gully in Central Otago. This started a gold rush. Dunedin became the richest city in the country. Some people in the South Island wanted to be independent. In 1865, a vote to make the South Island independent failed.
In the 1860s, many Chinese men came to work in the goldfields. They faced hostility from white settlers. Laws were made to stop them from coming to New Zealand.
Recent Earthquakes in Canterbury
The September 2010 Earthquake
On September 4, 2010, a strong earthquake hit the South Island. It had a magnitude of 7.1. The quake happened at 4:35 AM local time. Its center was 40 kilometers west of Christchurch. No one died in this earthquake.
The earthquake damaged sewers, gas, and water pipes. Power was lost to 75% of Christchurch. The Christchurch Hospital had to use emergency power.
A state of emergency was declared in Christchurch. The city center was closed. A curfew was put in place. The New Zealand Army helped police. All schools were closed for a few days.
Christchurch International Airport closed but reopened later that day. The earthquake caused widespread damage. Many aftershocks followed. The total cost of damage was estimated at $11 billion.
The February 2011 Christchurch Earthquake

A powerful aftershock hit on February 22, 2011, at 12:51 PM. It had a magnitude of 6.3. Its center was near Lyttelton, 10 kilometers southeast of Christchurch. It was only 5 kilometers deep.
Even though it was a smaller magnitude, this quake was very strong. It caused huge damage because it was shallow and close to the city. About a third of the buildings in the city center had to be pulled down.
Unlike the 2010 quake, this one happened on a busy weekday afternoon. This, along with its strength, led to 181 deaths.
New Zealand declared its first National State of Emergency. Many buildings were badly damaged. This included the famous Christchurch Cathedral.
Other countries quickly offered help. Search and Rescue teams came from Australia, the United States, and other nations. The Royal New Zealand Navy also helped.
The runway at Christchurch Airport was fine. Air New Zealand offered cheap flights for people to leave the city. Thousands of people temporarily moved away. On March 1, a week after the quake, New Zealand observed a two-minute silence.
The June 2011 Christchurch Earthquake
On June 13, 2011, Christchurch was hit again. A magnitude 5.7 quake struck around 1:00 PM. A magnitude 6.3 quake followed at 2:20 PM. It was similar to the February quake, 6 kilometers deep.
Phone lines and power were lost in some areas. Liquefaction, where the ground turns to liquid, happened in eastern parts of the city. Many people in Sumner left their homes.
More buildings in the city center were damaged. About 75 more buildings needed to be demolished. The Christchurch Cathedral lost its beautiful rose window. This made it less likely the cathedral could be fully restored.
Only one person died in this quake, but many were injured.
Population and People of the South Island
Population Growth and Distribution
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1991 | 852,843 | — |
| 1996 | 899,382 | +1.07% |
| 2001 | 906,759 | +0.16% |
| 2006 | 1,022,313 | +2.43% |
| 2013 | 1,058,058 | +0.49% |
| 2018 | 1,149,564 | +1.67% |
| 2023 | 1,185,282 | +0.61% |
The South Island has a smaller population than the North Island. It is also less diverse. As of 2023, about 1,185,282 people live here.
The population has grown by about 80,745 people since 2018. About 17.1% of people are under 15 years old. 19.0% are aged 15 to 29. 45.5% are 30 to 64, and 18.5% are 65 or older.
In the early days of European settlement, the South Island had more people than the North Island. This was partly due to the Otago Gold Rush in the 1860s. Since then, the South Island's share of the population has decreased. Now, the North Island's largest city, Auckland, has more people than the entire South Island. However, this difference has stayed about the same in recent years.
Culture and Identity

