United Kingdom facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "God Save the King"
|
|
|
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| National language | |
| Regional and minority languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2021/22)
|
|
| Religion
(2021/22)
|
List
46.5% Christianity
37.8% no religion 6.0% Islam 1.6% Hinduism 0.8% Sikhism 0.4% Buddhism 0.4% Judaism 0.6% other 5.9% not stated |
| Demonym(s) | |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Keir Starmer | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Lords | |
| House of Commons | |
| Formation | |
| 1535 and 1542 | |
| 24 March 1603 | |
| 22 July 1706 | |
| 1 May 1707 | |
| 1 January 1801 | |
| 6 December 1922 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
244,376 km2 (94,354 sq mi) (78th) |
|
• Land
|
242,741 km2 (93,723 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate
|
67,596,281 (22nd) |
|
• 2021/22 census
|
66,940,559 |
|
• Density
|
279/km2 (722.6/sq mi) (51st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2021) | ▼ 35.4 medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 15th |
| Currency | Pound sterling (GBP) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (GMT) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+1 (BST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +44 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB |
| Internet TLD | .uk |
The United Kingdom (UK), also known as Britain, is a country located in Northwestern Europe. It lies off the coast of mainland Europe and is made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the large island of Great Britain, the northeastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands nearby. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland. Otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is about 244,376 square kilometers (94,354 square miles), and in 2022, it had nearly 67.6 million people.
The Kingdom of Great Britain was formed in 1707 when the Kingdom of England (which included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland joined together. Later, in 1801, the Kingdom of Ireland also joined, creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1922, most of Ireland became independent as the Irish Free State. The remaining part, Northern Ireland, stayed with the UK, and the country's name changed in 1927 to its current form.
The UK was the first country to have an Industrial Revolution. It was a very powerful nation for most of the 1800s and early 1900s. At its largest in the 1920s, the British Empire covered almost a quarter of the world's land and people. However, after its involvement in the First World War and Second World War, Britain's economic power weakened. Many of its colonies then gained independence. Even so, British influence can still be seen in the laws and governments of many former colonies. British culture, especially its language, literature, music, and sports, is still important around the world. English is the world's most widely spoken language.
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy. This means it has a King or Queen as head of state, but the government is run by elected representatives in Parliament. The UK has three main legal systems: for England and Wales, for Scotland, and for Northern Ireland. Since 1999, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own governments and parliaments that handle many local matters. London is the capital and largest city of the UK. It is also the capital of England. Other important cities include Edinburgh (Scotland's capital), Cardiff (Wales's capital), and Belfast (Northern Ireland's capital).
The UK is a developed country with one of the world's largest economies. It has nuclear weapons and ranks high in military spending. The UK has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since 1946. It is also a member of many important international groups like the Commonwealth of Nations, NATO, and the G7.
Contents
What's in a Name? Understanding the UK's Titles
The name "United Kingdom" has changed over time. In 1707, the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland joined to form "Great Britain." Later, in 1801, Great Britain and Ireland united to become the "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland."
After most of Ireland became independent in 1922, only Northern Ireland remained part of the UK. So, in 1927, the name was officially changed to the "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland."
Even though the UK is one country, England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland are often called "countries" themselves. The UK Prime Minister's website has even called them "countries within a country." Sometimes, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland are also called "regions." Northern Ireland is sometimes called a "province."
The term "Great Britain" usually refers to the island that includes England, Scotland, and Wales. It is sometimes used to mean the whole UK, but it technically does not include Northern Ireland. People outside the UK sometimes mistakenly use "England" to mean the whole United Kingdom.
The word "British" is used for things related to the United Kingdom, like British citizens. People in the UK might call themselves British, English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, or Irish. They might even feel they have a mix of these identities.
A Journey Through Time: The UK's History
Early Beginnings and Roman Times

People first settled in what is now the UK around 30,000 years ago. The islands have been lived on continuously since the ice retreated about 11,500 years ago. By the end of prehistoric times, the people living there were mostly Celts.
The Romans arrived in 43 AD and ruled southern Britain for 400 years. After they left, Germanic settlers called Anglo-Saxons invaded. They pushed the Celtic people mostly into what is now Wales and Cornwall. Most of the Anglo-Saxon areas became the Kingdom of England in the 900s. In the north, Gaelic-speakers and Picts formed the Kingdom of Scotland in the 800s.
Medieval Times and the Magna Carta
In 1066, the Normans from northern France invaded England. They conquered England and parts of Wales and Ireland. They brought their feudalism and French culture, which greatly influenced the local ways of life. English kings later conquered Wales but could not take over Scotland. Scotland kept its independence, though it often fought with England.
In 1215, the Magna Carta was signed. This important document was the first to say that no government was above the law. It also stated that citizens have rights and deserve a fair trial.
English kings also fought many wars in France, like the Hundred Years' War. Meanwhile, the Scottish kings had an alliance with the French.
Early Modern Era and the Union of Crowns
During the early modern period, there were religious conflicts because of the Reformation. This led to Protestant churches becoming the official churches in each country. The English Reformation changed England's politics, laws, society, and culture in the 1500s. It also helped define England's national identity. Wales became fully part of the Kingdom of England. In Northern Ireland, lands were taken from Catholic nobles and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.
England grew into a powerful country with a strong navy. It became a leader in trade, industry, and science. The English Renaissance brought great poetry, music, and literature. England started building a trading empire.
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland were joined under one ruler, King James VI of Scotland. He became King James I of England and Ireland. However, each country still had its own government, laws, and religious systems.
In the mid-1600s, all three kingdoms were involved in wars, including the English Civil War. This led to the temporary removal of the monarchy and the execution of King Charles I. A short-lived republic was set up.
Even though the monarchy was brought back, these events made sure that kings could not have absolute power. The British constitution developed with a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. Science was encouraged with the founding of the Royal Society in 1660. Britain also started exploring and setting up colonies overseas, especially in North America and the Caribbean.
The Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800)

On May 1, 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was officially formed. This happened because of the Acts of Union 1707. In the 1700s, the idea of a cabinet government grew, with Robert Walpole becoming the first prime minister. There were several uprisings by people who wanted to bring back the Catholic House of Stuart to the throne. These were finally defeated in 1746.
British colonies in North America fought for independence in the American Revolutionary War and became the United States in 1783. After this, Britain focused its imperial ambitions more on Asia, especially India.
British merchants played a big part in the Atlantic slave trade between 1662 and 1807. They transported millions of enslaved people from Africa to work on plantations, mainly in the Caribbean and North America. However, due to pressure from the abolitionist movement, Parliament banned the slave trade in 1807. Slavery was banned throughout the British Empire in 1833. Britain then worked to end slavery worldwide.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922)

In 1801, the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland passed an Act of Union. This joined the two kingdoms, creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
After defeating France in the Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815), the UK became the main naval and imperial power. London became the world's largest city. Britain's strong navy meant it had no rivals at sea. This period, from 1815 to 1914, was called Pax Britannica (British Peace). During this time, the British Empire became the world's most powerful force. By 1851, Britain was known as the "workshop of the world" because of its industries.
Throughout the Victorian era, politics favored free trade. Parliament slowly gave more people the right to vote. The population grew very quickly, and many people moved to cities, causing social and economic challenges. By the late 1800s, Britain expanded its empire in Africa. Canada, Australia, and New Zealand gained self-governing status. At the start of the 1900s, Germany and the United States began to challenge Britain's industrial power.
World Wars and Ireland's Partition
Britain was one of the main Allies that defeated the Central Powers in the First World War (1914–1918). British forces fought across the British Empire and in Europe. Many men were lost in trench warfare, which had a lasting impact on the nation. After the war, Britain had a huge national debt. The government expanded voting rights to all adult men and most adult women in 1918. The British Empire reached its largest size under Prime Minister David Lloyd George.
By the mid-1920s, most British people could listen to BBC radio. Television broadcasts started in 1929. The rise of Irish nationalism led to the division of Ireland in 1921. The Irish Free State became independent in 1922, while Northern Ireland remained part of the UK. In 1928, women gained equal voting rights with men. The Great Depression (1929–1932) caused high unemployment and hardship in industrial areas.

Britain entered the Second World War in 1939 after Nazi Germany invaded Poland. Winston Churchill became prime minister in 1940. Despite its European allies being defeated early on, Britain and its Empire continued the war against Germany. In 1940, the Royal Air Force defeated the German Luftwaffe in the Battle of Britain. British cities were heavily bombed during the Blitz. Britain, the United States, and the Soviet Union formed the Grand Alliance in 1941. British forces played important roles in the Normandy landings of 1944 and the liberation of Europe. British scientists also helped develop the atomic bomb. The war greatly weakened Britain financially.
Post-War UK and the 21st Century
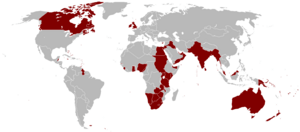
After the war, the UK was one of the "Big Three" powers that planned the post-war world. It helped create the United Nations and became a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. The Labour government under Clement Attlee introduced major reforms. Industries were nationalized, a welfare state was created, and the National Health Service (NHS) was set up to provide free healthcare.
Many colonies of the British Empire gained independence over the next three decades. Many joined the Commonwealth of Nations. The UK was the third country to develop nuclear weapons in 1952. The Suez Crisis of 1956 showed the limits of Britain's international power. The English language continued to spread globally, keeping British literature and culture influential.
In the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries due to a worker shortage. This made the UK a more multi-ethnic society. The UK joined the European Communities (EC) in 1973, which later became the European Union (EU) in 1992.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland experienced violence known as the Troubles. This conflict mostly ended with the 1998 Good Friday Agreement. In the 1980s, the government led by Margaret Thatcher introduced major economic changes. These included selling state-owned companies and making financial markets more open.

In 1982, Argentina invaded the Falkland Islands, leading to the 10-week Falklands War. British forces defeated the Argentines. The islanders strongly prefer to remain British. Towards the end of the 20th century, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland gained their own devolved governments. The UK remained a major global power with influence in diplomacy and military affairs.

In the early 2000s, the UK supported the United States in the "war on terror." British troops fought in Afghanistan and Iraq. The 2008 global financial crisis greatly affected the UK economy. In 2014, Scotland voted to remain part of the United Kingdom in an independence referendum.
In 2016, 51.9% of voters chose to leave the European Union, a process known as Brexit. The UK officially left the EU in 2020. The COVID-19 pandemic had a big impact on the UK's economy and society in 2020 and 2021. The UK was the first country to use an approved COVID-19 vaccine.
On September 8, 2022, Elizabeth II, the longest-reigning British monarch, passed away at 96. Her eldest son, Charles, became Charles III, the new King.
The UK's Landscape and Weather
Geography and Land Features

The United Kingdom covers about 244,376 square kilometers (94,354 square miles). It includes the island of Great Britain, the northeastern part of Ireland, and many smaller islands. The UK is located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. Its southeast coast is only about 35 kilometers (22 miles) from northern France, separated by the English Channel.
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich in London is the starting point for the Prime Meridian. This is the line of longitude that divides the Earth into eastern and western hemispheres.
Northern Ireland shares a 360-kilometer (224-mile) land border with the Republic of Ireland. The coastline of Great Britain is very long, about 17,820 kilometers (11,073 miles). The UK is connected to mainland Europe by the Channel Tunnel. This tunnel is 50 kilometers (31 miles) long, with 38 kilometers (24 miles) underwater. It is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.
The UK has different types of natural environments, including forests. About 13% of the UK's land area is covered by woodland.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Most of the United Kingdom has a mild climate with cool temperatures and plenty of rain all year. Temperatures usually stay between 0°C (32°F) and 30°C (86°F). Some higher areas in England, Wales, Northern Ireland, and most of Scotland have a colder, wetter climate. The highest mountains in Scotland can even have a tundra climate.
The wind usually comes from the southwest, bringing mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean. The eastern parts of the UK are drier because they are sheltered from these winds. Warm Atlantic currents, influenced by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters, especially in the west. Summers are warmest in southeast England and coolest in the north. Heavy snow can fall in winter and early spring, especially in high areas.
The UK gets about 1339.7 hours of sunshine per year. This is less than 30% of the possible sunshine hours. Since 1996, the UK has been getting more sunshine than its average from 1981 to 2010.
Climate change is having a serious impact on the country. For example, a third of the rise in food prices in 2023 was linked to climate change. The UK is working to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions to "net zero" by 2050.
Topography: Mountains, Rivers, and Lakes
England makes up 53% of the UK's land, covering 130,395 square kilometers (50,346 square miles). Most of England is lowland, but there are hills and mountains in the northwest. Famous lowland areas include Cornwall and the New Forest. Upland areas include the Lake District and the Pennines. Major rivers include the Thames and Severn. England's highest mountain is Scafell Pike, which is 978 meters (3,209 feet) tall.
Scotland makes up 32% of the UK, covering 78,772 square kilometers (30,414 square miles). It has nearly 800 islands, like the Hebrides and Shetland Islands. Scotland is the most mountainous part of the UK. The Scottish Highlands in the north and west have most of Scotland's mountains, including Ben Nevis, the highest point in the British Isles at 1,345 meters (4,413 feet).

Wales makes up less than 9% of the UK, covering 20,779 square kilometers (8,023 square miles). Wales is mostly mountainous, especially in the north. The highest mountains are in Snowdonia, including Snowdon (Yr Wyddfa), which is 1,085 meters (3,560 feet) tall. Wales has over 1,680 miles of coastline. The largest island off Wales is Anglesey.
Northern Ireland is separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea. It has an area of 14,160 square kilometers (5,467 square miles) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh, the largest lake in the British Isles, and the Giant's Causeway, a famous World Heritage Site. The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard, at 852 meters (2,795 feet).
The UK's Economy: How It Works

The UK has a social market economy, which means it balances free markets with social support. It is one of the largest economies in the world. Its money, the pound sterling, is one of the most traded currencies. London is the world's capital for foreign exchange trading.
The HM Treasury and the Chancellor of the Exchequer manage the government's money and economic plans. The Bank of England is the UK's central bank. It prints notes and coins. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland can also print their own notes. In 2022, the UK was the world's fourth-largest exporter. The UK's economy grew by 23% from 2019 to 2024. Inflation in the UK was 2% in May 2024, which is the government's goal.

The service sector makes up about 80% of the UK's economy. This includes things like finance, tourism, and technology. London is one of the world's biggest financial centers. Edinburgh is also an important financial hub.
The UK's technology sector is worth about US$1 trillion. London is known as Europe's technology capital. UK startups raised $6.7 billion in the first half of 2024, making it second globally for funds raised. The UK is home to 64 "unicorns," which are companies worth over $1 billion.
Tourism is very important to the UK's economy. London was Europe's most popular travel spot in 2022. The creative industries, like film and music, also add a lot to the economy. Lloyd's of London is the world's largest insurance market. The UK is also a major retail market in Europe.

The British car industry employs about 800,000 people. It makes £27 billion in exports each year. In 2023, the UK produced over 905,100 passenger cars. Britain is famous for cars like Mini, Jaguar, Rolls-Royce, and Range Rover. The UK is also a major center for making engines and is the world's fourth-largest exporter of engines. The UK's motorsport industry is also very big, with 7 of the 10 Formula One teams based there.
The aerospace industry is one of the largest in the world. It has an annual turnover of about £30 billion. The UK space industry was worth £17.5 billion in 2020/21. The UK Space Agency is investing £1.6 billion in space projects.
Agriculture in the UK is very efficient. It produces about 60% of the country's food needs. About two-thirds of farming is for livestock, and one-third is for crops. The UK also has a fishing industry and many natural resources like coal, oil, and natural gas. The UK has a high HDI ranking, meaning people generally have a good quality of life.
Science and Technology: Innovation in the UK
England and Scotland were key places for the Scientific Revolution starting in the 1600s. The UK led the Industrial Revolution from the 1700s and has continued to produce important scientists and engineers. Famous thinkers include Isaac Newton, who developed laws of motion and gravity. Charles Darwin created the theory of evolution. James Clerk Maxwell developed the theory of electromagnetism. More recently, Stephen Hawking made big advances in cosmology and black holes.
The Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) helps support science and technology in the UK. Universities in the UK do a lot of scientific research. In 2022, the UK's technology sector was worth $1 trillion. Cambridge University is known for producing many successful technology founders.
From 2020 to 2023, the UK was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index. This index looks at things like the political environment, education, and new ideas. In 2022, the UK produced 6.3% of the world's scientific research papers. It also had the third-highest share of scientific citations globally.
Transport: Getting Around the UK
The UK has a large road network. It includes 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads and 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways. The M25 motorway around London is one of the busiest bypasses in the world. In 2022, there were over 40.8 million vehicles in Great Britain.
The UK also has a large railway network of 10,072 miles (16,210 km). The British Rail network was privatized between 1994 and 1997, and passenger numbers quickly increased. Great British Railways is a new state-owned body planned to manage rail transport.
The Eurostar train offers direct service between London and Paris, taking about 2 hours and 16 minutes. It travels through the Channel Tunnel, which is the world's longest undersea tunnel. The Elizabeth line, a new rail link in London, opened in 2022. It was Europe's largest construction project at the time. Another big project is High Speed 2 (HS2), a new high-speed railway connecting London with Birmingham.
In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK. London's red double-decker buses are famous around the world. London's bus network is very large, with over 6,800 services daily.
In 2023, UK airports handled 272.8 million passengers. London Heathrow Airport is the world's second busiest airport by international passenger traffic. It is the main hub for British Airways.
Energy: Powering the Nation
In 2021, the UK was the world's 14th-largest energy consumer and 22nd-largest producer. It is home to major energy companies like BP and Shell.
The UK is a leader in fighting climate change. It has the world's first climate change act. It has also reduced its emissions faster than any major economy since 1990. In 2020, renewable energy sources provided 43% of the UK's electricity. The UK is one of the best places in the world for wind energy. In 2022, wind power generated 26.8% of the UK's electricity. The UK has the largest offshore wind farm in the world, off the coast of Yorkshire.
In 2023, the UK had 9 nuclear reactors that produced about 15% of its electricity. The UK government is investing in new types of nuclear reactors.
In 2021, the UK produced 935,000 barrels of oil per day. However, it has been importing more oil than it produces since 2005. The UK also produces natural gas, but production is declining. In 2020, the UK produced 1.8 million tonnes of coal. There are large coal reserves that could be used in the future.
Water Supply and Sanitation
Almost everyone in the UK has access to clean water and good sanitation. About 96% of homes are connected to the sewer system. In England and Wales, water services are provided by private companies. In Scotland and Northern Ireland, public companies provide these services.
People and Culture in the UK
Demographics: Who Lives in the UK?
In the 2011 census, the UK population was 63,181,775. It is the fourth-largest in Europe and 22nd-largest in the world. From 2014 to 2015, more people moved to the UK than left, which helped the population grow. Between 2001 and 2011, the population grew by about 0.7% each year. The number of people aged 0–14 decreased, while the number of people aged 65 and over increased. In 2018, the average age in the UK was 41.7 years.
| Nation | Land area | Population | Density (/km2) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (km2) | (%) | People | (%) | ||
| England | 130,310 | 54% | 57,106,398 | 84% | 438 |
| Scotland | 77,901 | 32% | 5,447,700 | 8% | 70 |
| Wales | 20,737 | 9% | 3,131,640 | 5% | 151 |
| Northern Ireland | 13,547 | 6% | 1,910,543 | 3% | 141 |
| United Kingdom | 242,495 | 100% | 67,596,281 | 100% | 279 |
England's population in 2011 was 53 million, about 84% of the UK total. It is one of the most densely populated countries, especially in London and the southeast. Scotland's population was 5.3 million, Wales's was 3.06 million, and Northern Ireland's was 1.81 million.
In 2017, the average number of children born per woman in the UK was 1.74. This is below the rate needed to replace the population (2.1). In 2011, 47.3% of births were to unmarried women. In 2015, about 1.7% of adults in the UK identified as gay, lesbian, or bisexual.
| Largest urban areas of the United Kingdom (England and Wales: 2011 census built-up area; Scotland: 2012 estimates urban area; Northern Ireland: 2001 census urban area) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | ||
 Greater London Urban Area |
1 | Greater London Urban Area | 9,787,426 | London | 11 | Bristol Urban Area | 617,280 | Bristol |  West Midlands Urban Area |
| 2 | Greater Manchester Urban Area | 2,553,379 | Manchester | 12 | Leicester Urban Area | 508,916 | Leicester | ||
| 3 | West Midlands Urban Area | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | 13 | Edinburgh Urban Area | 488,610 | Edinburgh | ||
| 4 | West Yorkshire Urban Area | 1,777,934 | Leeds | 14 | Belfast Urban Area | 483,418 | Belfast | ||
| 5 | Greater Glasgow | 1,199,629 | Glasgow | 15 | Brighton/Worthing/Littlehampton | 474,485 | Brighton | ||
| 6 | Liverpool Urban Area | 864,122 | Liverpool | 16 | South East Dorset conurbation | 466,266 | Bournemouth | ||
| 7 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | 17 | Cardiff Urban Area | 390,214 | Cardiff | ||
| 8 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle | 18 | Teesside | 376,633 | Middlesbrough | ||
| 9 | Nottingham Urban Area | 729,977 | Nottingham | 19 | The Potteries Urban Area | 372,775 | Stoke-on-Trent | ||
| 10 | Sheffield Urban Area | 685,368 | Sheffield | 20 | Coventry and Bedworth Urban Area | 359,262 | Coventry | ||
Ethnicity: A Diverse Population
Historically, British people are thought to come from various groups that settled there before the 1100s, including Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse, and Normans. Welsh people might be the oldest ethnic group in the UK. The UK has a long history of non-white immigration. Liverpool had a Black population as early as the 1730s. The UK also has the oldest Chinese community in Europe, dating back to the 1800s. In 2011, 87.2% of the UK population identified as white, while 12.8% identified as part of an ethnic minority group.
| Ethnic group | Population (absolute) | Population (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | ||
| White | 54,153,898 | 55,010,359 | 92.1% | 87.1% | |
| White: Gypsy, Traveller and Irish Traveller | – | 63,193 | – | 0.1% | |
| Asian and Asian British | Indian | 1,053,411 | 1,451,862 | 1.8% | 2.3% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1,174,983 | 1.3% | 1.9% | |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 451,529 | 0.5% | 0.7% | |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 433,150 | 0.4% | 0.7% | |
| Other Asian | 247,664 | 861,815 | 0.4% | 1.4% | |
| Black, African, Caribbean and Black British | 1,148,738 | 1,904,684 | 2.0% | 3.0% | |
| Mixed or multiple ethnic groups | 677,117 | 1,250,229 | 1.2% | 2.0% | |
| Other ethnic groups | 230,615 | 580,374 | 0.4% | 0.9% | |
| Total | 58,789,194 | 63,182,178 | 100.0% | 100.0% | |
Ethnic diversity varies across the UK. In 2005, 30.4% of London's population and 37.4% of Leicester's population were non-white. However, in areas like North East England, Wales, and the South West, less than 5% of the population were from ethnic minorities in 2001. In 2016, about 31.4% of primary school students and 27.9% of secondary school students in England were from ethnic minority groups.
Languages Spoken in the UK
The English language is the official and most spoken language in the UK. About 95% of the UK's population speaks only English. Another 5.5% speak languages brought by recent immigrants. These include South Asian languages like Punjabi, Urdu, and Bengali. According to the 2011 census, Polish is the second-largest language spoken in England, with 546,000 speakers.
Three native Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh, Irish, and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish, which almost died out, is now being revived. In 2021, 17.8% of people aged three or older in Wales spoke Welsh. About 200,000 Welsh speakers also live in England. In Northern Ireland, 12.4% of people had some ability in Irish, and 10.4% in Ulster-Scots. Over 92,000 people in Scotland could speak some Gaelic. The number of children learning Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is growing. Scots is also spoken, especially in Northern Ireland. About 151,000 people in the UK use British Sign Language (BSL).
Religion in the UK
Religion in the United Kingdom (2022 Census) Christianity (46.53%) No religion (37.75%) Islam (5.97%) Hinduism (1.59%) Sikhism (0.79%) Buddhism (0.43%) Judaism (0.41%) Other religion (0.58%) Not stated (5.91%)
Christianity has been the main religion in the UK for over 1,400 years. While many people still identify as Christian, fewer attend church regularly. Immigration and population changes have led to the growth of other faiths, especially Islam. This has led some to describe the UK as a multi-faith or non-religious society.
In the 2001 census, 71.6% of people said they were Christian. The next largest faiths were Islam (2.8%), Hinduism (1.0%), and Sikhism (0.6%). 15% said they had no religion. Between 2001 and 2011, the number of Christians decreased by 12%, while the number of people with no religion doubled. The Muslim population grew from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group.
The Church of England is the official church in England. The British monarch is its head. In Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognized as the national church, but it is not controlled by the state. There is no official church in Northern Ireland or Wales.
Migration: People Moving In and Out
Immigration is helping the UK population grow. From 1991 to 2001, about half of the population increase came from new arrivals and their children born in the UK. In 2014, 27% of births in the UK were to mothers born outside the UK.
In 2013, about 208,000 foreign nationals became British citizens. The most common nationalities for new citizens in 2014 were Indian, Pakistani, and Filipino. In 2022, net migration (people moving in minus people moving out) reached a record high of 764,000. In 2023, net migration was 685,000. More EU nationals left the UK than arrived in 2023.
Many people have also emigrated from Britain throughout history. Between 1815 and 1930, about 11.4 million people left Britain. Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad, mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States, and Canada.
Education: Learning in the UK

Education in the UK is managed separately by each country (England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland). About 38% of the UK population has a university or college degree, which is one of the highest percentages in Europe and the world. The UK is home to many famous universities, including the University of Oxford and University of Cambridge, which are often ranked among the best globally.
University tuition fees vary across the UK. In England and Wales, there is a maximum annual fee for UK citizens, which is paid back once they earn a certain income. Northern Ireland and Scotland have lower or no fees for their own citizens.
In 2022, the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) ranked British 15-year-olds 14th in the world for reading, mathematics, and science. The average British student scored well above the international average.
Healthcare: Looking After People's Health

The modern system of publicly funded healthcare in the UK began with the creation of the National Health Service (NHS) in 1949. The NHS is still the main healthcare provider in the UK and is very popular. Healthcare in the UK is managed separately by each country. Public healthcare is mostly free for all permanent residents and is paid for by taxes. In 2000, the World Health Organization ranked the UK's healthcare system as 15th best in Europe and 18th in the world.
Spending on healthcare has increased a lot since 1979. In 2017, the UK spent about £2,989 per person on healthcare. This is around the average for countries in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Different government bodies manage healthcare in England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. Each has its own policies, which can lead to some differences.
UK Culture: Arts, Food, and Sports
The culture of the United Kingdom is shaped by its island location, its long history, and being a union of four countries. Each country keeps its own traditions and symbols. Because of the British Empire, British influence can be seen in the language, culture, and legal systems of many former colonies, like the United States, Australia, and Canada. The UK's strong cultural influence has led it to be called a "cultural superpower." In 2023, a global survey ranked the UK third in "Most Influential Countries."
Literature: Stories and Poems
British literature includes writing from the UK, the Isle of Man, and the Channel Islands. Most of it is in English. In 2022, 669 million physical books were sold in the UK, a record high. Britain is famous for children's literature, with writers like Daniel Defoe, Rudyard Kipling, Lewis Carroll, Beatrix Potter, J.R.R. Tolkien, Roald Dahl, and J.K. Rowling (who wrote the best-selling Harry Potter series).
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is considered one of the greatest writers of all time. Other important English writers include Geoffrey Chaucer, William Wordsworth, Charles Dickens, H. G. Wells, George Orwell, and Ian Fleming. Agatha Christie is the best-selling novelist of all time. Many famous British novels were written by women, including works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, the Brontë sisters, and Jane Austen.
Scotland's writers include Arthur Conan Doyle (who created Sherlock Holmes), Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, and Robert Louis Stevenson. Edinburgh, Scotland's capital, was UNESCO's first City of Literature.
Welsh literature includes Britain's oldest known poem, Y Gododdin, from the 500s. It contains the earliest known mention of King Arthur. Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas are well-known Welsh poets.
Northern Ireland's most popular writer is C.S. Lewis, who wrote The Chronicles of Narnia. Many famous Irish writers, like Oscar Wilde and George Bernard Shaw, lived when all of Ireland was part of the UK. Many authors from other countries have also moved to the UK, such as Joseph Conrad and Salman Rushdie.
Philosophy: Thinking Deeply
The UK is known for "British Empiricism," a way of thinking that says knowledge comes from experience. Famous philosophers of this idea include John Locke and David Hume. "Scottish Philosophy" focuses on "common sense." Two Britons, Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill, are known for the idea of utilitarianism, which is about doing what brings the greatest good to the greatest number of people.
Music: Sounds of the UK
Many music styles are popular in the UK, including the traditional folk music of England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. Historically, there was great Renaissance music from the Tudor period. Later, composers like Henry Purcell and George Frideric Handel created important works. Handel's "Messiah" is famous worldwide. In the 1800s, Edward Elgar wrote music that rivaled European composers. Later, composers like Gustav Holst and Ralph Vaughan Williams were inspired by English folk music.
The term "pop music" started in Britain in the mid-1950s. Bands like the Beatles and the Rolling Stones made pop music very popular in the 1960s. Birmingham is known as the birthplace of heavy metal with the band Black Sabbath. British bands also helped create hard rock, glam rock, punk rock, and more. Modern UK is known for rappers like Stormzy and Little Simz.

The Beatles have sold over 1 billion records and are the most influential band in popular music history. Other famous British artists who have influenced music include the Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen, Led Zeppelin, and Elton John. Recent successful UK music acts include Adele, Ed Sheeran, Harry Styles, and Dua Lipa.
Many UK cities are known for their music. Liverpool has had more number-one hit singles per person than any other city. Glasgow is a UNESCO City of Music. Manchester helped spread dance music like acid house. London and Bristol are linked to electronic music styles like drum and bass and trip hop.
UK dance music has roots in Black British Sound System Culture and the New Age Traveller movement. It also took ideas from New Wave and Synth-pop. In the late 1980s, dance music became huge with Rave culture and Acid House. This led to genres like UK Garage, Drum and bass, and Dubstep. Famous UK dance acts include Orbital, the Prodigy, and Massive Attack.
Visual Art: Paintings and Sculptures

Major British artists include the Romantics William Blake and J. M. W. Turner. Famous portrait painters are Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud. Landscape artists include Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry. William Morris was a pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement. Other important artists are Francis Bacon, David Hockney, and sculptors like Antony Gormley and Henry Moore. In the late 1980s and 1990s, a group called the "Young British Artists" became famous, including Damien Hirst and Tracey Emin.
The Royal Academy in London promotes visual arts. Important art schools include the University of the Arts London and the Glasgow School of Art. Major art galleries in the UK include the National Gallery and Tate Modern, which is one of the most visited modern art galleries in the world.
Cinema: Films from the UK
The UK has greatly influenced the history of cinema. British directors like Alfred Hitchcock (who directed Vertigo) and David Lean (who directed Lawrence of Arabia) are highly praised. Recent popular directors include Christopher Nolan and Danny Boyle.
Many British actors have become internationally famous. Some of the most successful film series ever, like Harry Potter and James Bond, were produced in the UK.
In 2019, British films earned about £10.3 billion globally. The annual BAFTA Film Awards celebrate achievements in film. The UK's film and television studio space is growing, with more than 1 million square feet added in the past year.
Cuisine: British Food and Flavors

British food has developed from many influences, including its history, new settlers, and trade. Traditional English food is known for being simple and using high-quality natural ingredients. The traditional Sunday roast is a good example. It usually features roasted meat, like beef or chicken, served with vegetables, Yorkshire pudding, and gravy. Other traditional meals include meat pies and stews. A 2019 poll found that over 80% of people liked classic British foods like Sunday roast, Yorkshire pudding, Fish and chips, and a Full English breakfast.
The UK has many fine-dining restaurants, with 187 holding a Michelin Star in 2024. Sweet foods are common in British cuisine, and there are many British desserts. Afternoon tea is a light meal with tea, served in tea rooms and hotels. It dates back to the 1840s. More people in Britain are choosing vegan and vegetarian diets.
The British Empire helped introduce Indian cuisine to Britain. British food has taken in influences from immigrants, creating new dishes like chicken tikka masala. British people enjoy food from all over the world, including Europe, the Caribbean, and Asia.
Media: News, TV, and Games
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK's publicly funded radio, television, and internet broadcaster. It is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world. It runs many TV and radio stations in the UK and globally. The BBC World Service broadcasts news and discussions in over 40 languages.
Other major media companies in the UK include ITV and Sky. National newspapers include the Daily Mail, The Guardian, and The Times. Popular magazines include The Economist and Radio Times.
London is the main center for media in the UK, with most national newspapers and TV/radio stations based there. However, MediaCityUK in Manchester is also a big media hub. Edinburgh, Glasgow, and Cardiff are important for newspapers and broadcasting in Scotland and Wales. The UK publishing sector is large, with a turnover of about £20 billion. In 2015, the UK published more book titles per person than any other country.
In 2010, 82.5% of the UK population used the internet. The British video game industry is the largest in Europe by sales since 2022. It is also the world's third-largest producer of video games.
Sport: Games and Competitions
Many popular sports started or were greatly developed in the UK. These include football, tennis, rugby union, golf, boxing, and cricket. The rules for many modern sports were created in the UK in the late 1800s.
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the UK. England is recognized as the birthplace of club football. The Football Association is the oldest of its kind. Each of the four UK countries (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) has its own football association and national team. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world. The first international football match was played between England and Scotland in 1872.

In 2003, rugby union was the second most popular sport. It was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire. The first international rugby match was between England and Scotland in 1871. England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France, and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship. Every four years, the UK countries combine to form the British and Irish Lions team, which tours Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa.
London has hosted the Summer Olympic Games three times: in 1908, 1948, and 2012. Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games. This was the seventh time a UK country hosted the Commonwealth Games.
Symbols: What Represents the UK?

The flag of the United Kingdom is called the Union Flag (or Union Jack). It was created in 1606 by combining the flag of England (Saint George's cross) and the flag of Scotland (Saint Andrew's cross). In 1801, Saint Patrick's Flag was added. Wales is not shown on the Union Flag because it was part of England before the UK was formed. The national anthem of the UK is "God Save the King" (or "God Save the Queen" when the monarch is a woman).
Britannia is a symbol of the United Kingdom, coming from Roman times. Along with the The Lion and the Unicorn and the dragon, the bulldog is an iconic animal often seen with the Union Flag.
England, Wales, and Scotland each have their own national symbols and flags. Northern Ireland also has symbols, many of which are shared with the Republic of Ireland.
Images for kids
-
Stonehenge in Wiltshire is a ring of huge stones, each weighing about 25 tons. It was built between 2400 and 2200 BC.
-
The Roman Baths in Bath, Somerset, are very well preserved from the time of Roman Britain.
-
The Bayeux Tapestry shows the Battle of Hastings in 1066.
-
The start of the Battle of Trafalgar, painted by J.W. Carmichael.
-
Queen Victoria was the Queen of the United Kingdom and Empress of India during the 1800s.
-
Wreaths being placed at the Cenotaph in London during the Remembrance Sunday service.
-
Spitfire and Hurricane planes, like those used in the Battle of Britain during the Second World War.
-
The British Empire at its largest in 1921.
-
Concorde was a supersonic airliner that cut transatlantic flight time from 8 hours to 3.5 hours.
-
Canary Wharf in London, a symbol of the financial changes in the 1980s.
-
People campaigning for Brexit outside Parliament in London in November 2016.
-
A Satellite image of the United Kingdom (without Shetland).
-
The Pennine Way in the Yorkshire Dales in England.
-
Loch Leven, a freshwater lake in Scotland.
-
London is a huge financial center and one of the world's most connected cities in the global economy.
-
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom. Many modern central banks are based on its model.
-
Aston Martin cars are made in Gaydon, England.
-
A high-speed train on the East Coast Main Line in Northumberland.
-
Wind turbines near Ardrossan in Scotland. The UK is a great place for wind energy.
-
University of Oxford is known as one of the world's leading universities.
-
NHS Scotland's Queen Elizabeth University Hospital in Glasgow, the largest hospital campus in Europe.
-
William Shakespeare's First Folio from 1623.
-
The Proms is a classical music festival held at the Royal Albert Hall.
-
Glastonbury Festival is a five-day festival of performing arts in Somerset, England. It is the largest greenfield music festival in the world.
-
William Morris textile design from 1883.
-
The Angel of the North sculpture by Antony Gormley is a symbol of northern England.
-
The 2023 FA Cup final at Wembley Stadium between Manchester City and Manchester United.
-
Golf started at the Old Course at St Andrews in Scotland.
-
Union Jack flags on The Mall, London.
See also
 In Spanish: Reino Unido para niños
In Spanish: Reino Unido para niños