Mexico facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
United Mexican States
Estados Unidos Mexicanos (Spanish)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem:
Himno Nacional Mexicano |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Mexico City 19°26′N 99°8′W / 19.433°N 99.133°W |
| Official languages | Spanish (de facto) |
| Co-official languages |
|
| Ethnic groups | See below |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Mexican |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Claudia Sheinbaum | |
| Gerardo Fernández Noroña | |
| Sergio Gutiérrez Luna | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Independence
from Spain
|
|
| 16 September 1810 | |
|
• Declared
|
27 September 1821 |
| 28 December 1836 | |
|
• First constitution
|
4 October 1824 |
|
• Second constitution
|
5 February 1857 |
| 5 February 1917 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi) (13th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.58 (as of 2015) |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
61/km2 (158.0/sq mi) (142nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | ▼ 40.2 medium |
| HDI (2023) | high · 77th |
| Currency | Mexican peso (MXN) |
| Time zone | UTC−8 to −5 (See Time in Mexico) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−7 to −5 (varies) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +52 |
| ISO 3166 code | MX |
| Internet TLD | .mx |
|
|
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially known as the United Mexican States (Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is a large country in North America. It is located south of the United States and borders Guatemala and Belize to the south. Mexico has long coastlines on both the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
People from Mexico are called Mexicans. Most Mexicans speak Spanish. However, many also speak Native American languages like Nahuatl, Maya, and Zapotec. The capital and largest city of Mexico is Mexico City.
Contents
Exploring Mexico's Past
Before Europeans arrived, many amazing Native American cultures thrived in Mexico.
Ancient Civilizations of Mexico
The earliest known culture was the Olmecs in the south. They are famous for their huge stone heads. On the Yucatán peninsula, the Mayans built powerful city-states ruled by kings. The Mayans were strongest between 200 and 900 A.D.
Another important empire was Teotihuacan. It was a very large city, one of the biggest in the world at that time. After Teotihuacan declined, the Toltecs became powerful. Their influence reached from the southern U.S. to Costa Rica. A famous Toltec god was Quetzalcoatl. The Toltec culture also declined, and the Aztecs took over. The Aztecs called their empire Mexico. A well-known Aztec ruler was Moctezuma II.
Arrival of the Spanish
In 1519, the Spanish explorer Hernán Cortés arrived in Mexico. The Aztecs believed he might be the god Quetzalcoatl returning, so they did not fight him at first. Cortés made friends with the Aztecs' enemies. In 1521, they conquered the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. The Aztec Empire then became part of Spain, known as New Spain.
Mexico's Fight for Independence
In 1810, a Mexican priest named Miguel Hidalgo began the Mexican War of Independence. By 1821, the Spanish left, and Mexico became an independent country. The first leader was Agustin de Iturbide, who became emperor of the First Mexican Empire. But people were not happy, and in 1823, Mexico became a republic.
Challenges in the 19th Century
Antonio López de Santa Anna was a very important figure in early 19th-century Mexico, serving as president 11 times. When he became a dictator, Texas declared independence in 1836. The Battle of the Alamo was part of this Texas Revolution. Between 1846 and 1848, Mexico fought a war against the United States. Mexico lost large northern areas, which became part of the southwestern United States. After this war, Santa Anna was sent away.
From 1858 to 1861, Mexico had another war between liberals and conservatives. The liberal leader Benito Juárez won and became president. Juárez remained president until France invaded Mexico and made Maximilian of Habsburg emperor. But Maximilian was not popular. After more fighting, he was executed in 1867, and Juárez became president again.
The Mexican Revolution and Beyond
In 1876, Porfirio Díaz, a general who had fought the French, became president. He made the country richer, but poor people became even poorer. This led to Francisco I. Madero starting the Mexican Revolution in 1910.
For the next 10 years, Mexico was in chaos with many leaders and groups fighting. Famous figures from this time include Emiliano Zapata, Pancho Villa, and Francisco I. Madero. The fighting calmed down when Álvaro Obregón became president in 1920.
In 1929, President Plutarco Elías Calles founded the National Mexican Party, which later became the Institutional Revolutionary Party, or PRI. This party ruled Mexico for a very long time. Many PRI presidents were not popular. An exception was President Lázaro Cárdenas, who served from 1934 to 1940.
Over time, more people became unhappy with the PRI. In 1968, security forces shot at protesters, leading to many deaths in what became known as the Tlatelolco massacre. Another uprising happened in 1994 when Zapatistas rebelled in Chiapas.
The PRI stayed in power until 2000, when Vicente Fox of the National Action Party (PAN) was elected president. This ended the PRI's 71 years of rule.
In 2024, Claudia Sheinbaum won the presidential election. She became the first woman to lead Mexico when she took office on October 1, 2024.
Mexico's Diverse Geography
Mexico is a large country in the southern part of North America. It covers about 1,972,550 square kilometers (761,606 square miles), making it the 13th largest country in the world.
Land and Water Features
Mexico has coastlines on the Pacific Ocean, the Gulf of California, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. These last two are part of the Atlantic Ocean. Mexico also has about 6,000 square kilometers (2,317 square miles) of islands.
Most of Mexico's central and northern areas are at high altitudes. The highest mountains are in the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, which crosses Mexico from east to west. These include Pico de Orizaba (5,700 meters or 18,700 feet), Popocatépetl (5,462 meters or 17,920 feet), and Iztaccihuatl (5,286 meters or 17,343 feet).
Two large mountain ranges, the Sierra Madre Oriental and Sierra Madre Occidental, run from north to south. A third range, the Sierra Madre del Sur, runs from Michoacán to Oaxaca. Mexico also has many volcanoes.
Regions and Rivers
Mexico has nine main regions, including Baja California, the Mexican Plateau, and the Yucatán Peninsula. The Yucatán Peninsula is home to the Chicxulub crater, which scientists believe was caused by the impact that led to the extinction of the dinosaurs.
Even though Mexico is large, much of its land is not good for farming due to dry conditions or difficult terrain. About 54.9% of the land is used for agriculture. Mexico has several rivers, with the longest being the Rio Grande, which forms part of the border with the United States. The Usumacinta River forms part of the southern border with Guatemala.
Mexico's Climate Zones
Mexico's climate varies a lot because of its size and mountains. The Tropic of Cancer divides the country into two main climate zones: temperate (cooler winters) to the north and tropical (constant temperatures year-round) to the south.
Many parts of northern Mexico are dry with little rain. However, tropical lowlands in the south can get more than 2,000 millimeters (79 inches) of rain each year. Cities in the north like Monterrey can reach temperatures of 40°C (104°F) or more in summer. In the Sonoran Desert, temperatures can even go above 50°C (122°F).
Mexico has 7 major climate types. Most of the country has a temperate to dry climate. Coastal areas south of the Tropic of Cancer have warm, humid climates with average temperatures between 24°C and 28°C (75°F and 82°F) all year. Both Mexican coasts can experience strong hurricanes during summer and fall.
Amazing Biodiversity in Mexico
Mexico is one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries, meaning it has a huge variety of life. It ranks fourth globally in biodiversity, being home to 10–12% of all species on Earth!
Rich Animal and Plant Life
Mexico has the most reptile species in the world (707 known species). It ranks second for mammals (438 species) and fourth for amphibians (290 species). It also has 26,000 different plant species. Overall, Mexico is considered the second country in the world for ecosystems and fourth for total species.
About 2,500 species are protected by Mexican laws. Sadly, Mexico has faced issues with Deforestation and soil erosion, especially in rural areas. However, environmental protection laws have improved in major cities.
Protected Areas and Native Foods
Mexico has 170,000 square kilometers (65,637 square miles) of "Protected Natural Areas." These include 34 biosphere reserves, 67 national parks, and other protected zones.
Many plants that are now grown worldwide actually came from Mexico. Some native Mexican foods include maize (corn), tomato, beans, squash, chocolate, vanilla, avocado, guava, and many types of chiles like habanero and jalapeño. Many of these names come from the Nahuatl language.
How Mexico is Governed
Mexico is a constitutional federal democracy. This means it has a written constitution and a government where people vote for their leaders.
The President and Congress
The president is elected every 6 years and leads the country. The president is the head of state and government, and also the commander-in-chief of the military. The president chooses the Cabinet and can reject new laws.
Mexico's federal legislature is called the Congress of the Union. It has two parts: the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. The Congress makes federal laws, declares war, sets taxes, approves the national budget, and agrees to international treaties.
The Chamber of Deputies has 500 members. The Senate has 128 members. Both are elected through a mix of direct voting and proportional representation.
The Judicial System
The highest court in Mexico is the Supreme Court of Justice. It has eleven judges chosen by the president and approved by the Senate. The Supreme Court interprets laws and handles federal cases. Other courts also help make sure laws are followed fairly.
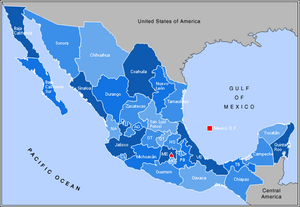
Mexico's States and Capital
Mexico is divided into 32 states, including Mexico City, which is the capital. Each state has its own government, but they are all part of the federal republic.
- 1. Aguascalientes
- 2. Baja California
- 3. Baja California Sur
- 4. Campeche
- 5. Chiapas
- 6. Chihuahua
- 7. Coahuila
- 8. Colima
- 9. Durango
- 10. Guanajuato
- 11. Guerrero
- 12. Hidalgo
- 13. Jalisco
- 14. Mexico
- 15. Michoacan
- 16. Morelos
- 17. Nayarit
- 18. Nuevo Leon
- 19. Oaxaca
- 20. Puebla
- 21. Queretaro
- 22. Quintana Roo
- 23. San Luis Potosí
- 24. Sinaloa
- 25. Sonora
- 26. Tabasco
- 27. Tamaulipas
- 28. Tlaxcala
- 29. Veracruz
- 30. Yucatán
- 31. Zacatecas
- 32. Mexico City
The People of Mexico
Mexico is the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world. It is also the second most populous country in Latin America, after Brazil.
Ethnic Backgrounds and Languages
About 60% of Mexicans have both Native American and European ancestors; these are called mestizos. Nearly 30% of Mexicans are of pure Native American descent, and 10% are of European descent.
Most Mexicans (90%) speak Spanish. However, about 10% of Mexicans speak one of the 68 recognized Native American languages. Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs, is the most widely spoken indigenous language, followed by Yucatec Maya. English is the most commonly taught foreign language in Mexico.
Religion in Mexico
Most people in Mexico are Roman Catholic (89%). About 6% are Protestant.
Mexico's Economy
Mexico has a strong and growing economy, especially in manufacturing.
Key Industries
The electronics industry in Mexico has grown a lot in the last ten years. Mexico has the sixth largest electronics industry in the world. It is the second largest exporter of electronics to the United States. Mexican factories make televisions, computers, mobile phones, and other electronic devices. Electronics make up 30% of Mexico's exports.
Mexico also produces more automobiles than any other North American country. Big car companies like General Motors, Ford, Chrysler, Volkswagen, and Nissan have factories in Mexico. Many new car plants have opened recently, bringing in billions of dollars in investment.
Tourism in Mexico
Mexico is one of the most visited countries in the world. It is the most visited country in the Americas after the United States.
Popular Attractions
Tourists love Mexico for its ancient Mesoamerican ruins, lively cultural festivals, beautiful colonial cities, nature reserves, and stunning beach resorts. Mexico's varied climates, from temperate to tropical, and its unique culture (a mix of European and Mesoamerican influences) make it a very attractive place to visit.
The busiest times for tourism are in December and mid-summer. There are also many visitors during the week before Easter and Spring break, especially college students from the United States who visit the beach resorts.
Mexican Culture and Traditions
Mexican culture is a rich blend of its long history, including Native American traditions and three centuries of Spanish rule.
Artistic Expressions
Painting is one of Mexico's oldest art forms, with cave paintings dating back 7,500 years. Ancient Mexican art can be seen in buildings, caves, and old books. Examples include the Maya murals of Bonampak and the murals in Teotihuacán.
During the colonial era, religious paintings were very important. Later, in the 18th century, portraits and paintings showing different racial groups became popular. Important painters from this time include Juan Correa and Miguel Cabrera.
In the 20th century, artists like Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siqueiros, and José Clemente Orozco became world-famous for their large murals on public buildings. These murals often showed Mexican history and culture. Frida Kahlo is another very important Mexican artist, known for her personal portraits.
Today, Mexico City has one of the highest numbers of art museums in the world, showcasing both traditional and modern art.
Architectural Wonders
The architecture of ancient Mexican civilizations changed over time, from simple to very complex. Teotihuacan, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a great example of ancient pyramid building. Maya cities show how large urban centers were built to fit into the thick jungle.
When the Spanish arrived, they brought European architectural styles, often mixed with Arab influences. Many monasteries were built with Romanesque, Gothic, or Mudéjar elements. Later, Baroque styles became popular for cathedrals and public buildings.
In the 19th century, after Mexico gained independence, neoclassical styles became common. In the 20th century, Mexican modernist architecture developed, especially seen in the Ciudad Universitaria, Mexico City, the main campus of the National Autonomous University of Mexico. This campus is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Architects like Luis Barragán, who won the Pritzker Prize (the highest award in architecture), combined traditional Mexican styles with modern design.
Delicious Mexican Cuisine
Modern Mexican cuisine began during the Spanish colonial era, mixing Spanish foods with native ingredients. Foods native to Mexico include corn, peppers, squash, avocados, sweet potato, turkey, and many types of beans. Some cooking methods, like nixtamalization of corn, also come from ancient peoples.
The Spanish brought pork, beef, chicken, sugar, milk, wheat, rice, and citrus fruits. From this mix came dishes like pozole, mole sauce, barbacoa, and tamales. Drinks like atole and aguas frescas were also created.
In 2010, Mexican food was recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible cultural heritage. This shows how important and unique Mexican cooking is to the world.
Literature and Storytelling
Mexican literature has roots in the ancient writings of Mesoamerica. Aztec poetry was often sung or chanted. Nezahualcoyotl is a well-known pre-Columbian poet.
After the Spanish conquest, historical stories were written. In the 17th century, famous writers included Juan Ruiz de Alarcón and Juana Inés de la Cruz, known as the "Ten Muse."
In modern times, important writers include Octavio Paz, who won the Nobel Prize in Literature, and Carlos Fuentes. Other notable authors are Elena Poniatowska and Juan Rulfo.
Mexican Cinema
Mexican films from the "Golden Age" in the 1940s and 1950s were very popular across Latin America and Europe. María Candelaria (1943) won an award at the Cannes Film Festival. Famous actors from this time include María Félix and Pedro Infante.
More recently, Mexican directors like Alejandro González Iñárritu, Alfonso Cuarón, and Guillermo del Toro have become world-renowned, winning many awards for their films.
Music and Dance
Mexico has a long history of music, from ancient times to today. Much colonial-era music was for religious purposes.
Traditional Mexican music includes mariachi, banda, norteño, ranchera, and corridos. Corridos were especially popular during the Mexican Revolution. Today, many Mexicans listen to modern pop and rock music in both English and Spanish.
Folk dance of Mexico is very important and varies by region. The Ballet Folklórico de México, founded in 1952, performs traditional music and dances from different periods of Mexican history.
Sports in Mexico
Organized sports in Mexico became popular in the late 19th century, though bullfighting has a much longer history.
Popular Sports
Mexico's most popular sport is association football (soccer). Mexico City hosted the Olympic Games in 1968, making it the first Latin American city to do so. Mexico also hosted the 1970 FIFA World Cup and the 1986 FIFA World Cup. It will be the first country to host or co-host the men's World Cup three times when it co-hosts the 2026 FIFA World Cup with Canada and the United States.
Mexico is also very strong in professional boxing, having won many Olympic boxing medals. The Mexican professional baseball league is called the Liga Mexicana de Beisbol. Lucha Libre (freestyle professional wrestling) is also a huge crowd-pleaser.
Despite efforts to ban it, bullfighting remains a popular sport in Mexico. Plaza México in Mexico City is the largest bullring in the world, holding 45,000 people.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
View of the Pyramid of the Sun in the ancient city-state of Teotihuacan, which was the 6th largest city in the world at its peak (1 AD to 500 AD)
-
Mural by Diego Rivera depicting a view from the Tlatelolco markets into Mexico-Tenochtitlan, the largest city in the Americas at the time.
-
View of the Plaza Mayor (today Zócalo) in Mexico City (ca. 1695) by Cristóbal de Villalpando
-
Luis de Mena, Virgin of Guadalupe and castas, showing race mixture and hierarchy as well as fruits of the realm, ca. 1750
-
General Antonio López de Santa Anna
-
Portrait of Liberal President Benito Juárez
-
The Execution of Emperor Maximilian, 19 June 1867. Gen. Tomás Mejía, left, Maximiian, center, Gen. Miguel Miramón, right. Painting by Édouard Manet 1868.
-
Francisco I. Madero, who challenged Díaz in the fraudulent 1910 election and was elected president when Díaz was forced to resign in May 1911.
-
Revolutionary Generals Pancho Villa (left) and Emiliano Zapata (right)
-
NAFTA signing ceremony, October 1992. From left to right: (standing) President Carlos Salinas de Gortari (Mexico), President George H. W. Bush (U.S.), and Prime Minister Brian Mulroney (Canada)
-
Vicente Fox and his opposition National Action Party won the 2000 general election, ending one-party rule.
-
Mexico City, the financial center of Mexico
-
The Central Eólica Sureste I, Fase II in Oaxaca.
-
Large Millimeter Telescope in Puebla.
-
Cancún and the Riviera Maya is the most visited region in Latin America
-
The Baluarte Bridge was the highest cable-stayed bridge in the world, the fifth-highest bridge overall and is the highest bridge in the Americas.
-
Las castas. Casta painting showing 16 racial groupings, 18th century, Museo Nacional del Virreinato, Tepotzotlán, Mexico.
-
Mexico–United States barrier between San Diego's border patrol offices in California, USA (left) and Tijuana, Mexico (right)
-
Central Library of the National Autonomous University of Mexico
-
Octavio Paz, the only mexican awarded with the Nobel Prize in Literature
-
Mexican composer Carlos Chávez
-
Televisa headquarters in Mexico City
See also
 In Spanish: México para niños
In Spanish: México para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |