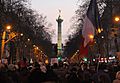France facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
French Republic
République française
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "La Marseillaise"
|
|
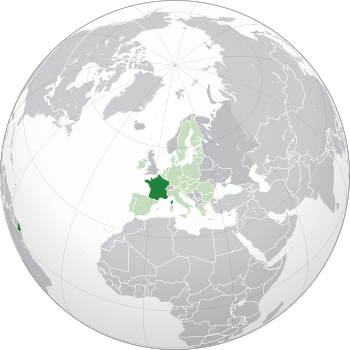
 Metropolitan France (European part of France) in Europe Metropolitan France (European part of France) in Europe Show France, its overseas territories and its exclusive economic zones Show France, its overseas territories and its exclusive economic zones |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Paris 48°51′N 2°21′E / 48.850°N 2.350°E |
| Official language and national language |
French |
| Nationality (2021) | |
| Religion
(2021)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | French |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Emmanuel Macron | |
| Sébastien Lecornu | |
| Gérard Larcher | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Establishment | |
| 10 August 843 | |
|
• French Republic — French First Republic
|
22 September 1792 |
|
• Current constitution — French Fifth Republic
|
4 October 1958 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
632,702.3 km2 (244,287.7 sq mi) (including metropolitan France and overseas France and excluding Terre Adelie) (42nd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.86 |
|
• Metropolitan France (DGCL)
|
543,941 km2 (210,017 sq mi) (50th) |
|
• Metropolitan France (INSEE)
|
543,908.3 km2 (210,004.2 sq mi) (50th) |
| Population | |
|
• January 2025 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
108/km2 (281/sq mi) (106th) |
|
• Metropolitan France, estimate as of January 2025[update]
|
|
|
• Density
|
122/km2 (316.0/sq mi) (97th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | ▲ 29.8 low |
| HDI (2023) | very high · 26th |
| Currency | |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +33 |
| ISO 3166 code | FR |
| Internet TLD | .fr |
|
Source gives area of metropolitan France as 551,500 km2 (212,900 sq mi) and lists overseas regions separately, whose areas sum to 89,179 km2 (34,432 sq mi). Adding these give the total shown here for the entire French Republic. The World Factbook reports the total as 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi).
|
|
France (French: France), officially known as the French Republic (French: République française), is a country in Western Europe. Its capital city is Paris. France is a founding member of the European Union and the United Nations. It is also part of the G8 and NATO.
France is famous for its rich culture, amazing buildings, and places like the Louvre Museum, the Eiffel Tower, and Mont Saint-Michel. The country is divided into 13 regions, which are then split into smaller departments.
France has been a major world power since the late 1600s. In the 18th and 19th centuries, it had a large colonial empire in West Africa and Southeast Asia. Today, France is the most visited country in the world, with about 82 million foreign tourists each year. It also has nuclear weapons and nuclear power plants.
Some well-known cities in France include Paris, Lyon, Marseille, Bordeaux, Lille, Toulouse, Nice, Strasbourg, Rennes and Nantes.
Contents
History of France
The name "France" comes from the Latin word Francia. This means "land of the Franks". The borders of modern France are similar to ancient Gaul. Celtic Gauls lived in Ancient Gaul.
Julius Caesar conquered Gaul for Rome in the 1st century BC. The Gauls then started speaking Latin, which later became the French language. Christianity became popular in France by the 4th and 5th centuries.
In the 4th century AD, Germanic tribes, especially the Franks, invaded Gaul. This is when the name Francie appeared. The Franks were the first European tribe after the Roman Empire fell to become Christian.
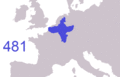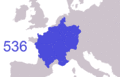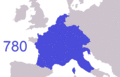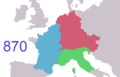
The Treaty of Verdun in 843 split Charlemagne's large empire into three parts. Western Francia was the biggest part, and it is similar to modern France.
The Carolingian dynasty ruled France until 987. Then, Hugh Capet became King. His family, including the Capetians, the House of Valois, and the House of Bourbon, united the country. They did this through many wars and family inheritances.
The monarchy was strongest in the 17th century under King Louis XIV. At that time, France had the largest population in Europe. It had a big impact on European politics, economy, and culture. French became the language used for diplomacy between countries. Many new ideas from the Enlightenment came from France. French scientists also made important discoveries in the 1700s. France also gained many lands overseas in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.

France was a monarchy until the French Revolution in 1789. King Louis XVI and his wife, Marie Antoinette, were executed in 1793. Many other French citizens were also killed. Napoleon Bonaparte took control in 1799. He later made himself Emperor of the First Empire (1804–1814). His armies conquered most of Europe. The metric system was created by French scientists during the French Revolution.
After Napoleon's defeat in 1815 at the Battle of Waterloo, another monarchy started. Later, Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte created the Second Empire in 1852. He was removed after France lost the Franco-Prussian War in 1870. The Third Republic then took over.
In the 19th century, the large French colonial empire included parts of West Africa and Southeast Asia. France influenced the culture and politics of these areas. Many former colonies still speak French today.
France was a major battleground in both the First and Second World Wars. During the First World War, millions died in the trenches. Over a million died in the Battle of the Somme alone. Conditions were very bad.
During the Second World War, Nazi forces took over France. The Allies landed in Normandy on June 6, 1944. This started the Battle of Normandy. German forces lost control of France in just a few months.
Geography of France
Location and Borders
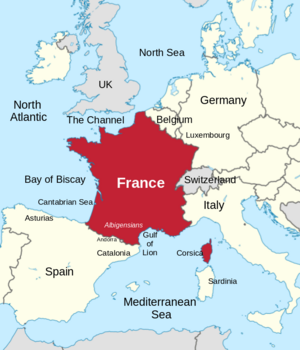
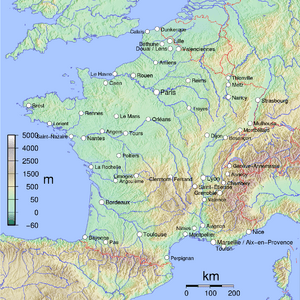
Most of France is in Western Europe. This part is called Metropolitan France. It is bordered by the North Sea to the north, the English Channel to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The Mediterranean Sea is to the southeast.
France shares land borders with Belgium and Luxembourg in the northeast. It borders Germany and Switzerland in the east. Italy and Monaco are to the southeast. Andorra and Spain are to the south and southwest. Most of France's land borders follow natural features like mountains and rivers. Because of its shape, France is often called l'Hexagone ("The Hexagon").
France also has several overseas regions around the world:
- In South America: French Guiana.
- In the Atlantic Ocean: Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy.
- In the Pacific Ocean: French Polynesia, New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna, and Clipperton Island.
- In the Indian Ocean: Réunion island, Mayotte, Kerguelen Islands, Crozet Islands, St. Paul and Amsterdam islands, and the Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean.
- In the Antarctic: Adélie Land.
France has land borders with Brazil and Suriname through French Guiana. It also borders the Kingdom of the Netherlands on Saint Martin.
Climate Zones
Most of Metropolitan France has an oceanic climate. This means it has mild temperatures and rainfall throughout the year. A small part near the Mediterranean Sea has a Mediterranean climate. This climate has hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
Because France is a large country, its climate changes in different areas:
- Western France has a true oceanic climate.
- Away from the coast, the climate is still oceanic but with more temperature changes.
- The Mediterranean and lower Rhône valley have a Mediterranean climate.
- The mountain climate is found in the Alps, Pyrenees, and other mountain ranges.
The overseas regions have different climates:
- Most have a tropical climate with high temperatures and wet and dry seasons.
- French Guiana has an equatorial climate with constant high temperatures and rain all year.
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the French Southern and Antarctic Lands have a subpolar climate. This means short, mild summers and long, very cold winters.
-
Vineyards in Côte de Nuits, Burgundy
-
Mediterranean vegetation (lavender) in Provence
-
Alpine climate (winter) in the French Alps
-
Mediterranean climate in Corsica
Environment and Nature

France was one of the first countries to create an environment ministry in 1971. Even though it is an industrial country, France has low carbon dioxide emissions. This is because France uses a lot of nuclear power for electricity. Nuclear power creates less pollution.
France has nine national parks and 46 natural parks. Forests cover 28% of France's land. These forests are very diverse, with over 140 types of trees. The government plans to protect 20% of its marine areas by 2020.
A regional nature park (parc naturel régional) protects beautiful rural areas. It helps keep the scenery and heritage safe. It also supports sustainable economic growth. These parks encourage research and education about nature. As of 2014, there are 49 such parks in France.
Divisions of France
France is divided into 13 main administrative regions. Twelve of these are in Metropolitan France, which is the part of the country in Europe.
These regions are:
- Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
- Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
- Brittany
- Centre-Val de Loire
- Corsica
- Grand Est
- Hauts-de-France
- Île-de-France
- Normandy
- Nouvelle-Aquitaine
- Occitanie
- Pays de la Loire
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
Corsica has a special status compared to the other regions.
France also has five overseas regions:
- Guadeloupe (in the Caribbean)
- French Guiana (in South America)
- Martinique (in the Caribbean)
- Réunion (in the Indian Ocean)
- Mayotte (in the Indian Ocean)
These overseas regions have the same status as the regions in mainland France.
Below the regions, France is divided into 101 departments. These departments are further split into 342 arrondissements. The smallest local division is the commune. In 2008, there were 36,781 communes in France.
Government and Politics
The government of France is a semi-presidential system. This means it has both a president and a prime minister. The rules for the government are set out in the French Constitution of the French Fifth Republic. The constitution says France is an "indivisible, secular, democratic, and social Republic". It also makes sure that the government's powers are separated.
Military of France

The French armed forces have four main parts:
- The Armée de Terre (Army)
- The Marine Nationale (Navy)
- The Armée de l'Air (Air Force)
- The Gendarmerie Nationale (a military police force for rural areas)
France has about 359,000 military members. It spends 2.6% of its total economic output (GDP) on defense. This is the highest percentage in the European Union. France and the UK together spend 40% of the EU's defense money. About 10% of France's defense budget goes to its nuclear weapons.
Foreign Relations
France is a member of the United Nations. It is one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council. This means it has veto rights on important decisions. France is also a member of the World Trade Organisation (WTO). Many international organizations have their headquarters in France, like the OECD, UNESCO, and Interpol.
France was a founding member of the European Union. After World War II, France and Germany became close allies. This helped them become influential countries in the EU. France is also a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Economy of France

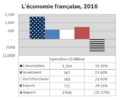
France's economy has almost 2.9 million registered companies. The government has a lot of influence over important industries. These include railways, electricity, aircraft, and telecommunications. For example, the government owns big companies like SNCF (trains) and EDF (electricity). France also has a big aerospace industry, led by Airbus. It can even launch rockets from French Guiana.
France has invested a lot in nuclear power. This makes France one of the countries with the lowest carbon dioxide emissions among the world's most industrial nations. In 2006, 78% of France's electricity came from its 59 nuclear power plants. This was a big increase from only 8% in 1973.
Agriculture and Food Production

France has always been a major producer of farm products. It has lots of fertile land and uses modern farming methods. Support from the EU also helps. This makes France the top agricultural producer and exporter in Europe. It is the world's third-biggest exporter of farm products.
France mainly exports wheat, poultry, dairy, beef, and pork. It also exports famous processed foods. While Rosé wines are mostly drunk in France, Champagne and Bordeaux wines are big exports. They are known all over the world.
France also makes rum from sugar cane. Most of these distilleries are in overseas territories like Martinique, Guadeloupe, and La Réunion.
Demographics and People
As of January 1, 2008, about 63.8 million people lived in France. This includes people in the Overseas Regions. About 61.8 million of these people live in mainland France.
Religion in France
| France religiosity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| religion | percent | |||
| Christianity | 54% | |||
| Not religious | 31% | |||
| Islam | 4% | |||
| Judaism | 1% | |||
| Other religions or no opinion |
10% | |||
France is a secular country. This means the government does not favor any religion. The constitution protects freedom of religion. About 51% of people in France are Roman Catholic. About 31% say they are agnostics or atheists. 4% are Muslim, 3% are Protestant, and 1% are Jewish. Another 10% belong to other religions or have no opinion.
A 2005 poll showed:
- 34% of French citizens believe in God.
- 27% believe in some kind of spirit or life force.
- 33% do not believe in any spirit, God, or life force.
Major Ethnic Groups
Most people in France today are descended from Celtic and Roman people. There are also significant minority groups, including:
- Germanic peoples
- Slavic people
- People from North Africa
- People from Sub-Saharan Africa (south of the Sahara desert)
- People from Indochina
- People from the Basque Country
Culture of France
Language in France
French is the official language of France. It is a Romance language, like Italian and Spanish. Many regional dialects are also spoken in France. For example, Alsatian, a German dialect, is spoken in Alsace.
French was a very important language for diplomacy and culture in Europe from the 17th to 19th centuries. It is still widely used today. Some people in France also speak Basque, Breton, Catalan, Corsican, German, Flemish, and Occitan.
French Literature

French literature began in the Middle Ages. Back then, French had many different dialects. Writers sometimes spelled words differently.
In the 17th century, important authors included Pierre Corneille, Jean Racine, Molière, Blaise Pascal, and René Descartes.
French literature and poetry became even better in the 18th and 19th centuries. The 18th century had writers like Voltaire and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. For children's literature, Charles Perrault wrote famous stories. These include "Little Red Riding Hood", "Beauty and the Beast", and "Sleeping Beauty".
Many famous French novels were written in the 19th century. Authors like Victor Hugo, Alexandre Dumas, and Jules Verne wrote popular books. These include The Three Musketeers, The Count of Monte-Cristo, Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea, and Les Misérables.
Famous novels in the 20th century were written by Marcel Proust, Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, Albert Camus, and Jean-Paul Sartre.
Popular Sports

The Tour de France cycling race in July is one of the most famous sporting events. It lasts three weeks and covers about 3,500 km across France. It ends in Paris on the Avenue des Champs-Elysées.
Football (soccer) is another very popular sport in France. The French team won the FIFA World Cup in 1998. They also won the UEFA European Football Championship in 1984 and 2000. France also hosts the 24 Hours of Le Mans car race.
France is closely linked to the Modern Olympic Games. At the end of the 19th century, Pierre de Coubertin suggested bringing the Olympic Games back. France hosted the Summer Olympics twice in Paris (1900 and 1924). France also hosted the Winter Games three times: in Chamonix (1924), Grenoble (1968), and Albertville (1992).
French Cuisine
French cooking has influenced food styles across Europe. French chefs work in restaurants all over the world. Modern haute cuisine (fine dining) started with chefs like La Varenne (1615–1678) and Marie-Antoine Carême (1784–1833). They created lighter foods with more herbs and creamy ingredients.
Many cooking techniques and dishes were invented in France. These include roux (a thickener) and ragout (a stew). Carême was a master pastry-maker. He also developed basic sauces, called 'mother sauces'.
Georges Auguste Escoffier (1846–1935) helped make French cuisine popular in the 20th century. He organized how large restaurants should work. He wrote Le Guide Culinaire in 1903, which set the rules for French cooking.
Cheese and wine are very important in French cuisine. In northern France, people often use butter for cooking. In the south, they prefer olive oil and garlic. Each region in France has its own special dish. For example, choucroute is from Alsace, and quiche is from Lorraine.
In November 2010, UNESCO added French gastronomy (the art of French cooking) to its list of the world's 'intangible cultural heritage'.
Tourism in France


France is the most visited country in the world. In 2012, 83 million foreign tourists visited. This number does not include people who just pass through France for less than 24 hours. France has 37 sites on UNESCO's World Heritage List. It has cities with great culture, beaches, ski resorts, and beautiful countryside. Small French villages are promoted by the group Les Plus Beaux Villages de France ("The Most Beautiful Villages of France").

France, especially Paris, has some of the world's largest and most famous museums. These include the Louvre Museum, the Musée d'Orsay (for impressionism), and Beaubourg (for Contemporary art). Disneyland Paris is Europe's most popular theme park.
The French Riviera (or Côte d'Azur) in southeast France is another major tourist spot. It gets 300 days of sunshine each year. It has 115 km of coastline and beaches, golf courses, and ski resorts.
Other popular tourist sites include:
- Eiffel Tower (6.2 million visitors)
- Palace of Versailles (2.8 million visitors)
- Arc de Triomphe (1.2 million visitors)
- Mont Saint-Michel (1 million visitors)
- The Châteaux (castles) of the Loire Valley, like Chenonceau.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
One of the Lascaux paintings: a horse – from about 17,000 BC. Lascaux is known for its detailed pictures of humans and animals.
-
Vercingetorix surrenders to Caesar during the Battle of Alesia. This Gallic defeat led to the Roman conquest of the country.
-
The Maison Carrée was a temple in the Gallo-Roman city of Nemausus (now Nîmes). It is one of the best-preserved Roman buildings.
-
When Clovis became Catholic in 498, the Frankish monarchy became hereditary.
-
Joan of Arc led the French army to important wins during the Hundred Years' War. This helped France win the war.
-
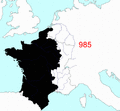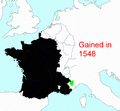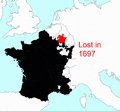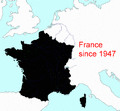
How the borders of Metropolitan France changed from 985 to 1947.
-
The Château de Chenonceau, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was built in the early 16th century.
-
Louis XIV, the "Sun King", was the absolute ruler of France. He made France the leading European power.
-
Opening of the Estates General at Versailles, May 5, 1789 by Auguste Couder.
-
The Storming of the Bastille on July 14, 1789, was a key event of the French Revolution.
-
Le Serment du Jeu de paume by Jacques-Louis David, 1791.
-
Napoleon, Emperor of the French, built a huge empire across Europe. His conquests spread the ideas of the French Revolution.
-
Animated map showing the growth and decline of the French colonial empire.
-
Charles de Gaulle was a hero in World War I and a leader in World War II. He later became President.
-
Republican marches were held across France after the January 2015 attacks. They were the largest public gatherings in French history.
-
Mont Blanc, the highest mountain in Western Europe, is on the border with Italy.
-
Rock formations near Roussillon, Vaucluse.
-
La Défense (seen from the Eiffel Tower) was ranked as the top business district in mainland Europe in 2017.
-
The Eiffel Tower is the world's most-visited paid monument. It is a symbol of both Paris and France.
-
Air France is one of the largest airlines in the world.
-
France is the biggest financial supporter of the European Space Agency. The Ariane rocket family is launched from French Guiana.
-
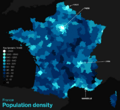
Population density in France by arrondissement. You can see the main city areas like Paris and Lyon.
-
Notre-Dame de Reims is where the Kings of France were crowned until 1825.
-
The École normale supérieure (ENS) in Paris. It has produced many Nobel Prize winners.
-
The Louvre Museum is one of the finest and most visited art museums in the world.
-
Claude Monet, who started the Impressionist art movement.
-
Le Penseur by Auguste Rodin (1902), at the Musée Rodin, Paris.
-
Saint Louis's Sainte-Chapelle shows the French influence on religious buildings.
-
Place de la Bourse in Bordeaux, an example of French baroque architecture.
-
Famous French writers. From top left: Molière, Victor Hugo, Charles Baudelaire, and Jean-Paul Sartre.
-
René Descartes, who founded modern Western philosophy.
-
Daft Punk, who helped create the French house music style.
-
A Palme d'Or from the Cannes Film Festival, one of the world's top film festivals.
-
Louis de Funès, a very popular French actor, played over 130 film roles.
-
Chanel's headquarters on Place Vendôme, Paris.
-
The Paris headquarters of Agence France-Presse, one of the world's oldest news agencies.
-
Germaine Tillion, Geneviève de Gaulle-Anthonioz, Pierre Brossolette, and Jean Zay entering the Pantheon in 2015. The Pantheon is a special place for famous French people.
-
A sculpture of Marianne, a symbol of the French Republic.
-
Some French cheeses with fruits.
-
The Tour de France started in 1903. It is the oldest and most famous cycling race in the world.
-
Pierre de Coubertin, who helped bring back the modern Olympic Games.
-
Zidane was named the best European footballer of the past 50 years in 2004.
See also
 In Spanish: Francia para niños
In Spanish: Francia para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |