Australia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Commonwealth of Australia
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "Advance Australia Fair"
|
|
Commonwealth of Australia Australian territorial claim in Antarctica
|
|
| Capital | Canberra 35°18′29″S 149°07′28″E / 35.30806°S 149.12444°E |
| Largest city | Sydney (metropolitan) Melbourne (urban) |
| Official language and national language | English (de facto) None (de jure) |
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Sam Mostyn | |
| Anthony Albanese | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Federation and creation of the Constitution
|
1 January 1901 |
| 15 November 1926 | |
| 9 October 1942 | |
|
• Australia Acts
|
3 March 1986 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
7,688,287 km2 (2,968,464 sq mi) (6th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.79 (2015) |
| Population | |
|
• 2025 estimate
|
|
|
• 2021 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
3.6/km2 (9.3/sq mi) (244th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2020) | ▼ 32.4 medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 10th |
| Currency | Australian dollar ($) (AUD) |
| Time zone | UTC+8; +9.5; +10 (AWST, ACST, AEST) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+10.5; +11 (ACDT, AEDT) |
| DST not observed in Qld, WA and NT | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +61 |
| ISO 3166 code | AU |
| Internet TLD | .au |
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a large country that includes the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and many smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country by land area. Australia is known for being the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with soils that are not very fertile.
Australia is a megadiverse country, meaning it has a huge variety of plants and animals. Its large size means it has many different landscapes and climates. You can find deserts in the middle, tropical rainforests in the north-east, tropical savannas in the north, and mountain ranges in the south-east.
The first people to live in Australia were Aboriginal Australians. Their ancestors arrived from Southeast Asia about 65,000 years ago, during the last ice age. They traveled by sea and settled the continent, forming about 250 different language groups. They have some of the longest-running artistic and religious traditions in the world.
Australia's written history began when Europeans started exploring. The Dutch explorer Willem Janszoon was the first known European to reach Australia in 1606. In 1770, the British explorer James Cook mapped the east coast and claimed it for Great Britain. The First Fleet of British ships arrived in Sydney in 1788 to start a new colony called New South Wales.
More Europeans arrived over the next decades. By the end of the gold rush in the 1850s, most of the continent had been explored by European settlers. Five more self-governing British colonies were set up. Over the 1800s, democratic parliaments were slowly created. This led to the federation of the six colonies and the start of the Commonwealth of Australia on January 1, 1901. This was the beginning of Australia gaining more independence from the United Kingdom, which was completed with the Australia Act 1986.
Australia is a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. It has six states and ten territories. Almost 28 million people live in Australia, and most live in cities along the eastern coast. Canberra is the capital city. Sydney is the largest city and a major financial hub. Other large cities include Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide. Australia is a very diverse and multicultural country, with many people having parents born overseas.
Australia has lots of natural resources and strong international trade. Its economy earns money from services, mining exports, banking, manufacturing, agriculture, and international education. Australia is ranked very high in the world for its quality of life, health, education, and freedoms.
Australia has a highly developed economy and one of the highest incomes per person globally. It is a regional power and has the world's thirteenth-highest military spending. Australia is part of many international groups like the United Nations, the G20, and the Commonwealth of Nations. It is also a close ally of the United States.
Contents
About the Name Australia
The name Australia comes from the Latin words "Terra Australis", which means "southern land". This name was used for a made-up continent in the Southern Hemisphere a long time ago. Some mapmakers in the 1500s used the word Australia on their maps, but not for the land we know today. When Europeans started exploring and mapping Australia in the 1600s, they naturally used the name Terra Australis for these new lands.
Before the early 1800s, Australia was mostly known as New Holland. This name was first given by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman in 1644. The explorer Matthew Flinders helped make the name Australia popular. He said it sounded "more agreeable to the ear." The name Australia was first officially used in April 1817 by Governor Lachlan Macquarie. In 1824, the British Admiralty agreed that the continent should officially be called Australia.
People often call Australia "Oz" or "the Land Down Under." Other nicknames include "the Great Southern Land" and "the Sunburnt Country." The last two come from Dorothea Mackellar's 1908 poem "My Country".
Australia's Story
First Peoples

