Africa facts for kids
| Area | 11,730,000 sq mi (30,400,000 km2) (2nd) |
|---|---|
| Population | 1,275,920,972 (2018; 2nd) |
| Population density | 94/sq mi (36/km2) |
| GDP (nominal) | $2.45 trillion (2019; 5th) |
| GDP (PPP) | $7.16 trillion (2019; 5th) |
| GDP per capita | $1,930 (2019; 6th) |
| Demonym | African |
| Countries | 54 (and 2 disputed) |
| Dependencies |
External (1)
|
| Languages | 1250–3000 native languages |
| Time zones | UTC-1 to UTC+4 |
| Largest cities | Largest urban areas: |
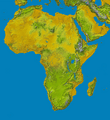
Africa is the second largest continent in the world, right after Asia. It makes up about one-fifth of all the land on Earth. Large bodies of water surround it. Africa has 54 fully recognized and independent countries. About 1.4 billion people live there, which is 16.72% of the world's population. Many scientists believe that the first humans evolved in Africa.
Contents
What is Africa's History Like?
The history of Africa goes back to the very first modern human beings. It continues to today, where it is a continent that is still developing.
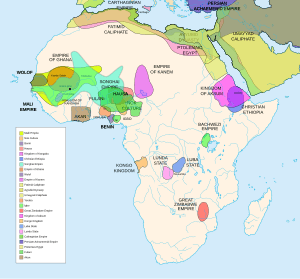
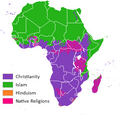
Africa's ancient history includes the rise of the Egyptian civilization. Other societies also grew outside the Nile River Valley. These societies traded and interacted with civilizations outside of Africa. In the late 600s, Islam spread to North and East Africa. This led to new cultures like the Swahili people. It also led to powerful kingdoms like the Mali Empire. Its king, Mansa Musa, became one of the richest people in the early 1300s.
What About Slavery in Africa?
Slavery has been a part of African history for a long time. Between the 600s and the 1900s, the Arab slave trade took about 18 million enslaved people from Africa. They were taken across the Sahara Desert and the Indian Ocean.
Later, between the 1400s and 1800s, the Atlantic slave trade took about 7–12 million enslaved people. They were forced to go to the New World (the Americas).
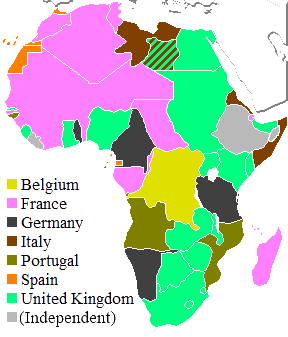
How Did Colonialism Affect Africa?
In the late 1800s, countries from Europe took control of much of Africa. They created many colonies and dependent territories. Only three states remained fully independent: the Darwiish State, Ethiopia (also called "Abyssinia"), and Liberia.
Egypt and Sudan were never officially made into European colonies. However, after the British took control in 1882, Egypt was under British rule until 1922.
What is Modern African History Like?
African countries started gaining their independence in 1951. Libya was the first former colony to become independent. Modern African history has seen many changes and some conflicts. However, the African economy has grown, and many countries have become more democratic.
Groups like the African Union are working to help countries cooperate more. They hope to bring more peace to the continent.
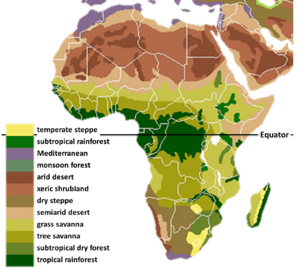
What is Africa's Climate Like?
Africa has many different types of climate from north to south. These include:
- Mountain and Mediterranean weather
- Dry, sandy deserts
- Fairly dry savannahs (grasslands)
- Rain forests
- More grasslands
- More deserts
Running from the northeast to the south is the East African Great Rift Valley. This area has mountains, volcanoes, deep rifts, valleys, rivers, and lakes.
How Does Rainfall Affect Africa?
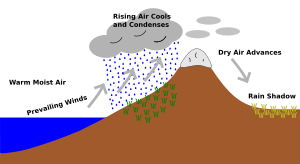
Most of North Africa is covered by the Sahara Desert. It is very dry and hot and does not get much rain. Rivers and water sources are rare in the Sahara. Water found underground, like springs, are very important. These often create oases. An oasis is a green area with plants in the middle of a desert.
Two rain shadows cause the Sahara Desert to be so dry. In that part of the world, winds mostly come from the east. These winds usually bring rain. But the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau block the monsoon rains. This stops the rain from reaching North Africa. Also, the Atlas Mountains near Africa's north coast block rain from coming in from the north.
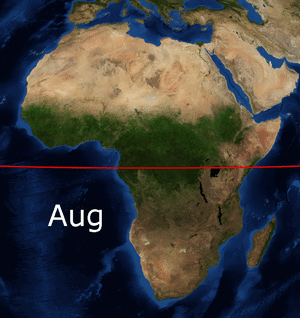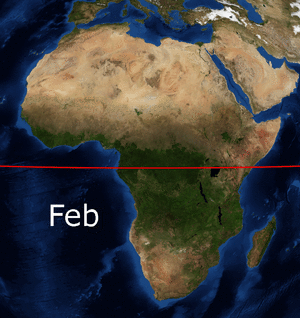
Conditions are different further south. Huge amounts of rain fall near the equator. The equator crosses the middle of Africa. This means much of Africa is located between the two tropics:
What Plants and Animals Live in Africa?

Africa has many kinds of wildlife. It is the only continent that still has many native species of large mammals. Some of these animals are found in very large numbers. You can find antelope, buffalo, zebras, cheetahs, elephants, lions, giraffes, rhinoceros, apes, hyenas, and many more. Over 2,000 types of fish live in Africa's lakes and rivers.
How is Africa Governed?
The African Union (AU) is an international organization. It was created to help keep peace among Africa's many countries. It has a government with law-making, justice, and executive parts. The African Union President leads it.
Who Are the People of Africa?
People from Africa are called Africans. People living north of the Sahara Desert are called Maghrebis. Those living south of the Sahara are called Subsaharans. Some languages spoken in eastern Africa include Swahili, Oromo, and Amharic. In western Africa, languages like Lingala, Igbo, and Fulani are spoken. The country with the most people in Africa is Nigeria.
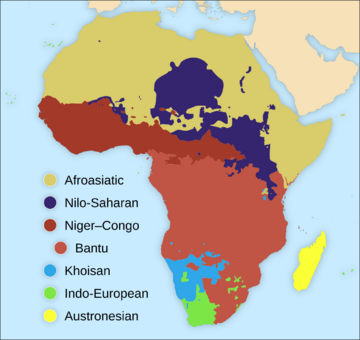
The Many Languages of Africa
Africa is home to well over a thousand languages, and some estimates say there are around two thousand! Most of these languages originated in Africa. It's common for people in Africa to speak several African languages, plus one or more European languages.
There are four main groups of languages native to Africa:
- The Afroasiatic languages are spoken by about 285 million people across North Africa, the Sahel, and the Horn of Africa.
- The Nilo-Saharan languages are spoken by 30 million people in countries like Chad, Ethiopia, and Sudan.
- The Niger-Congo language family covers most of sub-Saharan Africa and is one of the largest language families in the world.
- The Khoisan languages are mainly spoken in Southern Africa by about 400,000 people. Many of these languages are becoming rare.
After colonial rule ended, most African countries adopted European languages like English or French as their official languages. However, many countries also recognize and use their own native languages, such as Swahili and Hausa.
Countries in Africa
| Country | Area (mi²) |
Population | Year | Density (per mi²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Africa | |||||
| 919,595 | 45,377,509 | 2022 | 48 | Algiers | |
| 2,893 | 2,153,389 | 2019 | 740 | Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Santa Cruz de Tenerife |
|
| 7.1 | 85,144 | 2018 | 12,000 | — | |
| 384,345 | 106,055,142 | 2022 | 266 | Cairo | |
| 679,362 | 7,051,429 | 2022 | 10 | Tripoli | |
| 309 | 251,060 | 2021 | 810.7 | Funchal | |
| 4.7 | 86,384 | 2018 | 18,000 | — | |
| 172,317 | 37,754,017 | 2022 | 214 | Rabat | |
| 681,489 | 45,822,691 | 2022 | 64 | Khartoum | |
| 59,985 | 12,057,040 | 2022 | 197 | Tunis | |
| Western Sahara | 102,703 | 625,647 | 2022 | 6 | El Aaiún |
| Horn of Africa | |||||
| 8,950 | 1,015,699 | 2022 | 22 | Djibouti | |
| 38,996 | 3,641,048 | 2022 | 91 | Asmara | |
| 386,102 | 120,452,406 | 2022 | 298 | Addis Ababa | |
| 242,217 | 16,747,831 | 2022 | 66 | Mogadishu | |
| East Africa | |||||
| 9,915 | 12,573,322 | 2022 | 1,199 | Bujumbura | |
| 719 | 905,308 | 2009 | 1,210 | Moroni | |
| 219,746 | 56,054,400 | 2022 | 245 | Nairobi | |
| 224,632 | 29,063,124 | 2022 | 123 | Antananarivo | |
| 36,402 | 20,082,733 | 2022 | 526 | Lilongwe | |
| 784 | 1,275,836 | 2022 | 1,623 | Port Louis | |
| 145 | 285,503 | 2022 | 1,884 | Mamoudzou | |
| 303,623 | 32,943,169 | 2022 | 103 | Maputo | |
| 965 | 907,630 | 2022 | 928 | Saint-Denis | |
| 9,525 | 13,571,073 | 2022 | 1,360 | Kigali | |
| 178 | 99,521 | 2022 | 554 | Victoria | |
| 235,890 | 11,446,739 | 2022 | 47 | Juba | |
| 342,009 | 63,013,471 | 2022 | 175 | Dodoma | |
| 77,147 | 48,525,005 | 2022 | 593 | Kampala | |
| 287,024 | 19,376,272 | 2022 | 64 | Lusaka | |
| 149,364 | 15,280,042 | 2022 | 100 | Harare | |
| Central Africa | |||||
| 481,353 | 34,836,632 | 2022 | 68 | Luanda | |
| 182,514 | 27,819,516 | 2022 | 145 | Yaoundé | |
| 240,534 | 4,991,649 | 2022 | 20 | Bangui | |
| 486,180 | 17,334,293 | 2022 | 34 | N'Djamena | |
| 131,854 | 5,779,882 | 2022 | 42 | Brazzaville | |
| 875,313 | 94,809,089 | 2022 | 102 | Kinshasa | |
| 10,830 | 1,491,816 | 2022 | 130 | Malabo | |
| 99,487 | 2,326,964 | 2022 | 22 | Libreville | |
| 371 | 227,004 | 2022 | 591 | São Tomé | |
| Southern Africa | |||||
| 218,816 | 2,443,156 | 2022 | 11 | Gaborone | |
| 11,722 | 2,174,990 | 2022 | 183 | Maseru | |
| 317,874 | 2,629,611 | 2022 | 8 | Windhoek | |
| 468,376 | 60,750,322 | 2022 | 127 | Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria | |
| 6,641 | 1,183,323 | 2022 | 175 | Mbabane | |
| West Africa | |||||
| 43,537 | 12,735,234 | 2022 | 278 | Porto-Novo | |
| 105,638 | 22,008,021 | 2022 | 198 | Ouagadougou | |
| 1,556 | 567,629 | 2022 | 327 | Praia | |
| 122,780 | 27,637,309 | 2022 | 215 | Abidjan, Yamoussoukro | |
| 3,907 | 2,547,523 | 2022 | 618 | Banjul | |
| 87,854 | 32,323,235 | 2022 | 354 | Accra | |
| 94,873 | 13,819,375 | 2022 | 138 | Conakry | |
| 10,857 | 2,057,657 | 2022 | 181 | Bissau | |
| 37,189 | 5,286,815 | 2022 | 136 | Monrovia | |
| 471,118 | 21,375,017 | 2022 | 43 | Bamako | |
| 397,955 | 4,885,222 | 2022 | 12 | Nouakchott | |
| 489,075 | 25,895,281 | 2022 | 49 | Niamey | |
| 351,650 | 215,987,465 | 2022 | 586 | Abuja | |
| 151 | 6,112 | 2022 | 40 | Jamestown | |
| 74,336 | 17,594,382 | 2022 | 225 | Dakar | |
| 27,869 | 8,289,685 | 2022 | 286 | Freetown | |
| 21,000 | 8,652,723 | 2022 | 394 | Lomé | |
| Africa Total | 11,447,338 | 1,402,538,258 | 2022 | 117 | |
What is the African Diaspora?
The "African diaspora" refers to people of African descent who live outside of Africa. Here are some countries with many people of African heritage:
- Haiti: 98%
- Saint Kitts and Nevis: 96.9%
- Anguilla: 91.4%
- Bahamas: 86.1%
- Barbados: 81.1%
- Jamaica: 76.3%
- Dominican Republic: 71.1%
- Cayman Islands: 60.0%
- Trinidad and Tobago: 39.5%
- Cuba: 34.9%
- Turks and Caicos: 34.0%
- Belize: 29.8%
- Venezuela: 24.0%
- Panama: 22.0%
- Colombia: 21.0%
- Brazil: 13-19%
- United States: 12.9%
- Puerto Rico: 6.9%
- Argentina: less than 2%
Key Facts About Africa
- Africa is the second-largest continent in the world, after Asia. It has 54 countries.
- Large bodies of water surround Africa.
- Africa's climate changes a lot, from desert in the north to rainforest near the equator in the middle. Other parts have mountains or grasslands.
- Africa is home to many different kinds of wildlife. Each animal lives in the climate that suits it best.
- Africa has been shaped by the Egyptian civilization and by Islam.
- Slavery has been practiced in Africa for centuries. The Arab slave trade took 18 million enslaved people from Africa. The Atlantic slave trade took 7-12 million enslaved people to the New World.
- In the late 1800s, European countries took control of many African nations.
- In 1951, Libya became the first former colony to become independent.
- The African Union was created to help keep peace among Africa's many countries.
See Also
 In Spanish: África para niños
In Spanish: África para niños
Images for kids
-
The totality of Africa seen by the Apollo 17 crew
-
Lucy, an Australopithecus afarensis skeleton discovered 24 November 1974 in the Awash Valley of Ethiopia's Afar Depression
-
The Ezana Stone records King Ezana's conversion to Christianity and his subjugation of various neighboring peoples, including Meroë.
-
The intricate 9th-century bronzes from Igbo-Ukwu, in Nigeria displayed a level of technical accomplishment that was notably more advanced than European bronze casting of the same period.
-
Ruins of Great Zimbabwe (flourished eleventh to fifteenth centuries)
-
Savanna at Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania
-
The rock-hewn Church of Saint George in Lalibela, Ethiopia is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
-
Nok figure (5th century BC-5th century AD)