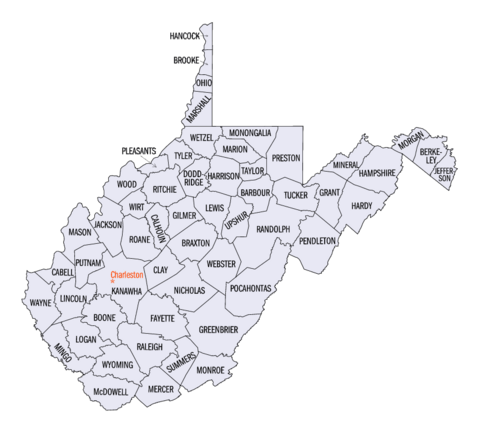
List of counties in West Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Counties of West Virginia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Location | State of West Virginia |
| Number | 55 |
| Populations | 5,000 (Wirt) – 174,805 (Kanawha) |
| Areas | 83 square miles (210 km2) (Hancock) – 1,040 square miles (2,700 km2) (Randolph) |
| Government | County government |
| Subdivisions | cities, towns, unincorporated communities, census designated place |
The U.S. state of West Virginia has 55 counties. Fifty of them existed at the time of the Wheeling Convention in 1861, during the American Civil War, when those counties seceded from the Commonwealth of Virginia to form the new state of West Virginia. West Virginia was admitted as a separate state of the United States on June 20, 1863. Five additional counties (Grant, Mineral, Lincoln, Summers, and Mingo) were formed from the original counties in the decades following admission.
After the Civil War, Berkeley County and Jefferson County, the two easternmost counties of West Virginia, refused to recognize their inclusion in the state, and the Virginia General Assembly passed legislation attempting to reclaim them. In March 1866, the United States Congress passed a joint mandate assenting to their inclusion in the new state, and the Supreme Court of the United States confirmed this outcome in the case of Virginia v. West Virginia (1871).
The West Virginia Constitution was ratified in 1872, replacing the state constitution created in 1863 when West Virginia became a state. Article 9, Section 8, of the West Virginia Constitution permits the creation of additional counties if a majority of citizens in the proposed new county vote for its creation and the new county has a minimum area of 400 square miles (1,036 km2) and a population of at least 6,000. Creation of a new county is prohibited if it would bring another county below these thresholds. Three counties (Greenbrier, Kanawha, and Randolph) have sufficient population (based on the 2020 United States Census) and land area to allow a new county to be split off. The remaining counties cannot be split, as either their land area would decrease to under 400 square miles, or their population would decrease to below 6,000.
The role of counties in local government had been minimized under the 1863 constitution, which vested most local government authority in a system of townships based on the New England model. The authors of the 1872 constitution chose to return to the system used in Virginia, in which each county was governed by a county court with combined authority for executive, legislative, and judicial functions of the county government. In 1880, West Virginia amended its constitution and replaced the county court system with an arrangement that divides county government powers between seven county offices, each of which is independently elected: the county commission, county clerk, circuit clerk, county sheriff, county assessor, county prosecuting attorney, and county surveyor of lands. Counties have only those powers that are expressly granted to them by the state Constitution or by state statute. These powers include, but are not limited to, maintaining the infrastructure of the state, funding libraries, maintaining jails and hospitals, and waste disposal. Reforming public education became a county function in 1933. In May 1933, a county unit plan was adopted. Under this plan, the state's 398 school districts were consolidated into the current 55 county school systems. This enabled public schools to be funded more economically and saved West Virginia millions of dollars.
Randolph County is the largest by area at 1,040 square miles (2,694 km2), and Hancock County is the smallest at 83 square miles (215 km2). Kanawha County contributed land to the founding of 12 West Virginia counties and has the largest population (174,805 in 2023). Wirt County has the smallest population (5,000 in 2023). The oldest county is Hampshire, established in 1754, and the newest is Mingo, established in 1895. Spruce Knob, located in Pendleton County, is the state's highest point at 4,863 feet (1,482 m). Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) codes, which are used by the United States government to identify counties uniquely, are five-digit numbers. For West Virginia, they start with 54 and end with the three-digit county code (for example, Barbour County has FIPS code 54001). Each county's code is provided in the table below, linked to census data for that county.