Most South Islanders identify as European (82.8%). Other groups include Māori (11.3%), Asian (10.5%), and Pacific peoples (3.4%). People can identify with more than one group.
Europeans are the majority in all South Island areas. This ranges from 75.9% in Christchurch to 92.1% in the Waimakariri district.
About 21.4% of South Islanders were born overseas. The most common birthplaces are England, Australia, the Philippines, China, and India.
About 48.6% of South Islanders are Christian. 3.1% follow other religions. 45.8% do not follow a religion. Anglicanism, Catholicism, and Presbyterianism are the largest Christian groups. These numbers vary by region. For example, Dunedin was founded by Scottish Presbyterians. Christchurch was founded by English Anglicans.
Major Towns and Cities
The South Island is mostly rural or natural reserves. However, there are 15 urban areas with more than 10,000 people.
| Name | Population (June 2023) |
% of island |
|---|---|---|
| Christchurch | 384,800 | 31.4% |
| Dunedin | 106,200 | 8.7% |
| Nelson | 51,900 | 4.2% |
| Invercargill | 51,000 | 4.2% |
| Blenheim | 30,500 | 2.5% |
| Rolleston | 29,600 | 2.4% |
| Queenstown | 29,000 | 2.4% |
| Timaru | 28,900 | 2.4% |
| Ashburton | 20,800 | 1.7% |
| Rangiora | 19,600 | 1.6% |
| Richmond | 19,200 | 1.6% |
| Mosgiel | 14,800 | 1.2% |
| Oamaru | 14,000 | 1.1% |
| Kaiapoi | 13,600 | 1.1% |
| Wānaka | 12,400 | 1.0% |
Economy and Energy in the South Island
Economic Activities
The South Island's economy mainly relies on tourism and primary industries. These include farming and fishing. Other important industries are manufacturing, mining, and construction. Energy supply, education, health, and community services also play a big part.
The total economic output of the South Island was about NZ$78.94 billion in 2022. This was 21.9% of New Zealand's total economy. The average economic output per person was about $65,875.
Energy Production
The South Island is a major center for making electricity. Most of this comes from hydroelectricity, especially in the southern part of the island. In 2010, the island made 41.5% of New Zealand's total electricity.
Almost all (98.7%) of the island's electricity comes from hydro power. This is mainly from the Waitaki, Clutha, and Manapouri schemes. The rest comes from wind power. Most of the electricity is used on the island. However, a lot is sent to the North Island through the HVDC Inter-Island link.
Drilling for oil and gas off the coast is becoming more important. Companies are exploring for oil in the Canterbury Basin near Dunedin. The Great South Basin is also a large area for oil and gas. It covers an area 1.5 times New Zealand's landmass.
Fun and Travel: Tourism in the South Island
Tourism brings a lot of money to the South Island. Popular activities include sightseeing and adventure tourism. You can go glacier climbing or bungy jumping. Hiking and kayaking are also popular.
More direct international flights to Christchurch, Dunedin, and Queenstown have brought more tourists.
Top tourist spots include Fiordland National Park, Abel Tasman National Park, and Westland Tai Poutini National Park. Also popular are Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park, Queenstown, Kaikōura, and the Marlborough Sounds. These are among the top 10 places to visit in New Zealand.
Ski Areas and Resorts
Here is a list of ski areas and resorts in the South Island:
| Name | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Awakino ski area | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Broken River | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Cardrona Alpine Resort | Otago | |
| Coronet Peak | Otago | |
| Craigieburn Valley | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Fox Peak | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Hanmer Springs Ski Area | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Invincible Snowfields | Otago | Helicopter access only |
| Mount Cheeseman | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Mount Dobson | Canterbury | |
| Mount Hutt | Canterbury | |
| Mount Olympus | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Mount Potts | Canterbury | Heliskiing and snowcatting only |
| Mount Robert | Tasman | Club Skifield |
| Ohau | Canterbury | |
| Porter Ski Area | Canterbury | |
| Rainbow | Tasman | |
| The Remarkables | Otago | |
| Round Hill | Canterbury | |
| Snow Farm | Otago | cross-country skiing |
| Snow Park | Otago | |
| Haupapa / Tasman Glacier | Canterbury | Heliskiing |
| Temple Basin | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Treble Cone | Otago |
Getting Around: Transport in the South Island
Roads and Highways
The South Island has a State Highway network that is 4,921 kilometers long. These roads connect towns and cities across the island.
Trains and Railways
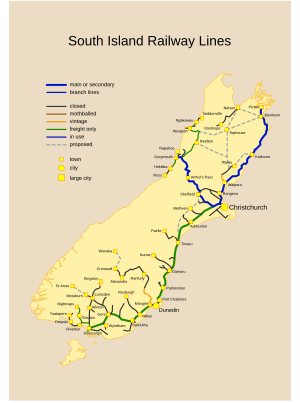
The South Island's railway network has two main lines. The Main North Line goes from Picton to Christchurch. The Main South Line goes from Lyttelton to Invercargill. These two lines make up the South Island Main Trunk Railway.
The Midland Line connects to the Main South Line in Rolleston. It goes through the Southern Alps via the Otira Tunnel to the West Coast. It ends in Greymouth.
Passenger trains used to be very common. Now, they are limited to the Coastal Pacific from Christchurch to Picton. The TranzAlpine goes from Christchurch to Greymouth. The Southerner train between Christchurch and Invercargill stopped running in 2002.
The South Island was the last place in New Zealand to use steam locomotives. The last steam-powered train ran on October 26, 1971.
Water Travel

The South Island is separated from the North Island by Cook Strait. This strait is 24 kilometers wide at its narrowest point. A ferry trip across it is 70 kilometers long.
Dunedin was once the home of the Union Steam Ship Company. This was the largest shipping company in the Southern Hemisphere.
Ports and Harbours
- Container ports: Lyttelton (Christchurch), Port Chalmers (Dunedin)
- Other ports: Nelson, Picton, Westport, Greymouth, Timaru, Bluff.
- Harbours: Akaroa Harbour, Otago Harbour, Halfmoon Bay (Stewart Island / Rakiura), Milford Sound / Piopiotahi.
- Freshwater ports: Queenstown and Kingston (Lake Wakatipu), Te Anau and Manapouri (Lake Manapouri)
Air Travel
Airports in the South Island


| Location | ICAO | IATA | Airport name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandra | NZLX | ALR | Alexandra Aerodrome |
| Ashburton | NZAS | ASG | Ashburton Aerodrome |
| Blenheim | NZWB | BHE | Blenheim Airport (Woodbourne) |
| Christchurch | NZCH | CHC | Christchurch International Airport (long-distance) |
| Dunedin | NZDN | DUD | Dunedin Airport (limited) |
| Greymouth | NZGM | GMN | Greymouth Aerodrome |
| Hokitika | NZHK | HKK | Hokitika Airport |
| Invercargill | NZNV | IVC | Invercargill Airport |
| Kaikōura | NZKI | KBZ | Kaikoura Aerodrome |
| Milford Sound | NZMF | MFN | Milford Sound Airport |
| Aoraki / Mount Cook | NZMC | MON | Mount Cook Aerodrome |
| Nelson | NZNS | NSN | Nelson Airport |
| Oamaru | NZOU | OAM | Oamaru Aerodrome |
| Queenstown | NZQN | ZQN | Queenstown Airport (limited) |
| Timaru | NZTU | TIU | Richard Pearse Airport |
| Wānaka | NZWF | WKA | Wānaka Airport |
| Westport | NZWS | WSZ | Westport Airport |
Exploring South Island Geography

The South Island is New Zealand's largest landmass. It covers 150,437 square kilometers. The Southern Alps run along its length. Aoraki/Mount Cook is the highest peak at 3,754 meters. There are 18 peaks over 3,000 meters tall.
The Canterbury Plains are on the east side. The West Coast is known for its rugged shorelines like Fiordland. It also has many native forests and the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers.
The beautiful scenery of the South Island has made it a popular place for movies. Parts of The Lord of the Rings trilogy were filmed here. The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe also used its landscapes.
Climate and Weather
The climate in the South Island is mostly temperate. The average temperature is 8 °C (46 °F). January and February are the warmest months. July is the coldest.
Temperatures can vary a lot. The highest recorded temperature was 42.4 °C (108.3 °F) in Rangiora. The lowest was −21.6 °C (−6.9 °F) in Ophir.
Rainfall also varies greatly. The West Coast gets a lot of rain. The Mackenzie Basin in Canterbury is very dry. Most areas get between 600 and 1600 mm of rain each year. Christchurch is the driest city, with about 640 mm of rain. Invercargill is the wettest, with about 1,150 mm.
The southern parts of the island are cooler and cloudier. They get about 1,400–1,600 hours of sunshine a year. The northern and northeastern parts are sunnier. They receive about 2,400–2,500 hours of sunshine.
Amazing Natural Features
Fiords of the South Island

The South Island has 15 named maritime fiords. They are all in the mountainous Fiordland area in the southwest. In New Zealand, these are spelled 'fiord'. However, they are often called 'Sound' in their names.
Many lakes in Fiordland and Otago also fill glacial valleys. Lake Te Anau has three arms that are fiords. Lake McKerrow is a fiord with a mouth filled with silt. Lake Wakatipu fills a large glacial valley.
The Marlborough Sounds are deep inlets on the northern coast. These are actually rias, which are drowned river valleys.
Glaciers of the South Island
Most of New Zealand's glaciers are in the South Island. They are usually found in the Southern Alps.
In the 1980s, there were about 3,155 glaciers in the South Island. About a sixth of these were larger than 10 hectares. Famous ones include the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers on the West Coast. The Tasman, Hooker, and Mueller glaciers are in the east.
Lakes of the South Island
New Zealand has about 3,820 lakes larger than one hectare. Much of the South Island's high country was covered by ice during past ice ages. Glaciers carved out large valleys. They also left piles of moraine (rocks and soil) that formed natural dams. When the glaciers melted, they left basins that became lakes.
The South Island has 8 of New Zealand's 10 biggest lakes. These include Lake Wakatipu, Lake Tekapo, and Lake Manapouri. The deepest lake is Lake Hauroko, at 462 meters deep. It is the 16th deepest lake in the world. Millions of years ago, Central Otago had a huge lake called Lake Manuherikia. Fossils of fish and crocodiles have been found there.
Volcanoes of the South Island

There are four extinct volcanoes on the South Island's east coast.
Banks Peninsula is the most famous volcanic feature. It is made of two old shield volcanoes, Lyttelton and Akaroa. These volcanoes formed about 8 to 11 million years ago. They were once offshore islands, rising about 1,500 meters above sea level. Their craters now form Lyttelton and Akaroa Harbours.
The Canterbury Plains formed from the erosion of the Southern Alps. The Port Hills, near Christchurch, are part of the old volcano rim.
The Otago Harbour was formed from a giant shield volcano. Its remains can be seen in the basalt hills around Port Chalmers. The last eruptions ended about 10 million years ago. This left the peak of Mount Cargill.
Timaru was built on hills made from lava flows. These came from the extinct Mount Horrible, which erupted thousands of years ago.
Te Wāhipounamu World Heritage Site
Te Wāhipounamu is a World Heritage site in the southwest South Island. Its Māori name means "the place of greenstone".
It was added to the World Heritage List in 1990. It covers 26,000 square kilometers. It includes Aoraki/Mount Cook, Fiordland, Mount Aspiring, and Westland National Parks.
This site is important because it shows some of the best examples of original plants and animals from Gondwanaland.
Protected Natural Areas
Forest Parks

There are six forest parks in the South Island. These are public lands managed by the Department of Conservation.
National Parks
The South Island has ten national parks. These are managed by the Department of Conservation.
From north to south, the National Parks are:
- Abel Tasman National Park
- Kahurangi National Park
- Nelson Lakes National Park
- Paparoa National Park
- Arthur's Pass National Park
- Westland Tai Poutini National Park
- Aoraki/Mount Cook National Park
- Mount Aspiring National Park
- Fiordland National Park
- Rakiura National Park (on Stewart Island, south of the South Island)
Other native reserves and parks include the Hakatere Conservation Park.
South Island's Unique Natural History
Birds of the South Island

Many bird species live only in the South Island. These include the kea, a mountain parrot. Other unique birds are the great spotted kiwi and the Okarito brown kiwi. You can also find the South Island kōkako and the South Island pied oystercatcher.
Other special birds are the Malherbe's parakeet and the king shag. The takahe, black-fronted tern, South Island robin, rock wren, wrybill, and yellowhead also live here.
Many South Island bird species are now extinct. This is mainly due to hunting by humans. Also, cats and rats brought by humans hunted them. Extinct species include the South Island goose and the South Island giant moa. The huge harpagornis and the South Island piopio are also gone.
Education and Healthcare
Learning Opportunities: Tertiary Education
The South Island has three universities and five polytechnic schools.
- Ara Institute of Canterbury
- Nelson Marlborough Institute of Technology
- Otago Polytechnic
- Southern Institute of Technology
- Tai Poutini Polytechnic
- University of Canterbury
- Lincoln University
- University of Otago
Since 2020, the polytechnics are part of the New Zealand Institute of Skills and Technology.
Staying Healthy: Healthcare Services

Healthcare in the South Island is provided by five District Health Boards (DHBs). These boards cover different geographical areas.
There are six major hospitals in the South Island. These are Christchurch Hospital, Dunedin Hospital, Grey Base Hospital (Greymouth), Nelson Hospital, Southland Hospital (Invercargill), and Timaru Hospital. Christchurch Hospital and Dunedin Hospital are the main specialist hospitals.
Emergency Medical Services
Several air ambulance and rescue helicopter services operate in the South Island. These services help people in emergencies.
Culture and Community
Art and Creativity
The South Island has many talented artists. Famous artists like Frances Hodgkins and Colin McCahon came from here.
The University of Canterbury School of Fine Arts started in 1950.
South Island Art Galleries include:
- Centre of Contemporary Art
- Christchurch Arts Centre
- Dunedin Public Art Gallery
Language and Dialects
Parts of the South Island, especially Southland and southern Otago, are known for a special way of speaking. This is called the "Southland burr". It is a Scottish-influenced dialect of English.
Media: News and Entertainment
Newspapers
The South Island has ten daily newspapers. It also has many weekly community newspapers. Major daily papers include the Ashburton Guardian and the Otago Daily Times. The Press and the Otago Daily Times are the biggest newspapers.
Television
The South Island has seven local TV stations. These stations broadcast only in one region or city. They show local news, community programs, and tourist information.
Radio Stations
Many radio stations serve communities across the South Island. Some are independent. Others are owned by larger companies like Radio New Zealand.
Museums to Explore
- Bluff Maritime Museum
- Canterbury Museum (currently closed for renovations)
- Ferrymead Heritage Park
- Nelson Provincial Museum
- Olveston House
- Otago Museum
- Otago Settlers Museum: Toitū
- Royal New Zealand Air Force Museum
- Southland Museum and Art Gallery
- World of Wearable Art
- Yaldhurst Museum
Sports and Recreation

The South Island has many professional sports teams. Rugby union and cricket are very popular. The Crusaders and Highlanders rugby teams represent the island.
In cricket, the South Island is represented by the Canterbury Wizards, Central Stags, and Otago Volts.
The South Island also has teams in basketball, soccer, ice hockey, and netball.
The North vs South match is a long-standing rugby game in New Zealand. The first game was in 1897.
Christchurch hosted the 1974 Commonwealth Games.
Images for kids
-
Ships in what is likely to be Akaroa Harbour some time in the early 19th century.
-
Benmore Dam is the largest of eight dams within the Waitaki power scheme and was commissioned in 1965.
See also
 In Spanish: Isla Sur para niños
In Spanish: Isla Sur para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |