India facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of India
Bhārat Gaṇarājya
|
|
|---|---|
|
National song: Vande Mataram (Sanskrit)
"I Bow to Thee, Mother" |
|
Territory controlled by India Territory claimed but not controlled
|
|
| Capital | New Delhi 28°36′50″N 77°12′30″E / 28.61389°N 77.20833°E |
| Largest city | Mumbai |
| Largest city | Delhi |
| Official languages | Hindi, English |
| Many regional languages | Over 400 languages spoken |
| Religion
(2011)
|
79.8% Hinduism, 14.2% Islam, 2.3% Christianity, 1.7% Sikhism, 0.7% Buddhism, 0.4% Jainism |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Droupadi Murmu | |
| C. P. Radhakrishnan | |
| Narendra Modi | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Rajya Sabha | |
| Lok Sabha | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Dominion
|
15 August 1947 |
|
• Republic
|
26 January 1950 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
3,287,263 km2 (1,269,219 sq mi) (7th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
9.6 |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
|
|
• 2011 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
433.3/km2 (1,122.2/sq mi) (30th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2021) | ▼ 25.5 low |
| HDI (2023) | medium · 130th |
| Currency | Indian rupee (₹) (INR) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Date format |
|
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +91 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN |
| Internet TLD | .in (others) |
India, officially known as the Republic of India, is a large country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country in the world by land area. Since 2023, India has become the most populated country globally. It is also the world's largest democracy.
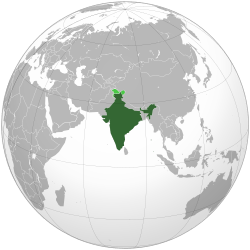
India is surrounded by the Indian Ocean to the south, the Arabian Sea to the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal to the southeast. It shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is close to Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a sea border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.
Modern humans first arrived in India about 55,000 years ago. Over time, settled life began in the Indus River basin 9,000 years ago. This led to the Indus Valley Civilisation, a very old city-based culture. Later, around 1200 BCE, Sanskrit language and early Hinduism began to spread. Around 400 BCE, the caste system developed within Hinduism. Also, Buddhism and Jainism started, offering new ways of thinking about society. Large empires like the Maurya Empire and Gupta Empire formed, bringing periods of great creativity in art and science.
In the early medieval period, religions like Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Zoroastrianism became established in India. Later, Muslim armies from Central Asia entered northern India, leading to the Delhi Sultanate in 1206. This connected northern India to the wider Islamic world. In the south, the Vijayanagara Empire created a strong Hindu culture. The Mughal Empire followed, bringing economic growth and beautiful Mughal architecture.
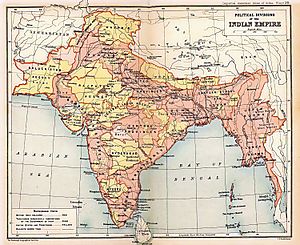
Gradually, the British East India Company took control, turning India into a colonial economy. British rule began in 1858. Modern ideas and technology were introduced, and a strong Indian independence movement grew. This movement, known for its nonviolent resistance led by Mahatma Gandhi, helped end British rule. In 1947, the British Indian Empire was divided into two independent countries: India and Pakistan. This division led to a huge movement of people and much loss of life.
Since 1950, India has been a federal republic with a democratic parliamentary system. It is a diverse country with many languages and cultures. India's population has grown a lot, and its economy has become one of the fastest-growing in the world, especially in IT services. Indian movies and music are also becoming popular globally. India has reduced poverty but still faces challenges like gender inequality and air pollution. India is a nuclear-weapon state and has a large military. It has ongoing disputes over Kashmir with Pakistan and China. India is also a megadiverse country with many different plants and animals, protected in special areas.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "India" comes from the Classical Latin word India. This word came from the Greek word Indos, which refers to the Indus River. So, "India" means the land of the Indus River. The ancient Greeks called the people living there Indoi, meaning 'people of the Indus'.
Another important name for India is Bharat. This name is found in old Indian stories and the Constitution of India. It was originally used for North India but became a common name for the whole country in the mid-1800s.
Hindustan is another name for India that became popular around the 1200s. It was widely used during the Mughal Empire. Hindustan can mean the northern part of India or almost the entire country.
India's Story: A Journey Through Time
Early Beginnings
The first modern humans arrived in India from Africa about 55,000 years ago. The oldest human remains found in South Asia are about 30,000 years old. Around 6500 BCE, people started farming and building permanent homes in places like Mehrgarh.
These early settlements slowly grew into the Indus Valley Civilisation, which thrived from 2500 to 1900 BCE. Cities like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa were centers of this culture. They were skilled in crafts and traded widely.
Between 2000 and 500 BCE, many parts of India moved from using copper to using iron. During this time, the Vedas, the oldest holy books of Hinduism, were written. This period also saw the start of the caste system, which organized society into different groups. In South India, large stone monuments called megaliths show that people were settling down and farming.

Around 600 BCE, smaller states in the Ganges Plain grew into 16 larger kingdoms called mahajanapadas. New religions also emerged. Jainism became important through its leader, Mahavira. Buddhism, based on the teachings of Gautama Buddha, attracted many followers. Both religions taught that giving up worldly desires was important.
By the 3rd century BCE, the Magadha kingdom grew into the powerful Maurya Empire. Its most famous ruler, Ashoka, later chose peace and spread the Buddhist teachings. In South India, the Cheras, Cholas, and Pandyas traded with the Roman Empire and other parts of Asia.
Between the 4th and 5th centuries, the Gupta Empire brought a period of great art and learning. Hinduism became stronger, and there was a flowering of sculpture, architecture, and literature. Indian science, astronomy, medicine, and mathematics also made big advances.
Medieval Times
From 600 to 1200 CE, India was made up of many regional kingdoms. No single ruler could control the entire subcontinent. During this time, the caste system changed and became different in various regions.
In the 6th and 7th centuries, devotional songs called Bhakti hymns became popular in the Tamil language. These songs spread across India, helping Hinduism grow and leading to the development of many modern Indian languages. Temples became important centers, attracting many people and helping cities grow. Indian culture and political ideas also spread to Southeast Asia.
After the 10th century, Muslim groups from Central Asia began to conquer parts of northern India. This led to the Delhi Sultanate in 1206. The Sultanate protected India from Mongol attacks and brought many scholars, traders, and artists to India. This created a mix of Indian and Islamic cultures in the north. In the south, the Vijayanagara Empire grew strong, influencing society for a long time.
Early Modern India
In the early 1500s, the Mughal Empire took over northern India. The Mughals created a strong, organized government. They encouraged art, literature, and architecture, leading to famous buildings like the Taj Mahal. This period brought economic growth and peace. New groups like the Marathas, Rajputs, and Sikhs also became powerful.
By the early 1700s, European trading companies, including the British East India Company, set up outposts along the coast. The British East India Company, with its strong navy and army, gained control over the Bengal region by 1765. They gradually took over most of India by the 1820s. India then became a source of raw materials for the British Empire. This period is often seen as the start of India's colonial era.
Modern India
India's modern age began around the mid-1800s. The British introduced railways, canals, and the telegraph. However, unhappiness with the East India Company grew, leading to the Indian Rebellion of 1857. This rebellion caused the British government to take direct control of India in 1858, ending the Company's rule.
After World War I, a new period began. Indians demanded more self-rule, and the nonviolent movement led by Mahatma Gandhi gained strength. In 1947, India gained independence but was divided into two countries: India and Pakistan.
India's constitution, completed in 1950, made it a secular and democratic republic. Since the 1980s, India has opened up its economy, leading to fast growth and a large middle class. India has become a major global player. However, it still faces challenges like poverty and social issues. India is unique among newer nations for its strong democratic freedoms.
India's Land and Nature
Geography and Climate

India is mostly located on the Indian Plate, which is part of the Indo-Australian Plate. About 75 million years ago, the Indian Plate moved northeast and crashed into the Eurasian Plate. This collision created the mighty Himalayas mountains. South of the Himalayas, a large plain formed, which is now the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
The older, stable part of India is called peninsular India. It extends north to the Satpura and Vindhya mountains. The Deccan Plateau is in the south, surrounded by the Western and Eastern Ghats mountain ranges.
India has a long coastline of about 7,517 kilometers (4,671 miles). This includes sandy beaches, rocky shores, and marshy areas. Major rivers like the Ganges and Brahmaputra flow from the Himalayas into the Bay of Bengal. Other important rivers like the Godavari and Krishna also flow into the Bay of Bengal, while the Narmada and Tapti flow into the Arabian Sea. India also has two groups of islands: the Lakshadweep coral islands and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which are volcanic.
India's climate is greatly affected by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert. These features drive the important summer and winter monsoons, which bring most of India's rainfall. The Himalayas block cold winds from Central Asia, keeping India warmer. India has four main climate types: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and montane (mountain). Temperatures in India have risen, and climate change is causing more droughts and affecting Himalayan glaciers.
Amazing Biodiversity


India is a "megadiverse country," meaning it has a very high number of different plant and animal species. Many of these species are found only in India. India is home to 8.6% of all mammal species, 13.7% of bird species, and many other types of animals and plants. About one-third of India's plant species are unique to the country. India also has four of the world's 34 biodiversity hotspots, which are areas with many unique species but also significant habitat loss.
India's densest forests are in places like the Andaman Islands and the Western Ghats. Other forests include temperate coniferous forests in the Himalayas and deciduous forests in eastern and central India. Notable trees include the Azadirachta indica (neem), used in traditional medicine, and the Ficus religiosa (peepul), which is a sacred tree.
Many Indian species came from the ancient southern supercontinent Gondwana. Later, when India collided with Asia, there was an exchange of species. However, some unique Indian animals became extinct due to volcanic activity and climate changes. Today, human activity is a big threat to India's wildlife. To protect its animals, India has expanded its system of national parks and protected areas. Laws like the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and Project Tiger help safeguard important wilderness areas. India has over 500 wildlife sanctuaries and 18 biosphere reserves.
How India is Governed
Politics and Elections


India is a parliamentary republic with many political parties. The two main national parties are the Indian National Congress (INC) and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). There are also over 50 regional parties.
For many years, the Congress party, led by figures like Jawaharlal Nehru and Indira Gandhi, held most of the power. After the 1980s, power began to be shared more with the BJP and strong regional parties, leading to coalition governments.
Government Structure

India is a federation with a parliamentary system, guided by the Constitution of India. This means power is shared between the central government and the states.
The Indian government has three main parts:
- The Executive includes the President of India, who is the ceremonial head of state, and the Prime Minister of India, who is the head of government and holds most of the power. The Prime Minister is supported by the party or group of parties with the most seats in parliament.
- The Legislature is the Parliament of India, which has two houses: the Rajya Sabha (upper house) and the Lok Sabha (lower house). Members of the Lok Sabha are directly elected by citizens.
- The Judiciary is an independent system with the Supreme Court of India at the top, followed by 25 high courts, and many local courts. The Supreme Court makes sure laws follow the constitution.
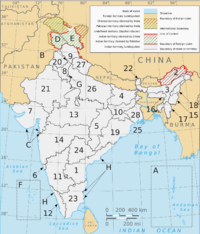
States and Territories
India is divided into 28 states and 8 union territories. All states and some union territories have their own elected governments. Other union territories are directly managed by the central government. In 1956, states were reorganized based on the languages spoken there. India also has many local government bodies in cities, towns, and villages.
States of India
Union Territories of India
India's Global Connections

India became a republic in 1950 and remained part of the Commonwealth of Nations. In the 1950s, India strongly supported countries gaining independence from colonial rule. It also played a key role in the Non-Aligned Movement, which meant not taking sides with major world powers during the Cold War.
India has had some conflicts with its neighbors. It went to war with China in 1962 and again in 1967. India has also had several wars with Pakistan, mostly over the disputed region of Kashmir. After the 1965 war with Pakistan, India developed close ties with the Soviet Union.

India developed nuclear weapons after China's nuclear test in 1964. India conducted its first nuclear test in 1974 and more tests in 1998. India has a "no first use" nuclear policy, meaning it will not use nuclear weapons first.
Since the end of the Cold War, India has increased its cooperation with the United States and the European Union. India's President is the supreme commander of its armed forces. With 1.45 million active troops, India has the world's second-largest military. India is also the world's second-largest arms importer.
India's Economy
India's economy is one of the largest in the world. In 2024, it was the fifth-largest economy by market exchange rates. It is also the third-largest when considering purchasing power parity (PPP), which compares how much you can buy with money in different countries. India has been one of the fastest-growing economies globally, with an average growth rate of 5.8% over the last two decades.
However, because India has such a large population, its income per person is still low. Most Indians are in the low-income group. Until 1991, India's government controlled the economy tightly. But after a financial crisis in 1991, India began to open its economy to foreign trade and investment.
India has the world's second-largest workforce, with about 522 million workers. The service sector (like IT and finance) makes up the largest part of India's economy (55.6% of GDP). The industrial sector is 26.3%, and agriculture is 18.1%. India also receives a lot of money from Indians working in other countries, which was $100 billion in 2022.
India's trade with other countries has grown a lot. In 2021, India was the world's ninth-largest importer and sixteenth-largest exporter. India is also the world's second-largest textile exporter.
Over 431 million Indians have moved out of poverty since 1985. India's middle class is expected to grow to about 580 million people by 2030. The income per person has steadily increased from $308 in 1991 to an estimated $2,731 in 2024.
Key Industries
The Indian car industry is the world's second-fastest growing. In 2022, India became the world's third-largest vehicle market. The Indian IT industry is also very important, employing 2.8 million people and making up 7.5% of India's GDP.
India is the world's third-largest producer of medicines and the largest producer of generic medicines. It supplies a large portion of global vaccine demand. India is also among the top 12 countries for biotechnology.
Energy Sources
India can generate 300 gigawatts of electricity, with 42 gigawatts coming from renewable sources. While coal usage is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions in India, renewable energy is becoming more competitive. India produces about 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Providing electricity and clean cooking fuel to more people are important goals for India.
Challenges India Faces
Despite its economic growth, India still faces challenges. In 2006, India had the largest number of people living below the international poverty line. By 2019, this number had significantly decreased to 10.2%. However, in 2014, about 30.7% of Indian children under five were underweight.
A 2018 report estimated that nearly 8 million people in India were in different forms of modern slavery, such as forced labor. The 2011 census showed 10.1 million child laborers, a decrease from 2001.
Economic differences between India's states have grown. The richest states have much higher incomes per person than the poorest. However, corruption is seen to have decreased, with India ranking 78th out of 180 countries in 2018.
People, Languages, and Beliefs
Population and Demographics
With over 1.4 billion people in 2023, India is the world's most populated country. Its population grew by 17.64% from 2001 to 2011. In 2020, the average age in India was 28.7 years. Medical advances and the "Green Revolution" in agriculture have helped India's population grow quickly.
Life expectancy in India is about 70 years. Many people have moved from rural areas to cities. In 2011, over 31% of the population lived in urban areas. There are 53 cities with over a million people, including Mumbai, Delhi, and Kolkata.
The literacy rate (ability to read and write) in 2011 was 74.04%. This means 81% of men and 65% of women could read and write. This is a big improvement from 1951, when only 18% of the population was literate.
Languages Spoken
India has many languages. About 74% of Indians speak Indo-Aryan languages, and 24% speak Dravidian languages. India does not have one national language. Hindi is the official language of the government, and English is widely used in business and education. Each state and union territory has its own official languages, and the constitution recognizes 22 "scheduled languages."
Religions in India
According to the 2011 census, the largest religion in India is Hinduism (79.80% of the population). This is followed by Islam (14.23%). Other religions include Christianity (2.30%), Sikhism (1.72%), Buddhism (0.70%), and Jainism (0.36%). India has the third-largest Muslim population in the world, even though it is not a Muslim-majority country.
Indian Culture
Art and Creativity
India has a very old and rich tradition of art. Indian art has influenced and been influenced by other parts of Asia. Early art includes seals from the Indus Valley Civilization. Later, much of the ancient Indian art was religious sculpture found in Buddhist and Hindu sites.
Gupta art, from around 300 to 500 CE, is considered a classical period. It saw a rise in Hindu sculpture, like at the Elephanta Caves. In South India, under the Pallava and Chola dynasties, sculpture in stone and bronze reached great heights. The bronze statues of Shiva as Nataraja (Lord of Dance) are famous symbols of India.
Ancient paintings are rare but can be seen in the Ajanta Caves. Later, Mughal and Rajput paintings focused on portraits and scenes of court life. In the 19th century, Kalighat paintings became popular, showing gods and daily life. The Bengal School of Art was an important movement in modern Indian painting.
-
Gupta terracotta relief, Krishna Killing the Horse Demon Keshi, 5th century
-
Elephanta Caves, triple-bust (trimurti) of Shiva, 18 feet (5.5 m) tall, c. 550
-
Chola bronze of Shiva as Nataraja ("Lord of Dance"), Tamil Nadu, 10th or 11th century
-
Jahangir Receives Prince Khurram at Ajmer on His Return from the Mewar Campaign, Balchand, c. 1635
Society and Family Life
The caste system has historically shaped social groups in India. While untouchability was abolished in 1950, some social differences related to caste still exist.
Traditionally, large joint families (where many generations live together) were common in India. However, nuclear families (parents and children only) are becoming more common in cities. Most marriages in India are still arranged by parents or elders. Divorce rates are very low.
Education in India

In 2011, about 73% of India's population was literate. This is a big improvement from 1951, when only 18% could read and write. The education system in India is the second-largest in the world, with many universities, colleges, and schools. India's improved education system has helped its economic growth.
Traditional Clothing
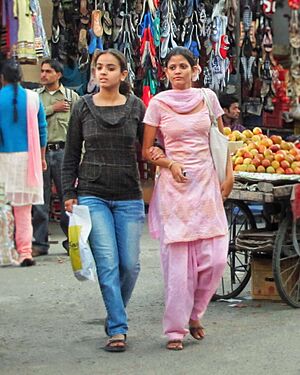
For a long time, the most common traditional dress in India was draped clothing. For women, this was the sari, a long piece of cloth wrapped around the body. It is usually worn with an underskirt and a blouse, or choli. For men, a similar but shorter cloth called the dhoti was worn around the lower body.
Stitched clothes became popular after Muslim rule began around 1300 CE. These include shalwars and pyjamas (types of trousers) and tunics like the kurta and kameez. Shalwars are wide at the waist and narrow at the bottom, while churidars are cut more narrowly. Kurtas are usually collarless shirts made of cotton or silk.
In recent years, fashion in India has changed a lot. In urban areas, saris are now mostly worn for special occasions. Younger women often prefer churidars or jeans. For formal events, men might wear bandgala jackets or sherwanis. The dhoti, once very common, is now rarely seen in cities.
Delicious Cuisine

A typical Indian meal usually has a plain cooked cereal, like steamed rice or chapati (flatbread), served with flavorful savory dishes. These dishes often include lentils, vegetables, poultry, fish, or meat. They are spiced with ingredients like ginger, garlic, coriander, cumin, and turmeric.
Meals are often served on a platter called a thali. The cereal is in the middle, and the other dishes are around it. People mix the cereal with the other dishes or use bread to scoop them up.
India has many different vegetarian cuisines, depending on the region and culture. A large part of India's population is vegetarian. While meat is eaten, dairy products are a more common source of animal protein.
The Mughal Empire brought new cooking techniques to India, like the pilaf. Dishes like biryani, which layers rice with spiced meat, became popular for special occasions. In Indian restaurants around the world, Punjabi cuisine is very common. Dishes like tandoori chicken, cooked in a special oven called a tandoor, became famous in the 1950s.
Sports and Fun
Many traditional Indian sports are still popular, such as kabaddi, kho kho, and martial arts like Kalarippayattu. Chess is believed to have started in India as chaturaṅga. India has produced many chess grandmasters and world champions. Parcheesi comes from Pachisi, another old Indian game.
Cricket is the most popular sport in India. The Indian team has won the Cricket World Cup twice, in 1983 and 2011. India has also won eight gold medals in field hockey at the Summer Olympics.
See also
 In Spanish: India para niños
In Spanish: India para niños
- Administrative divisions of India
- Outline of India