Indigenous Australians include two main groups: the Aboriginal peoples from the mainland (and nearby islands like Tasmania), and the Torres Strait Islanders, who are a different group from Melanesia. People are thought to have first lived on the Australian continent 50,000 to 65,000 years ago. They came by land bridges and short sea trips from what is now Southeast Asia.
The Madjedbebe rock shelter in Arnhem Land is the oldest place showing humans in Australia. The oldest human remains found are the Lake Mungo remains, which are about 41,000 years old. Aboriginal Australian culture is one of the oldest continuous cultures on Earth. When Europeans first arrived, Aboriginal Australians were skilled hunter-gatherers with many different ways of life and about 250 different language groups. They have an oral culture, meaning they pass down stories by speaking. Their spiritual beliefs are based on respecting the land and the Dreamtime.
The Torres Strait Islander people settled their islands about 4000 years ago. They are different from mainland Aboriginal peoples in their culture and languages. They were seafarers who got their food from farming and the ocean.
European Arrival and Settlement

The northern coasts of Australia were sometimes visited by Makassan fishermen from what is now Indonesia for trade. The first time Europeans officially saw the Australian mainland was by the Dutch. The ship Duyfken, led by Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon, was the first to map the Australian coast and meet Aboriginal people in 1606. Later that year, Spanish explorer Luís Vaz de Torres sailed through the Torres Strait Islands. The Dutch mapped the western and northern coastlines and named the continent "New Holland" in the 1600s.
In 1770, Captain James Cook sailed along and mapped the east coast. He named it "New South Wales" and claimed it for Great Britain. After losing its American colonies, the British Government sent the First Fleet of ships, led by Captain Arthur Phillip. Their goal was to start a new colony in New South Wales. They set up a camp and raised the Union Flag at Sydney Cove on January 26, 1788. This date later became Australia's national day.
Many early settlers were people who had been sent to Australia as punishment for crimes. They often worked as laborers for free settlers. The number of Indigenous people decreased for 150 years after European settlement, mainly due to diseases. Many also died in conflicts with settlers.
Growing Colonies

The British continued to explore other parts of the continent in the early 1800s. In 1803, a settlement was started in Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania). In 1813, explorers crossed the Blue Mountains west of Sydney, opening up the inland areas for European settlement. The British claimed the whole Australian continent in 1827.
As the population grew, new colonies were created from New South Wales: Tasmania in 1825, South Australia in 1836, Victoria in 1851, and Queensland in 1859. South Australia was a "free province" and never a penal colony. Western Australia also started as "free" but later accepted people sent there as punishment.
Between 1855 and 1890, the six colonies each gained responsible government. This meant they became democracies that managed most of their own affairs, while still being part of the British Empire. In the mid-1800s, explorers like Burke and Wills traveled further inland. A series of gold rushes starting in the 1850s brought many new migrants from China, North America, and Europe.
From 1886, Australian colonial governments began policies that led to many Aboriginal children being removed from their families. This is known as the Stolen Generations.
From Federation to World Wars

On January 1, 1901, the colonies joined together to form the Commonwealth of Australia. This was called federation. Australia became one of the first members of the League of Nations in 1920, and later the United Nations in 1945.
The Federal Capital Territory (now the Australian Capital Territory) was created in 1911 for the future capital city, Canberra. Melbourne was the temporary capital from 1901 to 1927. The Northern Territory also became part of the federal government in 1911.

In 1914, Australia joined the Allies in the First World War. About 416,000 Australians served, and about 60,000 were killed. Many Australians see the defeat of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZACs) at Gallipoli in 1915 as a very important moment for the nation. The anniversary is celebrated every year on Anzac Day.
From 1939 to 1945, Australia fought with the Allies in the Second World War. Australian forces fought in the Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East. After Britain's defeat in Asia in 1942 and the bombing of Darwin by Japan, many Australians believed a Japanese invasion was possible. This led Australia to rely more on the United States as its main ally, rather than the United Kingdom. Since 1951, Australia has been a formal military ally of the United States through the ANZUS treaty.
After the Wars and Today

After World War II, Australia saw big improvements in living standards and leisure time. The country encouraged a large wave of immigration from Europe, with new arrivals often called "New Australians".
Australia was part of the Western Bloc during the Cold War. It took part in the Korean War in the 1950s and the Vietnam War from 1962 to 1972. A 1967 referendum gave the Federal Government power to make policies for Aboriginal people, and all Indigenous Australians were included in the Census.
The Australia Act 1986 officially ended the remaining legal ties between Australia and the United Kingdom. However, in a 1999 vote, 55% of people rejected the idea of removing the Monarchy of Australia and becoming a republic.
After the September 11 attacks in the United States, Australia joined the US in the Afghanistan War (2001-2021) and the Iraq War (2003-2009). In the 21st century, Australia's trade has focused more on East Asia, with China becoming its biggest trading partner.
During the COVID-19 pandemic starting in 2020, some of Australia's largest cities had long lockdowns. Travel between states was also limited to slow the spread of the virus.
Australia's Land
Key Features
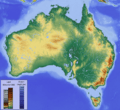
Australia is surrounded by the Indian and Pacific oceans. The Arafura and Timor seas separate it from Asia. The Coral Sea is off the Queensland coast, and the Tasman Sea is between Australia and New Zealand. Australia is the world's smallest continent and sixth largest country. Because of its size and isolation, it's often called the "island continent" and sometimes the world's largest island. Australia has over 34,000 km of coastline.
Mainland Australia stretches from about 9° to 44° South latitude and 112° to 154° East longitude. Its size gives it many different landscapes. There are tropical rainforests in the north-east, mountain ranges in the south-east, south-west, and east, and desert in the middle. The desert or semi-arid land, known as the outback, makes up most of the country. Australia is the driest inhabited continent. Its average rainfall is less than 500 mm per year.

The Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef, is off the north-east coast. It stretches for over 2,000 km. Mount Augustus in Western Australia is thought to be the world's largest single rock. At 2,228 m, Mount Kosciuszko is the highest mountain on the Australian mainland.
Eastern Australia has the Great Dividing Range, a mountain chain that runs along the coast. This range includes low hills and highlands that are usually no more than 1,600 m high. Between the coast and the mountains are coastal uplands and grasslands. Inland from the range are large areas of grassland and shrubland. The northernmost point of the mainland is the tropical Cape York Peninsula.

The landscapes of the Top End and the Gulf Country have a tropical climate. They include forests, woodlands, wetlands, grasslands, rainforests, and deserts. In the north-west are the sandstone cliffs of The Kimberley. The heart of the country has the uplands of central Australia. Famous features in the center and south include Uluru (also called Ayers Rock), a well-known sandstone rock, and large deserts like the Simpson and Great Victoria deserts. The famous Nullarbor Plain is on the southern coast.
Geology and Landforms
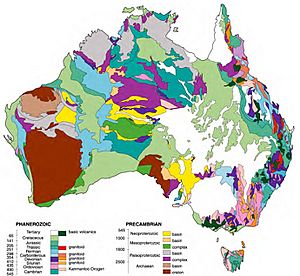
Australia sits on the Indo-Australian plate. Its mainland is the lowest and oldest landmass on Earth, with a very stable geological history. It has almost all known rock types from Earth's history, going back over 3.8 billion years.
Australia was once part of a huge supercontinent called Gondwana. It started to separate from Africa and India in the Permian period. It then separated from Antarctica over a long time, from the Permian to the Cretaceous periods. When the last ice age ended about 10,000 BC, rising sea levels formed Bass Strait, separating Tasmania from the mainland. Australia is still moving towards Eurasia at about 6 to 7 centimeters per year.
The Australian mainland and Tasmania are in the middle of a tectonic plate. This means they have no active volcanoes. However, some recent volcanic activity has happened in western Victoria and southeastern South Australia. Volcanoes also exist on the island of New Guinea (geologically part of Australia) and on Heard Island and McDonald Islands. Earthquake activity in Australia is also low.
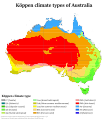
Climate and Weather
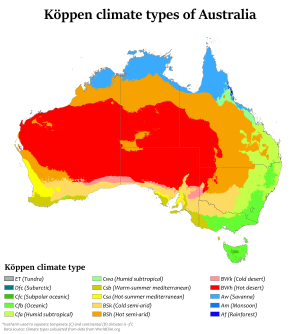
Australia's climate is greatly affected by ocean currents. These include the Indian Ocean Dipole and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, which can cause droughts. Tropical low-pressure systems also bring cyclones to northern Australia. These factors mean rainfall can change a lot from year to year.
Most of northern Australia has a tropical climate with rain mainly in summer (monsoon). The south-west has a Mediterranean climate. The south-east ranges from oceanic (Tasmania and coastal Victoria) to humid subtropical (northern New South Wales). The highlands have alpine weather. The middle of the country is dry or semi-arid.
Due to climate change, average temperatures in Australia have risen more than 1°C since 1960. Changes in rainfall and extreme weather make problems like drought and bushfires worse. 2019 was Australia's warmest year on record, and the 2019–2020 bushfire season was the worst ever.
Water restrictions are often in place in many areas because of growing populations and local droughts. After long periods of drought, major flooding often occurs, filling up rivers and overflowing dams. This happened in Eastern Australia in the early 2010s after the 2000s Australian drought.
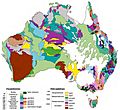
Plants and Animals
Even though most of Australia is dry, it has many different habitats, from alpine areas to tropical rainforests. Australia has an estimated 250,000 species of fungi, but only 5% have been named. Because Australia is so old, has very changeable weather, and has been isolated for a long time, much of its biota (plants and animals) is unique. About 85% of its flowering plants, 84% of mammals, over 45% of birds, and 89% of in-shore fish are found nowhere else. Australia has at least 755 species of reptiles, more than any other country.
Australian forests are mostly made up of evergreen trees, especially eucalyptus trees in less dry areas. Wattles are common in drier regions and deserts. Well-known Australian animals include the monotremes (the platypus and echidna); many marsupials like the kangaroo, koala, and wombat; and birds such as the emu and kookaburra. Australia is home to many dangerous animals, including some of the world's most venomous snakes. The dingo was brought to Australia about 4000 years ago by Austronesian people.
Many of Australia's plants and animals are threatened by human activities and introduced species like feral cats. These factors have led to Australia having the highest mammal extinction rate in the world. The federal Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 helps protect threatened species. Many protected areas have been created to save unique ecosystems. Australia has 16 natural World Heritage Sites.
How Australia is Governed
Australia is a constitutional monarchy, a parliamentary democracy, and a federation. This means it has a King or Queen, a parliament where people vote for their leaders, and power is shared between a central government and state governments. Its constitution has been mostly unchanged since 1901.
Government power is divided into three parts:
- Legislature: The Parliament, which makes laws. It includes the monarch (King Charles III), the Senate, and the House of Representatives.
- Executive: The Cabinet, led by the prime minister. The prime minister is the leader of the party that has the most support in the House of Representatives. The Governor-General formally appoints them.
- Judiciary: The High Court and other federal courts, which interpret and apply laws.
Charles III is the King of Australia. He is represented in Australia by the Governor-General at the federal level and by governors in each state. These representatives usually act on the advice of their ministers. This means the Governor-General mostly acts as a legal figurehead for the prime minister and Cabinet.
The Senate (the upper house of Parliament) has 76 senators. Each state has twelve senators, and the mainland territories (Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory) each have two. The House of Representatives (the lower house) has 151 members. These members are elected from different areas called "electorates" or "seats." The number of seats for each state depends on its population.
Elections for both houses are usually held at the same time. Voting and enrolling to vote are compulsory for all citizens aged 18 and over. The party with the most support in the House of Representatives forms the government, and its leader becomes Prime Minister.
There are two main political groups that usually form the government: the Australian Labor Party and the Coalition. The Coalition is a formal group of the Liberal Party and the National Party. The Coalition is generally considered centre-right, and the Labor Party is considered centre-left. The Australian Greens are also an important party.
The most recent federal election was held on May 21, 2022. The Australian Labor Party, led by Anthony Albanese, won the election and formed the government.
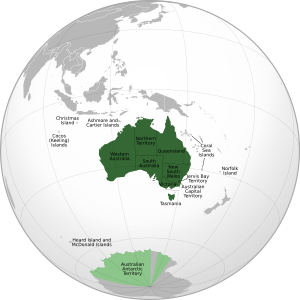
States and Territories
Australia has six states:
- New South Wales (NSW)
- Queensland (QLD)
- South Australia (SA)
- Tasmania (TAS)
- Victoria (VIC)
- Western Australia (WA)
It also has three mainland territories:
- Australian Capital Territory (ACT)
- Northern Territory (NT)
- Jervis Bay Territory (JBT)
The ACT and NT work much like states, but the federal Parliament can change their laws. States have the power to make laws on most topics, like education, health, and local government. However, federal laws are stronger if there is a conflict with state laws.
Each state and major mainland territory has its own parliament. The leader of the government in each state is called the Premier. In each territory, the leader is called the Chief Minister. The King is represented in each state by a governor.
The federal Parliament also directly manages external territories like Christmas Island and the Australian Antarctic Territory.
International Relations
In recent decades, Australia's international relations have focused on the Asia-Pacific region. Australia also maintains a close relationship with the United States through the ANZUS pact. Australia is a regional power and a member of groups like the Pacific Islands Forum and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Australia is part of several defense and intelligence groups, including the Five Eyes intelligence alliance with the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and New Zealand. It is also part of the AUKUS security treaty with the United States and United Kingdom.
Australia has worked to promote free trade around the world. It helped create the Cairns Group and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation. Australia is also a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the World Trade Organization. It has free trade agreements with many countries, including the United States, China, Japan, and New Zealand.
Australia has a very close relationship with its neighbor, New Zealand. Citizens can travel freely between the two countries. Australia is a founding member of the United Nations and provides aid to about 60 countries.
Military Forces
Australia's armed forces are called the Australian Defence Force (ADF). They include the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), the Australian Army, and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). In 2015, they had over 81,000 personnel, including regular and reserve members. The Governor-General is the official Commander-in-Chief.
In 2016–2017, Australia spent 2% of its GDP on defense. This made it the world's 12th largest defense budget. Australia has been involved in United Nations peacekeeping missions, disaster relief, and armed conflicts since the First World War.
Australia's Economy
Australia has a high-income mixed-market economy with many natural resources. It is the world's thirteenth-largest economy by its total value. As of 2021, Australia had the second-highest amount of wealth per adult globally.
Australia has about 13.5 million people in its workforce, and the unemployment rate was 3.5% in June 2022. The Australian dollar is the national currency. It is also used by three Pacific Island states: Kiribati, Nauru, and Tuvalu.
The service sector makes up about 71.2% of Australia's total economy. The industrial sector is 25.3%, and the agriculture sector is the smallest at 3.6%. Australia is the world's 21st-largest exporter and 24th-largest importer. China is Australia's biggest trading partner, buying about 40% of its exports. Other major export markets include Japan, the United States, and South Korea.
Australia has high levels of economic freedom and is ranked eighth in the Human Development Index. In 2019, it attracted 9.5 million international tourists. Tourism is an important part of the Australian economy.
Energy Sources
In 2003, Australia's energy came mostly from coal (58.4%) and hydropower (19.1%). In the 21st century, Australia has been trying to use more renewable energy sources and less fossil fuels. In 2020, Australia used coal for 62% of its energy. Wind power and solar power each made up 9.9% of energy.
In 2009, Australia's government aimed to get 20% of its energy from renewable sources by 2020. They reached this goal, with renewable resources making up 27.7% of Australia's energy in 2020.
Science and Technology
In 2019, Australia spent A$35.6 billion on research and development. This was about 1.79% of its total economy. The Australian tech sector contributes $167 billion a year to the economy and employs 861,000 people. Mining is the most advanced sector for technology in Australia, using drones and remote-controlled vehicles. Australia's startup ecosystem is growing quickly.
Australia consistently ranks high in the Global Innovation Index. In 2022, it was 25th out of 132 economies. Even though Australia has only 0.3% of the world's population, it contributed 4.1% of the world's research in 2020. This makes it one of the top 10 research contributors.
CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, does 10% of all research in the country. Its notable inventions include atomic absorption spectroscopy, key parts of Wi-Fi technology, and the first successful polymer banknote. Australia also plays a big role in space exploration. Facilities like the Square Kilometre Array and Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex help with deep space missions, especially for NASA.
Tourism in Australia
Tourism is a very important part of Australia's economy. It includes both local and international visitors. Australia is the fortieth most visited country in the world.

Some major Australian places for tourists to visit include:
- Great Barrier Reef
- Red Centre
- Great Ocean Road
- Barossa Valley
- Kakadu
- The Kimberley
- Kangaroo Island
- Byron Bay
- Tasmanian Wilderness
- Australian Alps
- Ningaloo
- Flinders Ranges
- Fraser Island
- Sydney Harbour Bridge
- Freycinet
- Gippsland
- Uluru
- Coober Pedy
- Sydney Opera House
- Phillip Island
- Melbourne Cricket Ground
- Blue Mountains
- Namadgi National Park
People of Australia

Australia has a low population density of about 3.4 people per square kilometer. This makes it one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. Most people live on the east coast, especially in the south-eastern region between South East Queensland and Adelaide.
Australia is highly urbanized, with 67% of the population living in the metropolitan areas of the capital cities in 2018. Cities with over one million people are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.
Like many other developed countries, Australia's population is getting older. This means there are more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2018, the average age of Australians was 38.8 years.
Ancestry and Immigration
Between 1788 and World War II, most settlers came from the British Isles (England, Ireland, and Scotland). There was also significant immigration from China and Germany in the 1800s. After World War II, Australia had a large wave of immigration from all over Europe.
Since the end of the White Australia policy in 1973, Australia has had an official policy of multiculturalism. There has been a large and ongoing wave of immigration from around the world, with Asia being the biggest source of immigrants in the 21st century.
Today, Australia has the world's eighth-largest immigrant population. Immigrants make up 30% of the population, which is the highest proportion among major Western nations. In 2020, the largest foreign-born groups were from England (3.8%), India (2.8%), and Mainland China (2.5%).
At the 2021 census, Australians were asked to name their ancestry. The most common individual ancestries were:
- English (33%)
- Australian (29.9%)
- Irish (9.5%)
- Scottish (8.6%)
- Chinese (5.5%)
- Italian (4.4%)
- German (4%)
- Indian (3.1%)
- Aboriginal (2.9%)
At the 2021 census, 3.2% of the Australian population identified as being Indigenous (Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders).
Languages Spoken
English is not officially the language of Australia by law, but it is the main and national language. Australian English has its own accent and words.
At the 2021 census, English was the only language spoken at home for 72% of the population. The next most common languages spoken at home were Mandarin (2.7%), Arabic (1.4%), and Vietnamese (1.3%).
Over 250 Australian Aboriginal languages are thought to have existed when Europeans first arrived. In 2018-19, more than 120 Indigenous language varieties were still in use or being brought back, but 70 of them were endangered. The 2021 census found that 167 Indigenous languages were spoken at home by Indigenous Australians.
The Australian sign language called Auslan was used at home by 16,242 people in 2021.
Religions

Australia has no state religion. The Australian Constitution says the federal government cannot create a religion or stop people from practicing their religion freely.
At the 2021 Census, 38.9% of the population said they had "no religion". This was up from 15.5% in 2001. The largest religion is Christianity (43.9% of the population). The biggest Christian groups are the Roman Catholic Church (20%) and the Anglican Church of Australia (9.8%).
Since World War II, immigration has led to the growth of non-Christian religions. The largest of these are Islam (3.2%), Hinduism (2.7%), and Buddhism (2.4%). In 2021, almost 8,000 people said they followed traditional Aboriginal religions. In Australian Aboriginal mythology, the Dreaming is a sacred time when spirit beings created the world and set up society's rules.
Health in Australia
Australia's life expectancy is 83 years (81 for males and 85 for females), which is the fifth-highest in the world. Australia has the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. In 2012, 63% of Australian adults were overweight or obese.
Australia spent about 9.91% of its total economy on health care in 2021. It started universal health care in 1975, called Medicare. This is funded by an income tax. The states manage hospitals, while the federal government helps pay for medicines and general doctor visits.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Australia had very strict quarantine rules. This led to one of the lowest death rates worldwide.
Education System

Going to school, or being registered for home schooling, is required throughout Australia. Education is managed by each state and territory, so the rules are slightly different. Generally, children must attend school from about age 5 to about 16. In some states, 16-17 year olds must either go to school or do vocational training, like an apprenticeship.
Australia's adult literacy rate was estimated to be 99% in 2003. However, a 2011–2012 report found that Tasmania had a lower literacy and numeracy rate of 50%.
Australia has 37 government-funded universities and three private universities. The OECD says Australia is one of the most expensive countries to attend university. There is also a system for vocational training called TAFE. About 58% of Australians aged 25 to 64 have vocational or university qualifications. Australia has the highest number of international students per person in the world. In 2019, there were 812,000 international students. Education is Australia's third-largest export, after iron ore and coal.
Australian Culture

Australia is home to many different cultures because of its history of immigration. Before 1850, Indigenous cultures were dominant. Since then, Australian culture has mainly been Western, strongly influenced by Anglo-Celtic settlers. Other influences come from Australian Aboriginal culture, traditions brought by immigrants from around the world, and the culture of the United States. Over the centuries, Australian culture has developed its own unique style.
Arts and Creativity

Australia has over 100,000 Aboriginal rock art sites. Traditional designs and stories are still important in contemporary Indigenous Australian art. Early colonial artists were fascinated by the new land. The impressionistic works of Arthur Streeton and Tom Roberts from the 19th-century Heidelberg School were the first "distinctively Australian" art movement. Later, modernists like Margaret Preston and Sidney Nolan explored new styles. The landscape remained central to the work of Aboriginal watercolourist Albert Namatjira.
Australian literature grew slowly after European settlement, though Indigenous oral traditions are much older. In the 19th century, Henry Lawson and Banjo Paterson wrote about life in the bush using unique Australian words. Their works are still popular. Paterson's bush poem "Waltzing Matilda" (1895) is seen as Australia's unofficial national anthem. The Miles Franklin Award is Australia's most important literary prize. Its first winner, Patrick White, later won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1973.
Many of Australia's performing arts groups get funding from the government. There is a symphony orchestra in each state and a national opera company, Opera Australia. Nellie Melba was a famous opera singer in the early 1900s. Ballet and dance are represented by The Australian Ballet. Each state also has a publicly funded theatre company.
Media and Entertainment

The Story of the Kelly Gang (1906), the world's first feature-length story film, led to a boom in Australian cinema during the silent film era. After World War I, Hollywood took over, and Australian film production almost stopped by the 1960s. With government help, the Australian New Wave of the 1970s brought successful films, many exploring Australian identity, like Wake in Fright and Gallipoli. Crocodile Dundee and the Mad Max series became international hits. The AACTAs are Australia's top film and television awards. Famous Academy Award winners from Australia include Nicole Kidman and Cate Blanchett.
Australia has two public broadcasters (the Australian Broadcasting Corporation and the multicultural Special Broadcasting Service). There are also three commercial television networks and many pay-TV services. Each major city has at least one daily newspaper. There are two national daily newspapers, The Australian and The Australian Financial Review.
Food and Drink

Most Indigenous Australian groups ate a simple hunter-gatherer diet of native plants and animals, called bush tucker. The first European settlers brought British and Irish cuisine to Australia. This influence can still be seen in popular dishes like fish and chips and the Australian meat pie.
After World War II, immigration changed Australian food. For example, Southern European migrants helped create a strong Australian coffee culture, leading to drinks like the flat white. Asian migration led to dishes like the Cantonese-influenced dim sim and Chiko Roll. Sausage sizzles, pavlovas, lamingtons, meat pies, Vegemite, and Anzac biscuits are seen as classic Australian foods.
Australia is a major exporter and consumer of wine. Australian wine is mostly made in the cooler southern parts of the country. Australia also ranks high in beer consumption. Each state and territory has many breweries. Australia is also known for its cafe and coffee culture in cities.
Sports and Fun

Cricket and football are the most popular sports in Australia. Australia is unique because it has professional leagues for four different types of football. Australian rules football, which started in Melbourne in the 1850s, is the most popular in most states. However, rugby league is more popular in New South Wales and Queensland. Soccer has the highest overall participation rates.
Cricket is popular everywhere and is often seen as the national sport. The Australian national cricket team played in the first Test match (1877) and the first One Day International (1971). They have also won the Cricket World Cup a record five times.
Australia is one of only five nations to have competed in every Summer Olympics of the modern era. It has hosted the Games twice: 1956 in Melbourne and 2000 in Sydney. Brisbane is set to host the 2032 Games. Australia has also participated in every Commonwealth Games.
Other major international events in Australia include the Australian Open tennis tournament and the Australian Formula One Grand Prix. The annual Melbourne Cup horse race and the Sydney to Hobart yacht race are also very popular. Australia is also known for water sports like swimming and surfing. The surf lifesaving movement started in Australia, and the volunteer lifesaver is an iconic symbol. Snow sports mainly happen in the Australian Alps and Tasmania.
Images for kids
See Also
 In Spanish: Australia para niños
In Spanish: Australia para niños