Illinois facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Illinois
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Land of Lincoln, Prairie State, The Inland Empire State
|
|||
| Motto(s):
State Sovereignty, National Union
|
|||
| Anthem: "Illinois" | |||
Location of Illinois within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Illinois Territory | ||
| Admitted to the Union | December 3, 1818 (21st) | ||
| Capital | Springfield | ||
| Largest city | Chicago | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Cook | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Chicagoland | ||
| Legislature | General Assembly | ||
| • Upper house | Illinois Senate | ||
| • Lower house | Illinois House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Illinois | ||
| U.S. senators | Dick Durbin (D) Tammy Duckworth (D) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 14 Democrats 3 Republicans (list) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 57,915 sq mi (149,997 km2) | ||
| • Land | 55,593 sq mi (143,969 km2) | ||
| • Water | 2,320 sq mi (5,981 km2) 3.99% | ||
| Area rank | 25th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 390 mi (628 km) | ||
| • Width | 210 mi (338 km) | ||
| Highest elevation | 1,235 ft (376.4 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation
(Confluence of Mississippi River and Ohio River)
|
280 ft (85 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 6th | ||
| • Density | 232/sq mi (89.4/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 12th | ||
| • Median household income | |||
| • Income rank | 17th | ||
| Demonym(s) | Illinoisan | ||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English | ||
| • Spoken language | English (80.8%) Spanish (14.9%) Other (5.1%) |
||
| Time zone | UTC−06:00 (CST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−05:00 (CDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
IL
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-IL | ||
| Traditional abbreviation | Ill. | ||
| Latitude | 36° 58′ N to 42° 30′ N | ||
| Longitude | 87° 30′ W to 91° 31′ W | ||
| Dance | Square dance |
|---|---|
| Bird | Northern cardinal |
| Fish | Bluegill |
| Flower | Violet |
| Tree | White oak |
Illinois (![]() i/ˌɪlɪˈnɔɪ/ IL-ih-NOY) is a state in the Midwestern United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northeast. The Mississippi River is to its west. The Wabash and Ohio rivers are to its south.
i/ˌɪlɪˈnɔɪ/ IL-ih-NOY) is a state in the Midwestern United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northeast. The Mississippi River is to its west. The Wabash and Ohio rivers are to its south.
Illinois has the sixth-largest population among the fifty U.S. states. It also has the fifth-largest economy. Its capital city is Springfield, located in the center of the state. The largest city is Chicago in the northeast.
For thousands of years, Native American cultures lived in the area. French explorers arrived in the 1600s. They settled near the Mississippi and Illinois rivers. This area was called the Illinois Country. It was part of New France.
After the U.S. became independent in 1783, American settlers arrived. Illinois became a state in 1818. The Erie Canal and new farming tools helped the state grow. Farmers from Germany and Sweden moved there. By the mid-1800s, Illinois became a major transportation hub. This was thanks to the Illinois and Michigan Canal and many railroads.
By 1900, more people moved to Illinois for factory and coal mining jobs. Many immigrants came from Eastern and Southern Europe. Illinois became a major manufacturing state. The Great Migration brought many Black families from the South. They settled in Chicago, which became a big cultural and economic center. About 65% of the state's 12.8 million people live in the Chicago area.
Illinois has two World Heritage Sites. These are the ancient Cahokia Mounds and some buildings designed by Frank Lloyd Wright. Many protected areas help save Illinois' nature and history. Important universities include the University of Chicago and University of Illinois.
Three U.S. presidents were elected while living in Illinois: Abraham Lincoln, Ulysses S. Grant, and Barack Obama. Ronald Reagan was also born and grew up in Illinois. The state's slogan, Land of Lincoln, honors Abraham Lincoln.
Illinois has a very diverse economy. Chicago is a global city with finance and trade. The north and center have strong industries and farms. The south has natural resources like coal and oil. Illinois is a major transportation hub. The Port of Chicago connects to the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. Chicago has been a railroad center since the 1860s. Its O'Hare International Airport is one of the world's busiest.
Contents
Understanding the Name Illinois
"Illinois" is the modern way to spell the name. Early French missionaries used it for the Illinois Native Americans. The name was spelled in many ways back then.
Scholars used to think "Illinois" meant 'man' or 'men'. But this is not correct in the Illinois language. The name actually comes from a word meaning 'he speaks the regular way'. The French borrowed this word. The current spelling "Illinois" started in the 1670s. The Illinois people called themselves Inoka.
Illinois History
Early Native American Life

Native Americans lived in Illinois for thousands of years. They lived along the rivers before Europeans arrived. The Koster Site shows people lived there for 7,000 years straight.
Cahokia was a large ancient city near Collinsville, Illinois. It was part of the Mississippian culture. People there built over 100 mounds, including Monks Mound. This mound is 100 feet high and covers 13.8 acres. It was the largest structure built by Native Americans north of Mexico. Cahokia was a busy city with homes, markets, and skilled workers.
The Cahokia civilization disappeared in the 1400s. No one knows exactly why. Some think they used up all the natural resources. Many tribes fought each other. Later, the Illinois Confederation became powerful. By 1673, they had over 10,000 people. Other tribes like the Potawatomi and Miami later moved into the area.
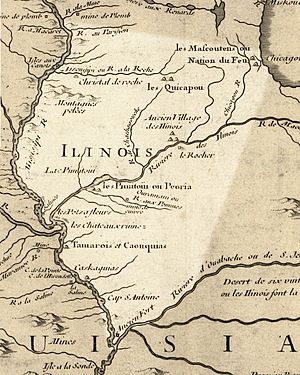
European Arrival and Early Settlements
French explorers Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet explored the Illinois River in 1673. Marquette started a mission there. In 1680, French explorers built a fort near Peoria. Another fort was built at Starved Rock in 1682.
French settlers came from Canada. They settled along the Mississippi River. Illinois was part of New France until 1763. Then, it became British land after the Seven Years' War. Many French people moved west to avoid British rule.
Few British settlers came to Illinois. The British government kept it as land for Native Americans. Later, it became part of the British Province of Quebec. In 1778, George Rogers Clark claimed Illinois for Virginia. After the U.S. became independent, Illinois became part of the Northwest Territory.
Becoming a State and Early Challenges
The Illinois Territory was created in 1809. Its first capital was Kaskaskia. Illinois became the 21st U.S. state in 1818.
The state's northern border was changed twice. This was to give Illinois more shoreline on Lake Michigan. It also included the Chicago River. This change was important for building a canal. The canal would connect the Great Lakes to the Mississippi River.
The capital moved to Vandalia in 1819. Then, in 1837, it moved to Springfield. Abraham Lincoln helped make this happen. The current Illinois State Capitol building was built in 1867.
Even though Illinois was a "free state," some people still held slaves. French settlers had Black slaves since the 1720s. American settlers also brought slaves from Kentucky. In 1824, Illinois residents voted against making slavery legal. However, laws were passed to prevent free Black people from settling in the state.
The winter of 1830–1831 was called the "Winter of the Deep Snow." Many travelers died because of the heavy snow. Other harsh winters followed. This led to crop failures in the north. The southern part of the state sent food north. This might be why the south is called "Little Egypt".
In 1832, the Black Hawk War took place. Native American tribes, led by Chief Black Hawk, tried to reclaim their land. They were defeated by the U.S. Militia. This ended Native American resistance in northern Illinois.
In 1839, the Latter Day Saints founded Nauvoo. It grew quickly and was once the state's largest city. But in 1844, their leader, Joseph Smith, was killed. Most Latter Day Saints then moved to Utah.
Chicago grew quickly after 1833. It became a major port and rail hub. By 1857, Chicago was Illinois's largest city. As mines and factories grew, labor unions formed in the state.
Illinois During and After the Civil War
During the American Civil War, Illinois sent over 250,000 soldiers to the Union Army. This was the fourth-highest number of soldiers from any state. The town of Cairo was an important supply base.
After the Civil War, Chicago's population grew very fast. Events like the Pullman Strike and Haymarket Riot were important for the American labor movement. In 1871, the Great Chicago Fire destroyed much of downtown Chicago.
Illinois in the 20th and 21st Centuries

By 1900, Illinois had nearly 5 million people. Many came for industrial jobs. The state became very important in the U.S. By the end of the 20th century, the population reached 12.4 million.
The Century of Progress World's Fair was held in Chicago in 1933. Oil was discovered in Illinois in 1937. By 1939, Illinois was the fourth-largest oil producer in the U.S. During World War II, Illinois made a lot of military equipment.
Chicago became an ocean port in 1959. This was due to the Saint Lawrence Seaway and the Illinois Waterway. In 1960, Ray Kroc opened the first McDonald's franchise in Des Plaines.
Illinois played a big part in the nuclear age. In 1942, the University of Chicago created the first self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. In 1957, Argonne National Laboratory started the first experimental nuclear power system. Illinois now leads all states in electricity from nuclear power.
In 1961, Illinois was the first state to change its criminal code. It removed old laws against certain private acts. The state's current constitution was adopted in 1970.
The first Farm Aid concert was held in Champaign in 1985. The Great Flood of 1993 caused major flooding along the Mississippi River.
In 2003, Governor George Ryan changed all death sentences in the state. This happened after several people were found innocent.
In 2002, Rod Blagojevich became governor. Barack Obama was an Illinois senator at this time. Obama later became president. Blagojevich was removed from office and sent to prison. He was the second Illinois governor in a row to be convicted of federal charges.
Pat Quinn replaced Blagojevich. Then Bruce Rauner became governor in 2014. There was a long budget disagreement from 2015 to 2018. In 2017, Rauner signed a law. It stopped state police from arresting people only for their immigration status.
In 2018, J. B. Pritzker became governor. Governor Pritzker declared a disaster due to the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020. This state of emergency ended in May 2023.
Illinois Geography
Land Features

Illinois is in the Midwestern United States. It is part of the Great Lakes region. Its eastern border is with Indiana. The southern border is with Kentucky, along the Ohio River. The western border is mostly the Mississippi River. The northern border is with Wisconsin. Illinois also shares a water border in Lake Michigan with Michigan, Wisconsin, and Indiana.
Most of Illinois is flat plains. But there are some small hills. In the northwest, the Driftless Area has higher, rougher land. Southern Illinois also has hills around the Shawnee National Forest.
Charles Mound is the highest point in Illinois. It is 1,235 feet above sea level. The lowest point is near Cairo, where the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers meet.
Illinois Regions

Illinois has three main geographic areas. Northern Illinois is mostly the Chicago metropolitan area. This includes Chicago and its suburbs. Chicago is a big, busy city. It is a major transportation center. Rockford is the third-largest city in Illinois. The Quad Cities area is also in northern Illinois.
The middle part of Illinois is Central Illinois. It used to be mostly prairie. Now it is mainly farmland. It has small towns and medium-sized cities. Major crops are corn and soybeans. Cities here include Peoria, Springfield (the state capital), and Champaign-Urbana.
The third area is Southern Illinois. This is south of U.S. Route 50. It includes "Little Egypt". This area has warmer winters and different crops. It also has some oil and coal mining. The Illinois suburbs of St. Louis, like East St. Louis, are in this region. This area is called the Metro-East.
Any area outside the Chicago metropolitan area is often called "downstate" Illinois.
Illinois Weather
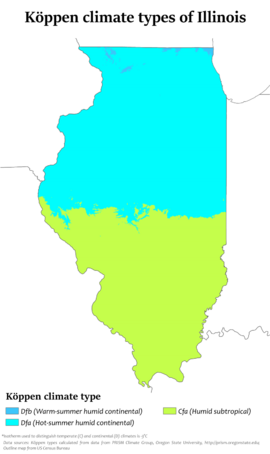
Illinois has a climate that changes a lot throughout the year. Most of Illinois has a humid continental climate. This means hot, humid summers and cold winters. The southern part of the state has a humid subtropical climate. This means milder winters.
Average yearly rainfall is about 48 inches in the south. It is around 35 inches in the north. The Chicago area gets over 38 inches of snow each year. The south gets less than 14 inches.
The highest temperature ever recorded was 117°F in East St. Louis in 1954. The lowest was -38°F near Mount Carroll in 2019.
Illinois has about 51 days of thunderstorms each year. It also gets many tornadoes, about 54 annually. Some of the deadliest tornadoes in history have happened in Illinois. The Tri-State Tornado of 1925 killed 695 people in three states. 613 of them were in Illinois.
| City | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairo | 43/25 | 48/29 | 59/37 | 70/46 | 78/57 | 86/67 | 90/71 | 88/69 | 81/61 | 71/49 | 57/39 | 46/30 |
| Chicago | 31/16 | 36/21 | 47/31 | 59/42 | 70/52 | 81/61 | 85/65 | 83/65 | 75/57 | 64/45 | 48/34 | 36/22 |
| Edwardsville | 36/19 | 42/24 | 52/34 | 64/45 | 75/55 | 84/64 | 89/69 | 86/66 | 79/58 | 68/46 | 53/35 | 41/25 |
| Moline | 30/12 | 36/18 | 48/29 | 62/39 | 73/50 | 83/60 | 86/64 | 84/62 | 76/53 | 64/42 | 48/30 | 34/18 |
| Peoria | 31/14 | 37/20 | 49/30 | 62/40 | 73/51 | 82/60 | 86/65 | 84/63 | 77/54 | 64/42 | 49/31 | 36/20 |
| Rockford | 27/11 | 33/16 | 46/27 | 59/37 | 71/48 | 80/58 | 83/63 | 81/61 | 74/52 | 62/40 | 46/29 | 32/17 |
| Springfield | 33/17 | 39/22 | 51/32 | 63/42 | 74/53 | 83/62 | 86/66 | 84/64 | 78/55 | 67/44 | 51/34 | 38/23 |
Major Cities and Towns
Chicago is the largest city in Illinois. It is also the third-most populated city in the United States. Over 7 million people in the Chicago area live in Illinois. Chicago itself has about 2.7 million residents.
Other large cities in Illinois with over 100,000 people include:
- Aurora
- Joliet
- Naperville
- Elgin
- Rockford (the largest city outside Chicago)
- Springfield (the state capital)
- Peoria
The largest city south of Springfield is Belleville. It has about 42,000 residents. It is part of the Metro East area near St. Louis. Other important urban areas are Peoria, Rockford, and Champaign–Urbana.
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chicago | 2,746,388 |
| 2 | Aurora | 180,542 |
| 3 | Joliet | 150,362 |
| 4 | Naperville | 149,540 |
| 5 | Rockford | 148,655 |
| 6 | Elgin | 114,797 |
| 7 | Springfield | 114,394 |
| 8 | Peoria | 113,150 |
| 9 | Waukegan | 89,321 |
| 10 | Champaign | 88,302 |
Illinois Population and People
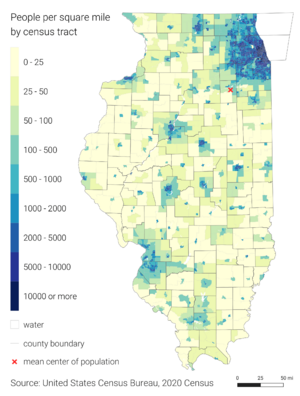
In 2020, Illinois had about 12.8 million people. It is the sixth-largest state by population. Illinois is the most populated state in the Midwest. The Chicago area has 65% of the state's residents. Chicago itself has about 21.4% of Illinois's population.
The five most populated counties are all in the Chicago area. These are Cook, DuPage, Lake, Will, and Kane counties. While the state's population has gone down a bit, the Chicago area is still growing. Most of the population decrease is from areas outside Chicago.
Illinois is the most diverse state in the Midwest. It has many different racial and ethnic groups. It also has a mix of religions and urban/rural areas. This makes Illinois a good example of the United States as a whole.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 2,458 | — | |
| 1810 | 12,282 | 399.7% | |
| 1820 | 55,211 | 349.5% | |
| 1830 | 157,445 | 185.2% | |
| 1840 | 476,183 | 202.4% | |
| 1850 | 851,470 | 78.8% | |
| 1860 | 1,711,951 | 101.1% | |
| 1870 | 2,539,891 | 48.4% | |
| 1880 | 3,077,871 | 21.2% | |
| 1890 | 3,826,352 | 24.3% | |
| 1900 | 4,821,550 | 26.0% | |
| 1910 | 5,638,591 | 16.9% | |
| 1920 | 6,485,280 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 7,630,654 | 17.7% | |
| 1940 | 7,897,241 | 3.5% | |
| 1950 | 8,712,176 | 10.3% | |
| 1960 | 10,081,158 | 15.7% | |
| 1970 | 11,113,976 | 10.2% | |
| 1980 | 11,426,518 | 2.8% | |
| 1990 | 11,430,602 | 0.0% | |
| 2000 | 12,419,293 | 8.6% | |
| 2010 | 12,830,632 | 3.3% | |
| 2020 | 12,812,508 | −0.1% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 12,710,158 | −0.9% | |
| Source: 1910–2020 | |||
Diversity in Illinois
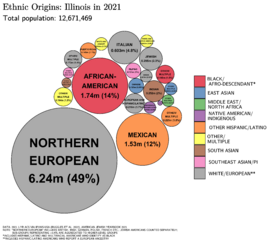
Illinois is a very diverse state. As of 2023, about 60.7% of the population is White. About 13.3% are Black or African American. About 6.0% are Asian.
The largest minority group in Illinois is Hispanic or Latino. They make up almost one-fifth of the population. Most Hispanics in Illinois are Mexican-American. Illinois has the largest Mexican population outside the Western U.S. Puerto Ricans are the second-largest Hispanic group. Most Hispanics live in Chicago or its suburbs.
Black Americans are the second-largest minority group. In 2023, over 1.9 million Illinoisans identified as Black. Most Black residents live in the Chicago area. Some areas in Southern and Central Illinois also have many Black residents. Illinois has a history of Black leaders in politics.
Asian-Americans are the third-largest minority group. Their population has grown quickly. Many are from India, the Philippines, and China. Most Asian residents live in the Chicago suburbs. They have the highest average income among major groups in the state.
Illinois has a small number of Native Americans and Pacific Islanders. Most Native Americans in Illinois also identify as Hispanic.
The largest European ancestry group in Illinois is German. Many people also have Irish, Polish, and Italian roots. These groups are mostly in Chicago and its suburbs. Illinois has the largest Polish-American population of any state.
Illinois also has a notable Arab population. Many live in the southern suburbs of Chicago. Illinois has the largest Palestinian population in the U.S.
Languages Spoken
English is the official language of Illinois. About 80% of people speak English as their first language. Most others speak it well as a second language.
Over 24% of people in Illinois speak another language at home. Spanish is the most common, spoken by over 14% of the population. Many people in the Chicago area also speak Polish.
Religious Beliefs
Religion in Illinois (2023) Protestantism (36%) No religion (29%) Roman Catholicism (23%) Islam (3%) Other Christian (3%) Judaism (2%) Buddhism (1%) Hinduism (1%) Other religion (2%) No response given/Unknown (0%)
The religious makeup of Illinois is similar to the rest of the U.S. About 62% of people in Illinois are Christians.
Roman Catholicism is the largest single Christian group. Many Catholics live in and around Chicago. This is because of the large Hispanic, Polish, Irish, and Italian communities. About 25% of the state's population is Catholic.
Protestant groups together make up 36% of the population. The United Methodist Church and Southern Baptist Convention are large Protestant groups. Illinois also has many Missouri Synod Lutherans.
Illinois was important in the early Latter Day Saint movement. Nauvoo was a gathering place for Mormons. Today, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has over 55,000 members in Illinois.
Other religions are also present. Many Muslims, Baháʼís, and Jewish people live in Illinois. Most are in the Chicago area. Muslims are the largest non-Christian group. Illinois has one of the highest concentrations of Muslims in the country.
The oldest and largest Baháʼí House of Worship in the world is in Wilmette, Illinois. It is a place for people of all faiths to gather and pray.
The Chicago area has a very large Jewish community. Many live in northern suburbs like Skokie. Illinois Governor JB Pritzker is Jewish.
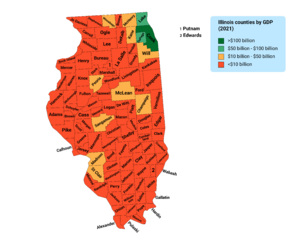
Illinois Economy
In 2022, Illinois's total economic output was $1.0 trillion. The unemployment rate in Illinois was 4.2% in February 2019. The minimum wage in Illinois will reach $15 per hour by 2025.
Farming and Food
Illinois is a major farming state. Its main farm products are corn, soybeans, hogs, cattle, and wheat. Illinois is usually one of the top two states for soybean and corn production.
Illinois is also a top producer of ethanol. Ethanol is a fuel made from corn. Illinois is a leader in making food and processing meat. The Archer Daniels Midland company in Decatur, Illinois, is a world leader in making ethanol from corn.
Manufacturing and Services
Illinois is a leader in manufacturing. In 2006, manufacturing added over $107 billion to the state's economy. About three-quarters of the state's factories are in the Chicago area. Key manufacturing industries include chemicals, machinery, and food.
Illinois's economy now relies more on high-value services. These include financial trading, higher education, and medicine. For example, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange started as a market for farm products. Other important industries are publishing and tourism.
Energy Production
Illinois uses more fuel than it produces. But it has large coal resources. Illinois exports electricity to other states. It ranks fifth in electricity production.
Illinois has a lot of coal underground. This coal has high sulfur content. This can cause acid rain. So, special equipment is needed to burn it cleanly. Most coal from Illinois is sent to other states and countries.
Illinois is a major refiner of oil in the Midwest. But it has very little crude oil itself.
Nuclear power started in Illinois. The first self-sustaining nuclear reaction happened at the University of Chicago. Illinois has six nuclear power plants. It leads the nation in nuclear power capacity. In 2007, nuclear power made 48% of Illinois's electricity.
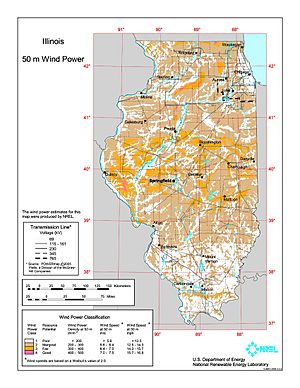
Illinois is also growing in wind power. Many areas are good for wind farms. In 2009, Illinois had over 1,100 megawatts of wind power. The state aims for 25% of its electricity to come from renewable resources by 2025.
Illinois is second in corn production. This corn is used to make 40% of the ethanol in the U.S.
Taxes in Illinois
Taxes in Illinois are collected by the state. The state income tax is a flat rate. In 2017, it was raised to 4.95% for individuals. The state sales tax is 6.25% for most goods. Property tax is a main source of money for local governments.
Chicago has one of the highest sales tax rates in the U.S. Illinois also has the second-highest real estate tax rate. Toll roads are also common in Illinois. Chicago has some of the most expensive toll roads. Illinois also has the 11th highest gasoline tax.
Illinois Culture
Museums and Zoos
Illinois has many museums. Most are in Chicago. Some of the best museums in the world are there. These include the John G. Shedd Aquarium, the Field Museum of Natural History, and the Art Institute of Chicago.
The Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum in Springfield is the largest presidential library. The Illinois State Museum tells the story of Illinois life and art.
The Chicago area also has two zoos. The Brookfield Zoo has over 2,300 animals. The Lincoln Park Zoo is in Chicago's Lincoln Park.
- Illinois Museums
-
Magnolia Manor in Cairo.
-
The Polish Museum of America in Chicago
-
A Railway Post Office at the Illinois Railway Museum in Union
Music Scene
Illinois is a leader in music education. Chicago is a major music center. It is where Chicago blues and house music were created.
The Great Migration brought jazz and blues music to Chicago. Famous blues artists included Muddy Waters and Howlin' Wolf. Jazz greats included Nat King Cole. Chicago is also known for its soul music.
In the 1930s, Gospel music became popular in Chicago. Later, heavy rock, punk, and hip hop also grew popular. Chicago has famous orchestras like the Chicago Symphony Orchestra.
Movies Filmed in Illinois
Filmmaker John Hughes set many of his movies in Chicago and its suburbs. Movies like Ferris Bueller's Day Off and Home Alone take place in the area. Many locations in his films are real places in Illinois.
Recreation and Parks
The Illinois state parks system started in 1908. It now has over 60 parks and many recreational areas.
National Park Service sites include the Illinois and Michigan Canal National Heritage Corridor. Also, the Lincoln Home National Historic Site in Springfield. The Shawnee National Forest is also managed by the federal government.
Sports Teams
Chicago has teams in all major sports leagues.
- Baseball: The Chicago Cubs play at Wrigley Field. They won the World Series in 2016. The Chicago White Sox won the World Series in 2005. They play at Rate Field.
- Football: The Chicago Bears play at Soldier Field. They have won nine NFL Championships.
- Basketball: The Chicago Bulls are famous for winning six NBA championships in the 1990s with Michael Jordan. The Chicago Sky won their first WNBA Championship in 2021.
- Hockey: The Chicago Blackhawks have won six Stanley Cups.
- Soccer: Chicago Fire FC plays in MLS. The Chicago Red Stars play in the National Women's Soccer League.
Illinois also has many minor league sports teams.
Many colleges in Illinois compete in NCAA Division I. The Illinois Fighting Illini and Northwestern Wildcats are in the Big Ten Conference.
Illinois has several tracks for motor racing. These include Chicagoland Speedway and Gateway Motorsports Park. They host NASCAR and other races.
Illinois has many golf courses. Some have hosted major tournaments like the U.S. Open and PGA Championship.
Illinois Government and Politics
State Government Structure
The government of Illinois has three parts: executive, legislative, and judicial. This is like the U.S. federal government.
The executive branch includes the Governor and other elected officials. The legislative branch is the Illinois General Assembly. It has the Illinois House of Representatives and the Illinois Senate. The judicial branch has the Supreme Court of Illinois and other courts.
Illinois is divided into 102 counties. Many counties are also divided into townships. Cities and villages have their own local governments.
Political Landscape

Illinois is currently a strong Democratic state. In the past, it was a swing state. But now, the Democratic Party usually wins. This is mainly because of Cook County and Chicago. These areas have many Democratic voters.
Areas outside Chicago are mostly Republican. But the Chicago area's votes are very powerful in state elections. This has led to some people in downstate Illinois wanting to separate.
Illinois used to be a "bellwether" state. This means it often voted for the winning presidential candidate. But since 1992, Illinois has consistently voted Democratic in presidential elections.
Famous Illinois Politicians
Three U.S. presidents have called Illinois their political home:
Ronald Reagan was born and grew up in Illinois. He later moved to California and became president. Hillary Clinton was born and raised in the Chicago suburbs. She was the first woman to run for president for a major party.
Illinois has had more African-American U.S. Senators than any other state. These include Carol Moseley-Braun, Barack Obama, and Roland Burris. Carol Moseley-Braun was the first African-American woman to be a U.S. Senator.
Several families in Illinois have been very important in politics. The Stevenson family had four generations of officeholders. The Daley family has been powerful in Chicago politics. Richard J. Daley and his son Richard M. Daley both served as Mayor of Chicago for many years. The Pritzker family is also important. J. B. Pritzker is the current governor.
Education in Illinois
The Illinois State Board of Education (ISBE) manages public education in the state. Local school districts run individual schools. The ISBE checks how schools are doing.
Education is required for ages 7–17. Schools are usually divided into elementary, middle, and high school.
Illinois has many colleges and universities. There are eleven "National Universities" in the state. Six of these are ranked among the top universities in the nation. These include the University of Chicago and Northwestern University. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is known for its engineering programs.
Illinois also has over twenty other four-year universities. There are also 49 public community colleges.
Schools in Illinois get most of their money from property taxes. This system has been called unfair in the past. There have been efforts to make school funding more equal.
Transportation in Illinois
Illinois is a major crossroads for transportation. This is because of its central location. It connects air, car, train, and truck traffic.
Airports

Chicago O'Hare International Airport (ORD) is one of the busiest airports in the world. It was the busiest from 1962 to 1998. It is a major hub for United Airlines and American Airlines. Midway Airport (MDW) is Chicago's second airport. It is a major hub for Southwest Airlines.
Highways
Illinois has many Interstate Highways. It has the most primary interstates (13) of any state. Illinois also has the third-most interstate mileage. Major interstates include I-55, I-57, I-70, I-80, I-90, and I-94.
The Illinois Department of Transportation (IDOT) maintains the U.S. Highways. There are 21 primary U.S. highways in Illinois.
Buses and Trains
Illinois has many intercity bus services. The Chicago Bus Station is the busiest.
Illinois has a large train network for passengers and freight. Chicago is a national Amtrak hub. It connects to many cities. There are also in-state Amtrak lines. Almost all major North American railways meet in Chicago. This makes it the largest rail hub in the country.
Chicago also has the Chicago Transit Authority's 'L' system. This is a train system for the city and nearby suburbs. Metra is a large commuter rail system. It uses existing lines to connect suburbs to Chicago.
Waterways
The Mississippi River and Illinois River are important for transporting goods. Lake Michigan connects Illinois to the Atlantic Ocean through the Saint Lawrence Seaway.
Images for kids
-
Rising waters in Alton in 1993.
See also
 In Spanish: Illinois para niños
In Spanish: Illinois para niños