Counties
| County |
FIPS code | County seat | Est. | Origin | Etymology | Population | Area | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
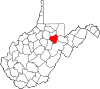
| Barbour County | 001 | Philippi | 1843 | Harrison, Lewis, and Randolph counties | Philip P. Barbour (1783–1841) United States Speaker of the House (1821–23) |
15,378 | 341 sq mi (883 km2) |
 |
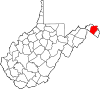
| Berkeley County | 003 | Martinsburg | 1772 | Frederick County (Virginia) | Norborne Berkeley (1717–70) Royal Governor of Virginia (1768–70) |
132,440 | 321 sq mi (831 km2) |
 |
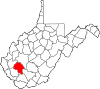
| Boone County | 005 | Madison | 1847 | Cabell, Kanawha, and Logan counties | Daniel Boone (1734–1820) American frontiersman |
20,576 | 503 sq mi (1,303 km2) |
 |
| Braxton County | 007 | Sutton | 1836 | Kanawha, Lewis, and Nicholas counties | Carter Braxton (1736–97) Signer of the Declaration of Independence |
12,162 | 514 sq mi (1,331 km2) |
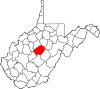 |
| Brooke County | 009 | Wellsburg | 1796 | Ohio County | Robert Brooke (1761–1800) Governor of Virginia (1794–96) |
21,373 | 89 sq mi (231 km2) |
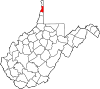 |
| Cabell County | 011 | Huntington | 1809 | Kanawha County | William H. Cabell (1772–1853) Governor of Virginia (1805–08) |
92,082 | 282 sq mi (730 km2) |
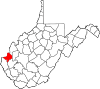 |
| Calhoun County | 013 | Grantsville | 1856 | Gilmer County | John C. Calhoun (1782–1850) United States Vice President (1825–32) |
5,959 | 281 sq mi (728 km2) |
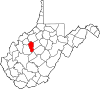 |
| Clay County | 015 | Clay | 1858 | Braxton and Nicholas counties | Henry Clay (1777–1852) United States Senator Kentucky (1823–25) United States Speaker of the House (1849–52) |
7,783 | 342 sq mi (886 km2) |
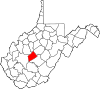 |
| Doddridge County | 017 | West Union | 1845 | Harrison, Lewis, Ritchie, and Tyler counties | Philip Doddridge (1773–1832) United States Congressman (Virginia) (1829–32) |
7,680 | 320 sq mi (829 km2) |
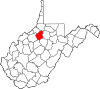 |
| Fayette County | 019 | Fayetteville | 1831 | Kanawha, Greenbrier, Logan, and Nicholas counties | Marquis de Lafayette (1757–1834) French-born American Revolutionary War General |
39,072 | 664 sq mi (1,720 km2) |
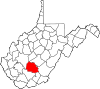 |
| Gilmer County | 021 | Glenville | 1845 | Kanawha and Lewis counties | Thomas Walker Gilmer (1802–44) United States Secretary of the Navy (1844) Governor of Virginia (1840–41) |
7,254 | 340 sq mi (881 km2) |
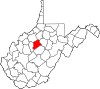 |
| Grant County | 023 | Petersburg | 1866 | Hardy County | Ulysses S. Grant (1822–85) United States President (1869–77) |
10,921 | 477 sq mi (1,235 km2) |
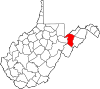 |
| Greenbrier County | 025 | Lewisburg | 1778 | Montgomery County (Virginia) and Botetourt County (Virginia) | Greenbrier River | 32,149 | 1,021 sq mi (2,644 km2) |
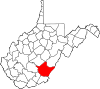 |
| Hampshire County | 027 | Romney | 1754 | Augusta County (Virginia) and Frederick County (Virginia) | County of Hampshire in England | 23,649 | 642 sq mi (1,663 km2) |
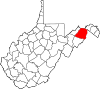 |
| Hancock County | 029 | New Cumberland | 1848 | Brooke County | John Hancock (1737–93) One of the Signers of the Declaration of Independence Governor of Massachusetts (1780–85) and (1787–93) |
28,145 | 83 sq mi (215 km2) |
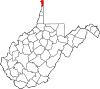 |
| Hardy County | 031 | Moorefield | 1786 | Hampshire County | Samuel Hardy (1758–85) Virginia delegate to the Continental Congress (1783–85) |
14,251 | 583 sq mi (1,510 km2) |
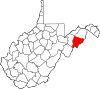 |
| Harrison County | 033 | Clarksburg | 1784 | Monongalia County | Benjamin Harrison V (1726–91) Governor of Virginia (1781–84) |
64,639 | 416 sq mi (1,077 km2) |
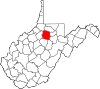 |
| Jackson County | 035 | Ripley | 1831 | Kanawha, Mason, and Wood counties | Andrew Jackson (1767–1845) United States President (1829–37) |
27,593 | 466 sq mi (1,207 km2) |
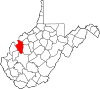 |
| Jefferson County | 037 | Charles Town | 1801 | Berkeley County | Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) United States President (1801–09) |
59,787 | 210 sq mi (544 km2) |
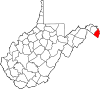 |
| Kanawha County | 039 | Charleston | 1789 | Greenbrier and Montgomery County (Virginia) | Kanawha River | 174,805 | 903 sq mi (2,339 km2) |
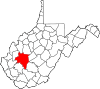 |
| Lewis County | 041 | Weston | 1816 | Harrison County | Charles Lewis (1736–74) American Colonel killed at the Battle of Point Pleasant |
16,500 | 389 sq mi (1,008 km2) |
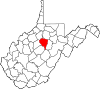 |
| Lincoln County | 043 | Hamlin | 1867 | Boone, Cabell, Kanawha, and Putnam counties | Abraham Lincoln (1809–65) United States President (1861–65) |
19,701 | 438 sq mi (1,134 km2) |
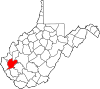 |
| Logan County | 045 | Logan | 1824 | Cabell and Kanawha counties, Giles County (Virginia), and Tazewell County (Virginia) | Chief Logan (c. 1723-80) Mingo leader |
30,827 | 454 sq mi (1,176 km2) |
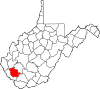 |
| Marion County | 049 | Fairmont | 1842 | Harrison and Monongalia counties | Francis Marion (1732–95) American Revolutionary War General (1757–82) |
55,807 | 310 sq mi (803 km2) |
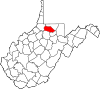 |
| Marshall County | 051 | Moundsville | 1835 | Ohio County | John Marshall (1755–1835) United States Secretary of State (1800–01) Chief Justice of the United States (1801–35) |
29,405 | 307 sq mi (795 km2) |
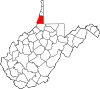 |
| Mason County | 053 | Point Pleasant | 1804 | Kanawha County | George Mason (1725–92) United States Constitutional Convention "Father of the Bill of Rights" |
24,765 | 432 sq mi (1,119 km2) |
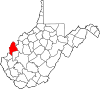 |
| McDowell County | 047 | Welch | 1858 | Tazewell County (Virginia) | James McDowell (1795–1851) Governor of Virginia (1843–46) |
17,439 | 535 sq mi (1,386 km2) |
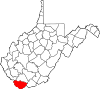 |
| Mercer County | 055 | Princeton | 1837 | Giles County (Virginia) and Tazewell County (Virginia) | Hugh Mercer (1726–77) American Revolutionary War General (1775–76) |
58,057 | 420 sq mi (1,088 km2) |
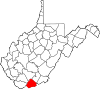 |
| Mineral County | 057 | Keyser | 1866 | Hampshire County | abundant mineral resources | 26,867 | 328 sq mi (850 km2) |
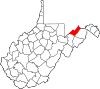 |
| Mingo County | 059 | Williamson | 1895 | Logan County | Mingo Native Americans | 22,023 | 423 sq mi (1,096 km2) |
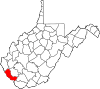 |
| Monongalia County | 061 | Morgantown | 1776 | Augusta County (Virginia) | Latin derivation for Monongahela River | 107,718 | 361 sq mi (935 km2) |
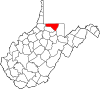 |
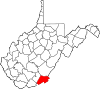
| Monroe County | 063 | Union | 1799 | Greenbrier County | James Monroe (1758–1831) United States Senator (Virginia) (1790–94) Governor of Virginia (1799–1802) and (1811) United States President (1817–25) |
12,382 | 473 sq mi (1,225 km2) |
 |
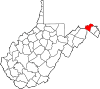
| Morgan County | 065 | Berkeley Springs | 1820 | Berkeley and Hampshire counties | Daniel Morgan (1736–1802) United States Congressman (Virginia) (1797–99) |
17,649 | 229 sq mi (593 km2) |
 |
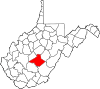
| Nicholas County | 067 | Summersville | 1818 | Greenbrier, Kanawha, and Randolph counties | Wilson Cary Nicholas (1761–1820) United States Senator (Virginia) (1799–1804) Governor of Virginia (1814–16) |
24,169 | 649 sq mi (1,681 km2) |
 |
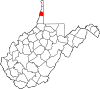
| Ohio County | 069 | Wheeling | 1776 | Augusta County (Virginia) | Ohio River | 41,194 | 106 sq mi (275 km2) |
 |
| Pendleton County | 071 | Franklin | 1788 | Augusta County (Virginia), Rockingham County (Virginia), and Hardy | Edmund Pendleton (1721–1803) First Continental Congress (1774) |
6,029 | 698 sq mi (1,808 km2) |
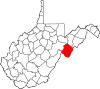 |
| Pleasants County | 073 | Saint Marys | 1851 | Ritchie, Tyler, and Wood counties | James Pleasants, Jr. (1769–1836) United States Senator (Virginia) (1819–22) Governor of Virginia (1822–25) |
7,428 | 131 sq mi (339 km2) |
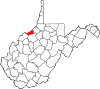 |
| Pocahontas County | 075 | Marlinton | 1821 | Bath County (Virginia), Pendleton, and Randolph | Pocahontas (c. 1595–1617) Powhatan Native American slave of early English settlers |
7,765 | 940 sq mi (2,435 km2) |
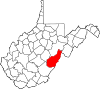 |
| Preston County | 077 | Kingwood | 1818 | Monongalia County | James Patton Preston (1774–1843) Governor of Virginia (1816–19) |
34,099 | 648 sq mi (1,678 km2) |
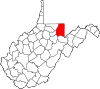 |
| Putnam County | 079 | Winfield | 1848 | Cabell, Kanawha, and Mason counties | Israel Putnam (1718–90) American Revolutionary War General |
56,962 | 346 sq mi (896 km2) |
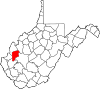 |
| Raleigh County | 081 | Beckley | 1850 | Fayette County | Sir Walter Raleigh (1554–1618) English explorer and poet |
72,356 | 607 sq mi (1,572 km2) |
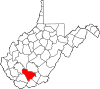 |
| Randolph County | 083 | Elkins | 1787 | Harrison County | Edmund Jennings Randolph (1753–1813) Governor of Virginia (1786–88) First United States Attorney General (1789–94) |
27,350 | 1,040 sq mi (2,694 km2) |
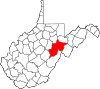 |
| Ritchie County | 085 | Harrisville | 1843 | Harrison, Lewis, and Wood counties | Thomas Ritchie (1778–1854) nationally influential Virginia newspaper publisher |
8,167 | 454 sq mi (1,176 km2) |
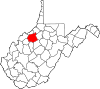 |
| Roane County | 087 | Spencer | 1856 | Gilmer, Jackson, and Kanawha counties | Spencer Roane (1762–1822) Virginia Supreme Court Justice (1794–1822) |
13,743 | 484 sq mi (1,254 km2) |
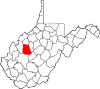 |
| Summers County | 089 | Hinton | 1871 | Fayette, Greenbrier, Mercer, and Monroe counties | George W. Summers (1804–68) United States Congressman (Virginia) (1843) |
11,581 | 361 sq mi (935 km2) |
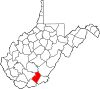 |
| Taylor County | 091 | Grafton | 1844 | Barbour, Harrison, Marion counties | John Taylor of Caroline (1753–1824) United States Senator (Virginia) (1792–94) and (1803) and (1822–24) |
16,388 | 173 sq mi (448 km2) |
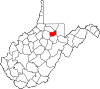 |
| Tucker County | 093 | Parsons | 1856 | Randolph County | Henry St. George Tucker (1780–1848) United States Congressman (Virginia) (1815–19) Virginia Supreme Court (1831–41) |
6,604 | 419 sq mi (1,085 km2) |
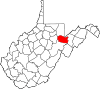 |
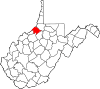
| Tyler County | 095 | Middlebourne | 1814 | Ohio County | John Tyler, Sr. (1747–1813) Governor of Virginia (1808–11) |
7,919 | 258 sq mi (668 km2) |
 |
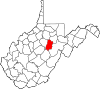
| Upshur County | 097 | Buckhannon | 1851 | Barbour, Lewis, and Randolph counties | Abel Parker Upshur (1790–1844) United States Secretary of the Navy (1841–43) United States Secretary of State (1843–44) |
23,529 | 355 sq mi (919 km2) |
 |
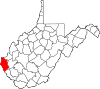
| Wayne County | 099 | Wayne | 1842 | Cabell County | "Mad" Anthony Wayne Major General (1745–96) American Revolutionary War (1775–83) and (1792–96) United States Congressman Georgia (1791) |
37,686 | 506 sq mi (1,311 km2) |
 |
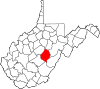
| Webster County | 101 | Webster Springs | 1860 | Braxton, Nicholas, and Randolph counties | Daniel Webster (1782–1852) United States Senator Massachusetts (1827–41) and (1845–50) United States Secretary of State (1841–53) and (1850–52) |
8,045 | 556 sq mi (1,440 km2) |
 |
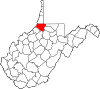
| Wetzel County | 103 | New Martinsville | 1846 | Tyler County | Lewis Wetzel (1763–1808) noted frontiersman |
13,890 | 359 sq mi (930 km2) |
 |
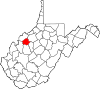
| Wirt County | 105 | Elizabeth | 1848 | Jackson and Wood counties | William Wirt (1772–1834) United States Attorney General (1817–29) |
5,000 | 233 sq mi (603 km2) |
 |
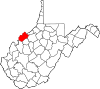
| Wood County | 107 | Parkersburg | 1798 | Harrison County | James Wood (1741–1813) Governor of Virginia (1796–99) |
83,052 | 367 sq mi (951 km2) |
 |
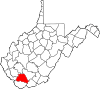
| Wyoming County | 109 | Pineville | 1850 | Logan County | derived from Lenape Native American term for "wide plain" | 20,277 | 501 sq mi (1,298 km2) |
 |
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Condados de Virginia Occidental para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Condados de Virginia Occidental para niños
- List of governors of West Virginia
- List of National Historic Landmarks in West Virginia
- List of West Virginia counties by socioeconomic factors

