United States facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
United States of America
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: "In God We Trust"
Other traditional mottos:
"E pluribus unum" (Latin)
"Out of many, one" "Annuit cœptis" (Latin) "Providence favors our undertakings" "Novus ordo seclorum" (Latin) "New order of the ages" |
|
|
Anthem: "The Star-Spangled Banner
|
|
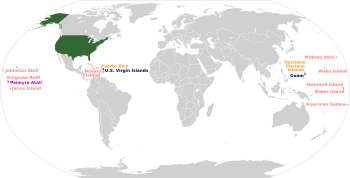 Show the U.S. and its territories Show the U.S. and its territories |
|
| Capital | Washington, D.C. 38°53′N 77°1′W / 38.883°N 77.017°W |
| Largest city | New York City 40°43′N 74°0′W / 40.717°N 74.000°W |
| Official languages | None at the federal level |
| National language | English |
| Ethnic groups
(2020)
|
By race:
By origin:
|
| Religion
(2023)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | American |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Donald Trump | |
| JD Vance | |
| Mike Johnson | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence
from Great Britain
|
|
| July 4, 1776 | |
| March 1, 1781 | |
| September 3, 1783 | |
| June 21, 1788 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total area
|
3,796,742 sq mi (9,833,520 km2) (3rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
7.0 (2010) |
|
• Land area
|
3,531,905 sq mi (9,147,590 km2) (3rd) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
|
|
• 2020 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
87/sq mi (33.6/km2) (185th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2023) | ▼ 41.6 medium |
| HDI (2022) | very high · 20th |
| Currency | U.S. dollar ($) (USD) |
| Time zone | UTC−4 to −12, +10, +11 |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−4 to −10 |
| Date format | mm/dd/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | US |
| Internet TLD | .us |
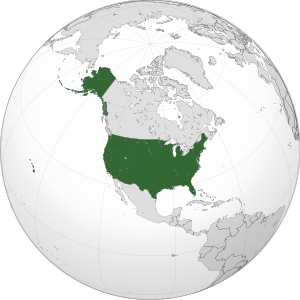
The United States of America (USA) is a large country in North America. It is often called the United States (U.S.) or America. It has forty-eight states that are connected, plus Washington, D.C., the capital city. These states are located between the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Canada borders the U.S. to the north, and Mexico to the south.
The state of Alaska is in the northwest part of North America. It borders Canada to the east and Russia across the Bering Strait to the west. The state of Hawaii is a group of islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. The U.S. also owns territories in the Caribbean and Pacific. New York City is the largest city by population. The United States is the third or fourth-largest country by total area and the third-largest by land area. It is also the third-largest country by population, with about 331 million people.
The United States is known for being very diverse, with people from many different backgrounds. This is because many people have moved there from all over the world. The U.S. economy is the largest in the world. In 2016, its total economic output was about US$20.4 trillion.
The country began with thirteen colonies of Great Britain along the Atlantic coast. On July 4, 1776, these colonies declared their independence from Great Britain. This led to the American Revolutionary War. The colonies won this war, becoming the first successful colonial war of independence. The U.S. Constitution was adopted on September 17, 1787. It created a strong central government. The Bill of Rights, which protects many basic rights, was added in 1791.
In the 1800s, the U.S. gained land from France, Spain, the United Kingdom, Mexico, and Russia. It also took over the Republic of Texas and the Republic of Hawaii. A major conflict happened in the 1860s: the American Civil War. This war was fought between the farming South and the industrial North over slavery and states' rights. The North won, which prevented the country from splitting and ended legal slavery. By the 1870s, the U.S. had the largest economy in the world. After the Spanish–American War and World War I, the U.S. became a strong military power. In 1945, after World War II, the U.S. was the first country with nuclear weapons. It also became a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and a founding member of NATO. After the Cold War ended, the U.S. became the world's only superpower. It spends about half of all money on military globally and is a major force in the world's economy, politics, and culture.
Contents
Geography and Environment
The United States is a federal republic made of fifty states, a federal district, and several territories.
The connected part of the United States (the lower 48 states) covers about 2,959,064 square miles (7,663,941 km2). Alaska is the largest state, covering about 663,268 square miles (1,717,856 km2). Hawaii is a group of islands in the central Pacific, covering 10,931 square miles (28,311 km2).
The U.S. is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area (land and water). It is behind Russia and Canada, and similar in size to China. When only land area is counted, the U.S. is the third largest, after Russia and China.

Along the Atlantic coast, there is a flat plain. Further inland, you find deciduous forests and rolling hills. The Appalachian Mountains separate the eastern coast from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwest. The Mississippi River and Missouri River form the world's fourth-longest river system. They flow mostly north to south through the center of the country. To the west, the flat, rich prairie of the Great Plains stretches out.
The Rocky Mountains are on the western edge of the Great Plains. They run north to south across the country, with some peaks over 14,000 feet (4,300 m) high in Colorado. Further west are the rocky Great Basin and deserts like the Chihuahua and Mojave. The Sierra Nevada and Cascade Range mountains are near the Pacific coast. Both ranges also have peaks over 14,000 feet.
Because of its large size and varied land, the United States has many different climate types. East of the 100th meridian, the climate is humid continental in the north and humid subtropical in the south. Southern Florida and Hawaii have a tropical climate. The Great Plains are semi-dry. Western mountains have an alpine climate. The climate is dry in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington. Most of Alaska is subarctic or polar. Extreme weather is common. States near the Gulf of Mexico often get hurricanes. Most of the world's tornadoes happen in the U.S., mainly in the Midwest's Tornado Alley.
The U.S. has a huge variety of plants and animals. About 17,000 types of vascular plants grow in the connected U.S. and Alaska. Hawaii has over 1,800 types of flowering plants, many of which are unique to the islands. The U.S. is home to more than 400 kinds of mammals, 750 kinds of birds, and 500 kinds of reptiles and amphibians. About 91,000 insect species have been found.
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 helps protect animals and plants that are in danger. The government owns 28.8% of the country's land. Much of this is protected, like the fifty-eight national parks and hundreds of other parks and forests.
History of the United States
Early Peoples and European Arrivals

It is believed that the first people in the U.S. came from Asia. They arrived between 12,000 and 40,000 years ago, or even earlier. Some groups, like the Mississippian culture in the southeast, developed advanced farming and built large communities. The number of native people in America went down after Europeans arrived. This was mainly due to diseases like smallpox and measles.
In 1492, Christopher Columbus reached some Caribbean islands. This was the first contact with native people by Europeans. On April 2, 1513, Juan Ponce de León landed in what he called "La Florida". This was the first recorded European arrival on the U.S. mainland. Spanish settlements followed in the present-day southwestern United States. French traders set up outposts around the Great Lakes. France eventually claimed much of North America.
The first successful English settlements were Jamestown in 1607 and the Plymouth Colony in 1620. By 1634, about 10,000 Puritans had settled in New England. Between the 1610s and the American Revolution, many convicts were also sent to the colonies. Starting in 1614, the Dutch settled along the lower Hudson River, including New Amsterdam on Manhattan Island.
Independence and Growth
Tensions between the American colonies and the British grew in the 1760s and 1770s. This led to the American Revolutionary War, from 1775 to 1781. On June 14, 1775, the Second Continental Congress created the Continental Army led by George Washington. On July 4, 1776, the Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. This document, mostly written by Thomas Jefferson, stated that "all men are created equal" and have "certain natural rights." This day is now celebrated as Independence Day.
After the British were defeated by American and French forces, Great Britain recognized the independence of the United States. A convention in 1787 created a stronger national government. The U.S. Constitution was approved in 1788. The first President, George Washington, took office in 1789. The Bill of Rights, which protects personal freedoms, was added in 1791.
Attitudes towards slavery began to change. Northern states ended slavery between 1780 and 1804. The Second Great Awakening, starting around 1800, led to movements against slavery.
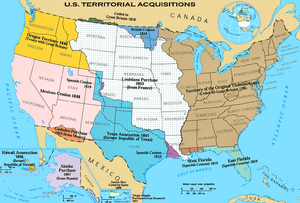
Americans wanted to expand westward. This caused many wars and policies that took land from native peoples. The Louisiana Purchase in 1803 almost doubled the country's size. The War of 1812 strengthened U.S. nationalism. Spain gave up Florida and other land in 1819. The U.S. took over the Republic of Texas in 1845. The idea of Manifest Destiny became popular. The 1846 Oregon Treaty gave the U.S. control of the American Northwest. The U.S. victory in the Mexican–American War in 1848 led to gaining California and much of the American Southwest. The California Gold Rush of 1848–49 brought more people west. New railways made it easier for settlers but increased conflicts with Native Americans. Many buffalo were killed, which greatly affected the plains Indians.
Civil War and Industrial Growth
Tensions between slave and free states grew. Arguments over state and federal power and violent conflicts over slavery in new states led to the American Civil War. Abraham Lincoln, from the antislavery Republican Party, was elected president in 1860. Seven slave states declared they were leaving the Union and formed the Confederate States of America. When the Confederates attacked Fort Sumter, the Civil War began. Four more slave states joined the Confederacy. Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation aimed to end slavery. After the Union won in 1865, three changes to the U.S. Constitution freed nearly four million African Americans, made them citizens, and gave them voting rights. The war greatly increased federal power.

After the war, the assassination of Abraham Lincoln led to the Reconstruction era. Policies were put in place to rebuild the Southern states and protect the rights of newly freed slaves. This era ended in 1877. Soon after, Jim Crow laws took away voting rights from many African Americans. In the North, cities grew, and many immigrants arrived from Southern and Eastern Europe. This led to rapid industrialization. The wave of immigration, lasting until 1929, provided workers and changed American culture.
The 1867 Alaska Purchase from Russia completed the country's mainland expansion. The Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890 was the last major armed conflict of the Indian Wars. In 1893, the native monarchy of the Hawaiian Kingdom was overthrown. The U.S. took over Hawaii in 1898. Victory in the Spanish–American War that same year showed the U.S. was a world power. This led to the U.S. gaining Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. The Philippines became independent later, but Puerto Rico and Guam are still U.S. territories.
World Wars and Great Depression
When World War I started in Europe in 1914, the U.S. stayed neutral at first. But in 1917, the U.S. joined the Allies, helping to defeat the Central Powers. The U.S. Senate did not approve the Treaty of Versailles, choosing to stay out of European affairs. In 1920, women gained the right to vote with a constitutional amendment.
The 1920s were a time of success, known as the Roaring Twenties. This period ended with the Wall Street Crash of 1929, which caused the Great Depression. After being elected president in 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt started the New Deal. These policies increased government involvement in the economy. From 1920 to 1933, alcohol was banned. The Dust Bowl in the 1930s caused many farmers to move to the West Coast.

The U.S. was neutral at the start of World War II. But it began supplying the Allies in March 1941. On December 7, 1941, the U.S. joined the Allies against the Axis Powers after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. World War II boosted the U.S. economy, creating jobs and bringing many women into the workforce. The U.S. was the only major country to become richer from the war. In 1945, the U.S. developed the first nuclear weapon. It used these weapons on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. Japan surrendered on September 2, ending the war.
Cold War and Civil Rights
After World War II, the Cold War began. The United States and the Soviet Union became rivals. The U.S. supported democracy and capitalism, while the Soviet Union favored communism. Both sides supported different governments and fought in proxy wars. From 1950 to 1953, U.S. troops fought Chinese communist forces in the Korean War. During this time, a period called McCarthyism led to political mistreatment and prejudice against people thought to be communists.

In 1961, the Soviet Union launched the first human into space. This led President John F. Kennedy to challenge the U.S. to send "a man to the Moon", which happened in 1969. Kennedy also faced a tense nuclear conflict with the Soviet Union over Cuba. A growing Civil Rights Movement, led by African-Americans like Rosa Parks and Martin Luther King, Jr., used peaceful protests to fight segregation and discrimination. After Kennedy's death in 1963, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 were passed.
Presidents Lyndon B. Johnson and Richard Nixon oversaw the Vietnam War in Southeast Asia, which was unsuccessful. A counterculture movement grew, opposing the war and supporting black nationalism. New feminist movements also emerged, seeking equal rights for women.
In 1974, due to the Watergate scandal, Nixon became the first president to resign. He was replaced by Vice President Gerald Ford. The presidency of Jimmy Carter in the 1970s faced economic problems and the Iran hostage crisis. The election of Ronald Reagan in 1980 brought changes in U.S. policy, including changes to taxes and spending. His second term saw diplomatic progress with the Soviet Union. The later collapse of the Soviet Union ended the Cold War.
Modern History
Under President George H. W. Bush, the U.S. played a major global role, as seen in the Gulf War (1991). The U.S. economy grew for a long time from 1991 to 2001, during the presidency of Bill Clinton. A scandal led to his impeachment in 1998, but he finished his term. The 2000 presidential election was very close. The Supreme Court decided that George W. Bush, son of George H. W. Bush, became president, even though he had fewer votes than his opponent Al Gore.
On September 11, 2001, the Al-Qaeda group attacked the Twin Towers in New York City and the Pentagon near Washington, D.C.. Nearly three thousand people died. In response, the Bush administration started the "War on Terror." In late 2001, U.S. forces invaded Afghanistan, overthrowing the Taliban government and destroying Al-Qaeda's training camps. In 2003, the U.S. and its allies invaded Iraq and removed dictator Saddam Hussein. Bush was re-elected in 2004.
In 2005, Hurricane Katrina caused great damage along the Gulf Coast. The city of New Orleans was devastated, and 1,833 people died.
On November 4, 2008, during a global economic downturn, Barack Obama was elected president. He was the first African American to hold the office. In May 2011, American Special forces killed Osama bin Laden in Pakistan. Barack Obama was re-elected in 2012. During his second term, he led the war against the Islamic State and restored diplomatic relations with Cuba.
On November 8, 2016, Republican leader Donald Trump won the presidency against Hillary Clinton. He took office on January 20, 2017.
In the 2020 presidential election, Joe Biden was elected as the 46th president. On January 6, 2021, supporters of Donald Trump stormed the United States Capitol in an attempt to stop the presidential vote count.
Government
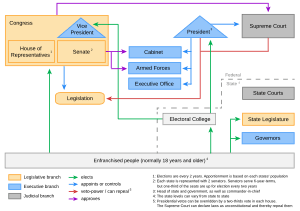
The United States is the world's oldest federation. It is a constitutional republic and representative democracy. This means that the people elect representatives to make laws. The government works using a system of checks and balances from the U.S. Constitution. The Constitution is the country's main legal document.
There are three main parts, or branches, of the government:
- The executive branch
- The legislative branch
- The judicial branch
State governments work in a similar way to the federal government. Each state has its own executive, legislative, and judicial branches. A governor leads the executive branch in each state.
Executive Branch: The President's Role
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out and enforcing laws. The President is the leader of this branch and also the head of the armed forces. The President is elected by the U.S. Electoral College.
The President can veto a bill passed by Congress, stopping it from becoming a law. The President can also issue "executive orders" to ensure laws are followed.
The President oversees many government departments that manage daily tasks. For example, the Department of Commerce handles trade rules. The President chooses the heads of these departments and nominates federal judges. However, the Senate must approve these choices. A President can serve two four-year terms.
Legislative Branch: Making Laws
The legislative branch makes laws. This branch is called the United States Congress. Congress has two parts, or "houses."
One house is the House of Representatives. Representatives are elected by voters from specific areas within each state. The number of Representatives a state has depends on its population. Representatives serve two-year terms. There are 435 Representatives in total. The leader of the House is the Speaker of the House.
The other house is the Senate. Each state has two senators, no matter its size. Since there are 50 states, there are 100 senators. The Senate must approve the President's treaties and appointments of officials. Senators serve six-year terms. The Vice President of the United States is the president of the Senate. However, a senator usually acts as the temporary president.
Representatives and senators suggest new laws, called "bills." A bill can be voted on by the whole house, or it might first go to a small group called a committee. If one house passes a bill, it goes to the other house. If both houses pass it, it goes to the President. The President can sign the bill into law or veto it. If the President vetoes it, Congress can vote again. If two-thirds of Congress votes for the bill, it becomes law even without the President's signature.
Under the American system of federalism, Congress cannot directly control states. Instead, Congress can offer federal money or use special situations like national emergencies to encourage states to follow federal law.
Judicial Branch: Interpreting Laws
The judicial branch explains what laws mean. This branch includes the Supreme Court and many lower courts. If the Supreme Court decides a law goes against the Constitution, that law is "struck down" and is no longer valid.
The Supreme Court has nine judges, called justices. The President nominates them, and the Senate must approve them. One justice is the chief justice, who leads the court. A Supreme Court justice serves until they die or resign. When a justice leaves, the President nominates a new person. If the Senate agrees, that person becomes a justice.
Important court cases, like Marbury v. Madison (1803), have shown that the Supreme Court is the final interpreter of the U.S. Constitution. It has the power to strike down any law that conflicts with it.
Politics
The United States of America has 50 states, 5 territories, and 1 district (Washington, D.C.). States can make laws about things within their borders. Federal law covers things that involve more than one state or other countries. If federal and state laws conflict, federal law usually takes priority. Each state has its own constitution, which sets up its government.
The federal government and most state governments are mainly run by two political parties: the Republicans and the Democrats. There are also smaller parties, like the Libertarian Party and the Green Party.
Political Divisions
States of the U.S.
The United States has grown from 13 original colonies to 50 states. Forty-eight of these states are connected and form the contiguous United States. These "lower 48" states can be reached by road without crossing into another country. They stretch from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west.
The two other states are not connected to the lower 48. Alaska is reached by going through Canada. Hawaii is in the middle of the Pacific Ocean.
Washington, D.C., the national capital, is a federal district. It was created from land given by Maryland and Virginia in 1791. It is not part of any state. Some people in D.C. want it to become a state or for Maryland to take back its land. This would give them the right to vote in Congress.
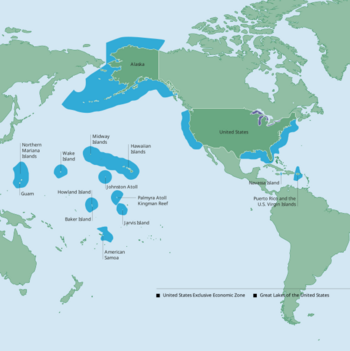
Territories and Possessions
The United States also has sixteen lands that are not states. Many of these are colonial territories. None of them share a land border with the main U.S. People live in five of these places:
The Philippines used to be a U.S. possession. Palau, the Federated States of Micronesia, and other Pacific island nations were governed by the U.S. as a United Nations "Trust Territory." All these places later became independent.
The U.S. armed forces have bases in many countries. The U.S. Navy base at Guantánamo Bay was rented from Cuba.
Counties and Cities
All states are divided into smaller areas. Most are called counties. However, Louisiana uses "parish," and Alaska uses "borough."
There are many cities in the United States. One city in each state is the state capital. This is where the state government meets. The capital is not always the largest city. For example, New York City is the largest city in New York State, but the state capital is Albany. Other big cities include Los Angeles, California; Chicago, Illinois; Seattle, Washington; Miami, Florida; Houston and Dallas, Texas; and Boston, Massachusetts.
Foreign Relations and Military
The United States has a big influence on global economics, politics, and the military. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. The headquarters of the United Nations is in New York City. The U.S. is also a member of the G7, G20, and Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Most countries have embassies in Washington, D.C., and many have consulates across the U.S. Similarly, almost all nations host American diplomatic missions. However, Iran, North Korea, Bhutan, and Taiwan do not have formal diplomatic relations with the U.S. The U.S. has a "special relationship" with the United Kingdom and strong ties with Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, South Korea, and Israel.
The President is the commander-in-chief of the country's armed forces. The President appoints its leaders, including the secretary of defense. The United States Department of Defense manages the armed forces, which include the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, and Air Force. The Coast Guard is part of the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime. In 2008, the armed forces had 1.4 million active-duty personnel. There were also hundreds of thousands in the Reserves and National Guard.
The military budget of the United States in 2011 was over $700 billion. This was 41% of all military spending worldwide. U.S. troops left Iraq in December 2011. About 90,000 U.S. troops were serving in Afghanistan in April 2012.
Economy
The United States has a capitalist economy. The country has many natural resources, including gold, coal, and uranium. Farming makes the U.S. one of the top producers of corn, wheat, sugar, and tobacco. Housing makes up about 15% of the country's GDP. The U.S. also produces cars, airplanes, and electronics. About three-quarters of Americans work in the service industry.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 3,929,000 | — | |
| 1800 | 5,308,000 | 35.1% | |
| 1810 | 7,240,000 | 36.4% | |
| 1820 | 9,638,000 | 33.1% | |
| 1830 | 12,866,000 | 33.5% | |
| 1840 | 17,063,000 | 32.6% | |
| 1850 | 23,192,000 | 35.9% | |
| 1860 | 31,443,321 | 35.6% | |
| 1870 | 38,558,371 | 22.6% | |
| 1880 | 50,189,209 | 30.2% | |
| 1890 | 62,979,766 | 25.5% | |
| 1900 | 76,212,168 | 21.0% | |
| 1910 | 92,228,531 | 21.0% | |
| 1920 | 106,021,568 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 123,202,660 | 16.2% | |
| 1940 | 132,164,569 | 7.3% | |
| 1950 | 151,325,798 | 14.5% | |
| 1960 | 179,323,175 | 18.5% | |
| 1970 | 203,211,926 | 13.3% | |
| 1980 | 226,545,805 | 11.5% | |
| 1990 | 248,709,873 | 9.8% | |
| 2000 | 281,421,906 | 13.2% | |
| 2010 | 308,745,538 | 9.7% | |
The United States has people from many different racial and ethnic backgrounds. About 80% of people in the U.S. are descended from European immigrants. Many have roots in Germany, England, Scotland, Ireland, and Italy. About 13% of people are African-American, mostly descended from African slaves. Asian-Americans make up 5% of the population, but a larger part on the West Coast, like 13% in California. Hispanic-Americans make up 15% of the nation. The original peoples, called Native Americans or American Indians, are a very small group.
About 11% of people in the U.S. were born in another country. 18% speak a language other than English at home. For adults aged 25 and older, 80% have finished high school, and 25% have a bachelor's degree or higher.
The 2000 Census found that 43 million people identified as German-American, 30.5 million as Irish-American, 24.9 million as African-American, 24.5 million as English-American, and 18.4 million as Mexican-American.
The U.S. has the largest number of immigrants in the world. Many come from Mexico, China, India, the Philippines, and El Salvador. Immigration from Africa has also increased, with many coming from Nigeria, Ethiopia, Egypt, Ghana, and Kenya.
Money and Wealth
The social structure in the U.S. has a wide range of wealth. Some Americans are much richer than others. The average income for an American in 2002 was $37,000 a year. However, the richest 1% of Americans have as much money as the poorest 90%. In 2000, 51% of homes had a computer, and 41% had Internet access. By 2004, this grew to 75%. Also, 67.9% of American families owned their homes in 2002. There are 200 million cars in the U.S., which is about two cars for every three Americans.
Religion in the U.S.
There are many different religions in the U.S. The largest religion is Christianity, including groups like Catholicism, Protestantism, and Mormonism. Other religions include Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism.
The United States is one of the most religious countries in the Western world, and most Americans believe in God. The number of Christians in the U.S. has gone down slightly over the years. In 1990, 86.2% called themselves Christian, and in 2007, 78.4% did. Other religions include Judaism (2.3%), Islam (0.8%), and Buddhism (0.7%). About 16.1% of people say they have no religion.
Languages Spoken
| Languages (2017) | |
|---|---|
| English (only) | 239 million |
| Spanish | 41 million |
| Chinese | 3.5 million |
| Tagalog | 1.7 million |
| Vietnamese | 1.5 million |
| Arabic | 1.2 million |
| French | 1.2 million |
| Korean | 1.1 million |
| Russian | 0.94 million |
| German | 0.92 million |
English (American English) is the main language spoken in the U.S. While there is no official language at the federal level, some laws require English. In 2010, about 230 million people, or 80% of those aged five and older, spoke only English at home. Spanish is the second most common language, spoken by 12% of the population at home. It is also the most widely taught second language. Some Americans want to make English the country's official language, as it is in at least 28 states.
Both Hawaiian and English are official languages in Hawaii. While New Mexico and Louisiana do not have official languages, they have laws that support the use of Spanish and French, respectively. Other states, like California, publish government documents in Spanish. Many areas with many non-English speakers provide government information in other common languages.
Several U.S. territories recognize their native languages along with English. For example, Samoan and Chamorro are recognized in American Samoa and Guam. Spanish is an official language in Puerto Rico and is spoken more than English there.
Education System
In most U.S. states, children must attend school from age six or seven (kindergarten or first grade) until they turn eighteen (the end of high school). Some states allow students to leave school at sixteen or seventeen. About 12% of children attend private schools. Just over 2% of children are homeschooled.
Culture
American popular culture is known worldwide. It has a big influence on many parts of the world, especially the Western world. American music is heard globally, and American movies and television shows are seen in most countries.
Federal Holidays
The U.S. celebrates several federal holidays each year:
| Date | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | Celebrates the beginning of the year. |
| 3rd Monday in January | Martin Luther King, Jr. Day | Honors Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., an African-American civil rights leader. |
| 3rd Monday in February | President's Day | Honors all American presidents, especially George Washington and Abraham Lincoln. |
| Last Monday in May | Memorial Day | Honors military members who died in service. It also marks the start of summer. |
| July 4 | Independence Day | Celebrates the Declaration of Independence. Also known as "The Fourth of July." |
| 1st Monday in September | Labor Day | Celebrates the achievements of workers. It marks the traditional end of summer. |
| 2nd Monday in October | Columbus Day | Honors Christopher Columbus, who arrived in the Americas. (Not celebrated in some states.) |
| November 11 | Veterans Day | Honors all military service members, past and present. |
| 4th Thursday in November | Thanksgiving | Celebrates the autumn harvest. It marks the start of the "holiday season." |
| December 25 | Christmas | Celebrates the birth of Jesus Christ. Many non-Christians also celebrate it as a winter holiday. |
The U.S. Flag
The American flag has 50 stars on a blue background and 13 stripes (seven red and six white). It is a symbol of the United States, like the Bald eagle. The 50 stars represent the 50 states. The red color stands for courage. Blue represents justice. White stands for peace and cleanliness. The 13 stripes represent the 13 original colonies.
American Cuisine
Hamburger is considered a national dish of the United States. Some foods like chocolate chip cookies and corndogs were invented in the U.S. The U.S. is home to many fast food restaurants, including McDonald's. Hot dogs are popular in the U.S. but came from Germany. Many soft drinks like Coca-Cola and Pepsi are American.
Music in the U.S.
The most popular music styles in the U.S. are rock, pop, country, R&B, and hip hop. Famous American musicians include Taylor Swift, Eminem, Beyoncé, Mariah Carey, Britney Spears, Katy Perry, Madonna, Miley Cyrus, Lil Wayne, and Snoop Dogg.
Images for kids
-
An artistic recreation of The Kincaid Site from the prehistoric Mississippian culture as it may have looked at its peak 1050–1400 AD
-
Italian explorer Christopher Columbus arrives in America and takes possession of Guanahani
-
Castillo de San Marcos in St. Augustine, Florida, the oldest continuously occupied European-established settlement in the United States
-
The signing of the Mayflower Compact, 1620
-
The Battle of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania during the Civil War by Thure de Thulstrup
-
U.S. President Ronald Reagan at his "Tear down this wall!" speech in Berlin, Germany on June 12, 1987. The Iron Curtain of Europe showed the division of the world's superpowers during the Cold War.
-
The bald eagle has been the national bird of the United States since 1782.
-
Donald Trump, the 45th President of the United States.
-
The Statue of Liberty in New York City is a symbol of both the U.S. and the ideals of freedom, democracy, and opportunity.
-
Map of U.S. Economic Exclusion Zone, highlighting states, territories and possessions
-
Congressional leadership meeting with then-President Obama in 2011.
-
The United Nations Headquarters was built in Midtown Manhattan in 1952.
-
A tract housing development in San Jose, California.
-
The University of Virginia, founded by Thomas Jefferson in 1819, is one of the many public universities in the United States.
-
Apple pie is a food commonly associated with American cuisine.
-
Roasted turkey is a traditional menu item of an American Thanksgiving dinner.
-
Mark Twain, American author and humorist.
-
Times Square in New York City, the hub of the Broadway theater district
-
The Grammy Award is awarded to leading music artists.
-
The Hollywood Sign in Los Angeles, California
-
Swimmer Michael Phelps and then-President George W. Bush August 10, 2008 at the National Aquatic Center in Beijing. Phelps is the most decorated Olympic athlete of all time.
-
The corporate headquarters of the American Broadcasting Company in New York City
-
Astronaut James Irwin walking on the Moon next to Apollo 15's landing module and lunar rover in 1971. The effort to reach the Moon was triggered by the Space Race.
-
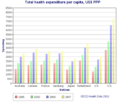
Health spending per capita, in US$ PPP-adjusted, compared amongst various first world nations.
See also
 In Spanish: Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Estados Unidos para niños